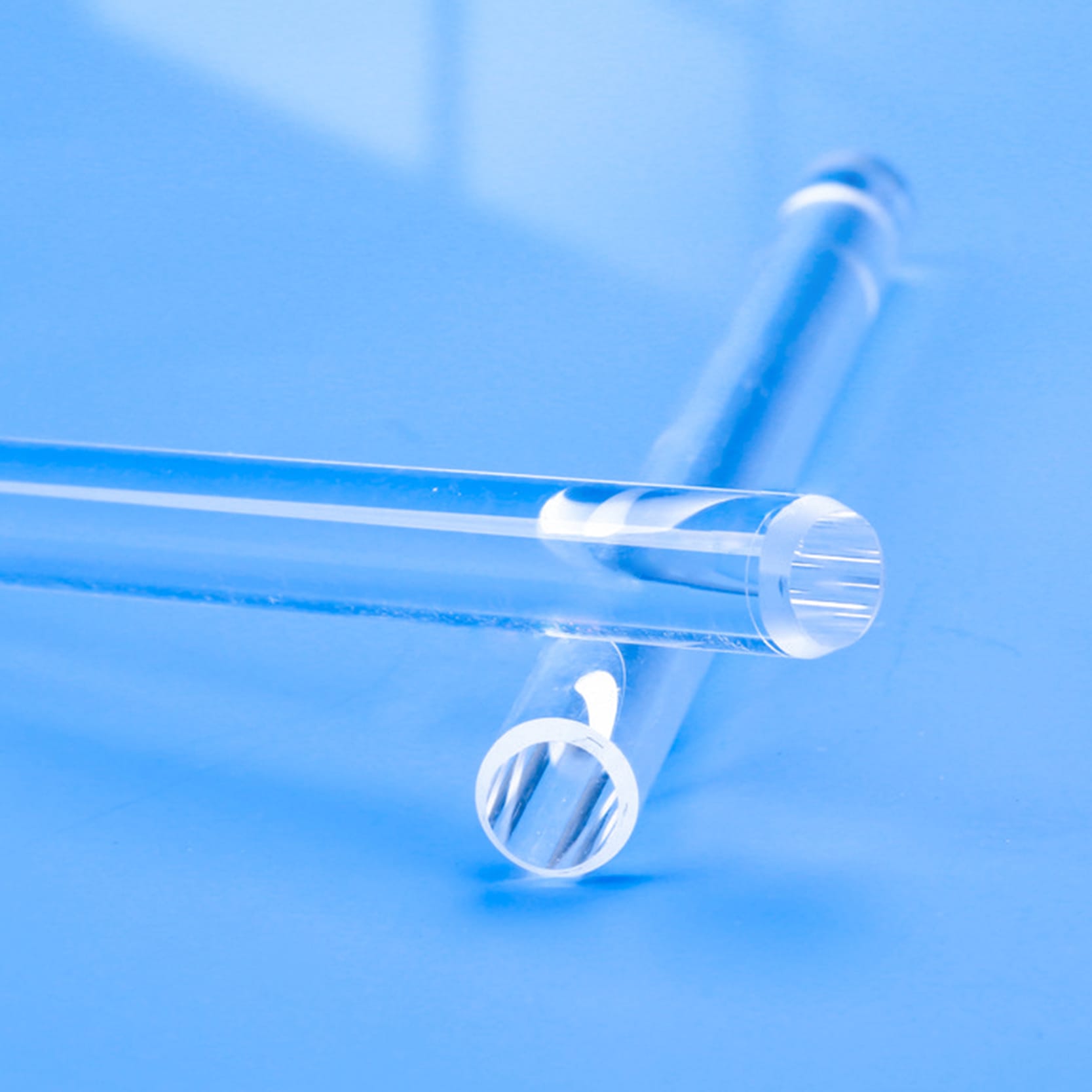
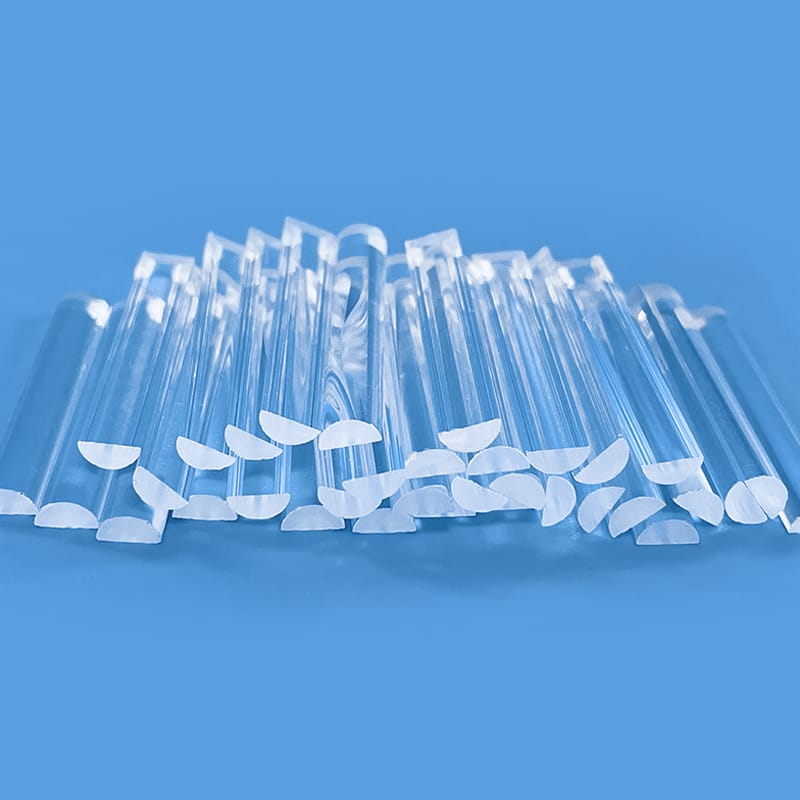
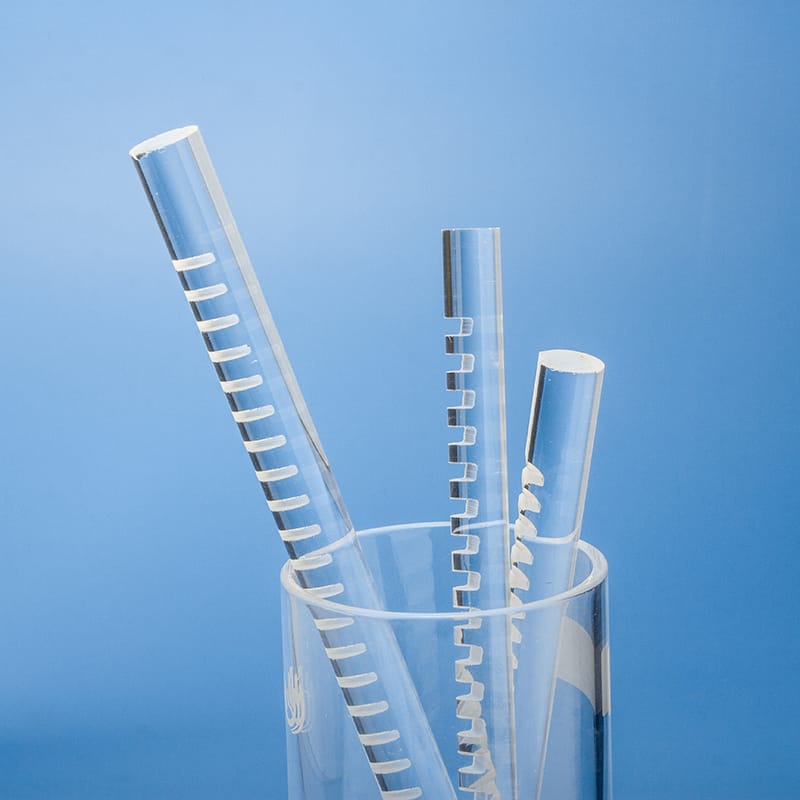
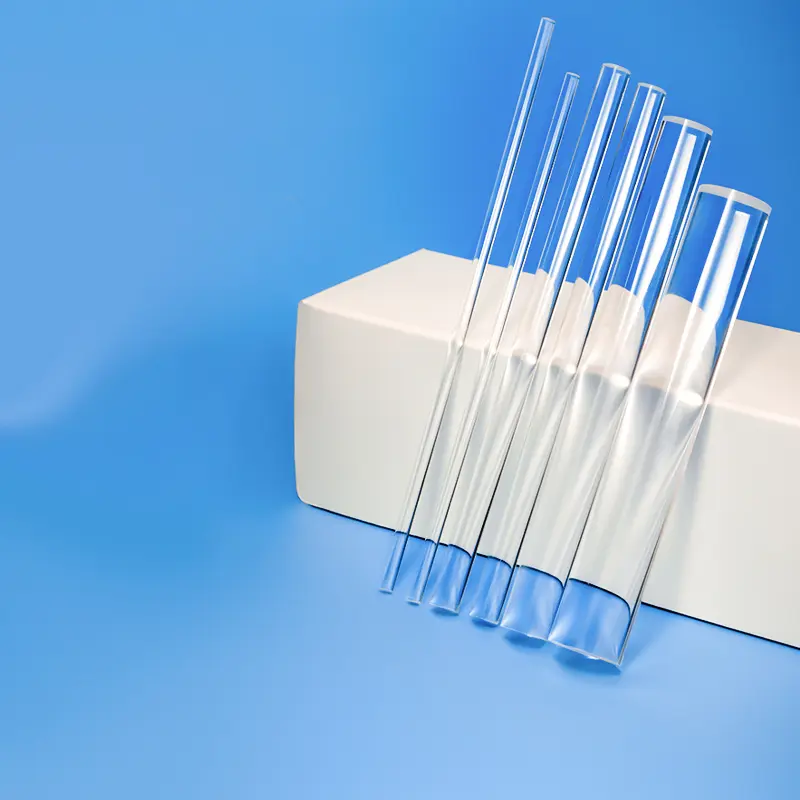
Nos tiges guides de lumière en quartz de haute pureté et tubes en silice fondue offrent une clarté optique et une transmission UV exceptionnelles. Conçus pour des applications exigeantes, ils présentent une résistance supérieure à la chaleur et une stabilité chimique. Idéaux pour les équipements optiques, analytiques et liés aux UV, ces composants de précision sont disponibles avec des dimensions personnalisées.
| Diamètre | Longueur |
|---|---|
| 10mm | 300mm |
| 10mm | 600mm |
| 12mm | 300mm |
| 12mm | 600mm |
| 14mm | 300mm |
| 14mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 300mm |
| 15mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 300mm |
| 16mm | 600mm |
| 16mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 1200mm |
| 18mm | 300mm |
| 18mm | 600mm |
| 18mm | 1000mm |
| 18mm | 1200mm |
| 20mm | 300mm |
| 20mm | 600mm |
| 20mm | 1000mm |
| 20mm | 1200mm |
| 22mm | 300mm |
| 22mm | 600mm |
| 22mm | 1000mm |
| 22mm | 1200mm |
| 25mm | 300mm |
| 25mm | 600mm |
| 25mm | 1000mm |
| 25mm | 1200mm |
| 28mm | 300mm |
| 28mm | 600mm |
| 28mm | 1000mm |
| 28mm | 1200mm |
| 30mm | 300mm |
| 30mm | 600mm |
| 30mm | 1000mm |
| 30mm | 1200mm |
| 32mm | 300mm |
| 32mm | 600mm |
| 32mm | 1000mm |
| 32mm | 1200mm |
| 35mm | 300mm |
| 35mm | 600mm |
| 35mm | 1000mm |
| 35mm | 1200mm |
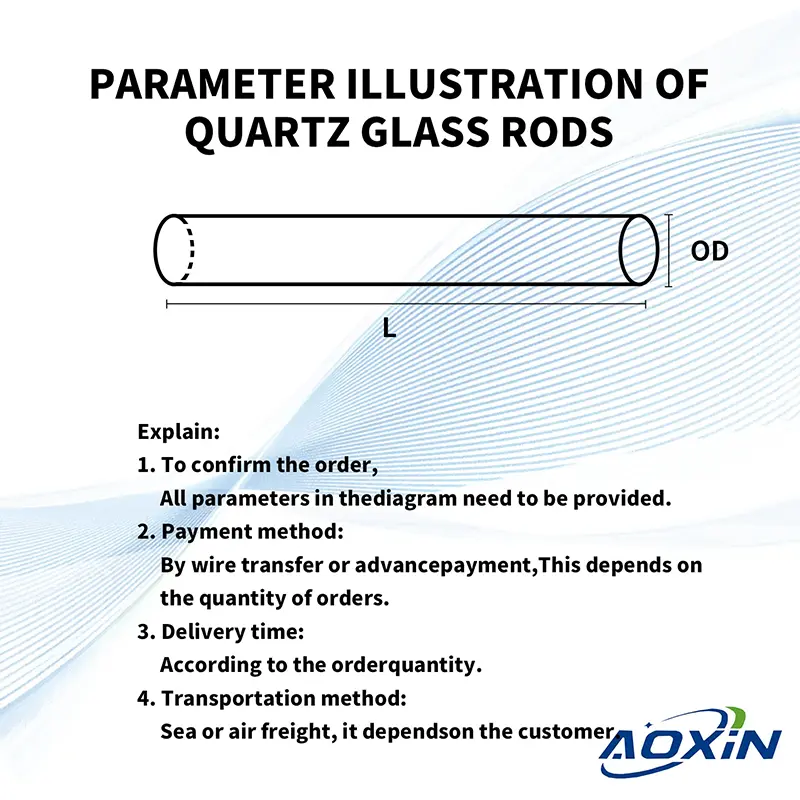
Remarques:
Pour confirmer la commande,
Les paramètres suivants sont requis :
① Diamètre extérieur ② Longueur ③ Quantité
- Méthode de paiement :
Par T/T ou prépaiement
Cela dépend de la quantité de la commande. - Delivery time:
According to the order quantity. - Méthode d'expédition :
Par mer ou par air
Cela dépend du client.
| Contenu des propriétés | Valeurs des propriétés |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densité | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureté | Dureté Mohs de 5,5 à 6,5; Dureté Knoop 570 (sous une charge de 100g) |
| Résistance à la traction | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² ou 48 MPa); 7 000 psi |
| Résistance à la compression | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coefficient de dilatation thermique | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductivité thermique | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Chaleur spécifique | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Point de ramollissement | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Point de recuit | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Point de contrainte | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Température de travail | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Résistivité électrique | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Taille | Sur mesure |
| Logo | Personnalisation du logo disponible |

Il existe deux principales méthodes de production de tiges en quartz : la méthode continue et la méthode de fusion à la flamme (également connue sous le nom de méthode de fusion gazeuse).
Méthode continue: Dans cette méthode, le sable de quartz est alimenté par le haut dans un four, qui comprend un creuset en quartz métallique entouré d'éléments de chauffage électrique. Le sable de quartz fond à des températures élevées. Le matériau fondu passe ensuite à travers un orifice de moulage au fond du creuset, produisant des tiges, des tubes, des feuilles ou d'autres formes de produits spécifiées.
Méthode de fusion à la flamme : Cette méthode consiste à utiliser de l'hydrogène et de l'oxygène pour fondre du cristal de quartz incolore. Le matériau fondu est formé en verre de quartz par la fusion et la congélation des particules cristallines dans la flamme. Le verre de quartz est ensuite retiré de la flamme par différentes méthodes et transformé en tiges de quartz de la forme souhaitée.
Haute résistance à la température
Le verre de quartz présente une excellente résistance aux températures élevées, maintenant sa stabilité dans des environnements à haute température.
Faible coefficient d'expansion thermique
Le coefficient de dilatation thermique du verre de quartz est extrêmement bas, variant de 1/12 à 1/20 de celui du verre ordinaire, ce qui contribue à sa stabilité face aux variations de température.
Résistance à la corrosion
Le verre de quartz résiste à une variété d'acides, de bases et de sels, à l'exception de l'acide fluorhydrique et de l'acide phosphorique chaud au-dessus de 300 degrés Celsius.
Taux de transmission de lumière élevé
Le taux de transmission de la lumière peut atteindre 99,9 %, garantissant une haute transmittance des signaux lumineux lors de la transmission.
Scénario d'application
Secteur de la communication
Dans les systèmes de communication par fibre optique, les tiges de guidage de lumière en quartz servent de support pour transmettre des signaux lumineux de l'émetteur au récepteur, permettant une transmission de données à haut débit et à grande capacité.
Ils sont également utilisés dans des équipements tels que des lasers et des amplificateurs optiques pour améliorer les performances et la stabilité des systèmes de communication.
Domaine médical
Dans la chirurgie au laser, les médecins utilisent des tiges de guide lumineux en quartz pour transmettre les faisceaux laser à la zone de traitement, permettant ainsi des procédures chirurgicales précises.
Ils sont également utilisés dans les systèmes d'imagerie optique pour aider les médecins à observer les structures internes, améliorant ainsi la précision du diagnostic.
Domaine de recherche scientifique
Les chercheurs utilisent des barres de guidage en quartz pour mettre en place des systèmes expérimentaux optiques afin d'étudier les phénomènes optiques et les propriétés des matériaux optiques.
Ils sont également utilisés dans des équipements tels que des interféromètres laser et des capteurs optiques pour des mesures et des expériences de précision.
Autres domaines
Dans le domaine de la biotechnologie, les barres de guidage en quartz sont utilisées pour la détection et l'analyse par fluorescence, permettant une détection rapide et très sensible des biomolécules.
Dans le traitement laser, ils sont utilisés pour la découpe laser et le marquage laser, caractérisés par une haute densité d'énergie, une haute précision et une grande efficacité.
Ils sont également utilisés dans la fabrication de divers instruments optiques tels que les microscopes, les télescopes et les caméras thermiques, en transmettant la lumière et en modifiant sa direction pour obtenir des effets d'observation spécifiques
Les barres de guidage lumineuses en quartz présentent une excellente stabilité à long terme dans diverses environnements. Elles possèdent un haut degré de stabilité chimique, leur permettant de maintenir leurs performances et leur intégrité dans une large gamme d'environnements chimiques. De plus, le coefficient d'expansion thermique du verre de quartz est parmi les plus bas des verres industriels courants, ce qui signifie qu'il conserve une bonne stabilité dimensionnelle lors des variations de température et résiste très bien aux chocs thermiques.
Les tiges guides lumineux en quartz possèdent une stabilité chimique extrêmement élevée et sont presque non réactives avec la plupart des substances acides et alcalines, à l'exception de l'acide fluorhydrique. Cette résistance à la corrosion les rend inestimables dans les environnements où le contact fréquent avec des matériaux corrosifs est courant.
Les tiges d'agitation en quartz offrent une résistance supérieure à haute température et une stabilité chimique par rapport aux tiges en plastique. De plus, elles possèdent une grande résistance structurelle, sont moins sujettes à la rupture et ont une longue durée de vie.
Questions fréquemment posées
Nous sommes spécialisés dans la fabrication intégrée de composants en verre de quartz de haute pureté. Nos principales gammes de produits comprennent :
Tubes et barres de quartz: Une large gamme de diamètres et de spécifications.
Plaques et disques de quartz: Découpés et polis avec précision pour usages optiques et industriels.
Verrerie de laboratoire en quartz: Une gamme complète de verrerie standard et sur mesure, incluant béchers, fioles et nacelles.
Quartz de qualité semi-conducteur: Composants de haute pureté tels que les tubes de traitement et les porteurs pour la fabrication de semi-conducteurs.
Composants fabriqués sur mesure: Nous pouvons produire des pièces complexes adaptées à vos conceptions et spécifications uniques.
Oui. La fabrication sur mesure est au cœur de notre activité. Forts de plus d'une décennie d'expérience spécialisée, nous nous associons à des entreprises pour leur offrir des services OEM/ODM experts. Nos capacités incluent le soudage, la rectification, le perçage, le polissage, le pliage et d'autres techniques d'usinage de précision, afin de créer des composants qui répondent précisément à vos exigences.
La qualité est primordiale dans notre processus de fabrication. Nous sommes un fabricant certifié ISO 9001:2015, garantissant que nos processus répondent aux normes internationales de gestion de la qualité.Nos produits subissent également des tests SGS rigoureux pour leur pureté et leurs performances. Nous utilisons des matières premières de haute pureté (jusqu'à 99,998% de SiO2) pour produire des articles en quartz fondu et en silice fondue dotés d'une stabilité thermique exceptionnelle, d'une résistance aux températures élevées et d'une inertie chimique.
Nous avons rationalisé notre processus pour qu'il soit le plus efficace possible :
Soumettez votre demande de devis (RFQ) : Envoyez-nous vos dessins techniques, spécifications et exigences via notre formulaire de contact sur le site web ou par e-mail.
Réponse rapide : Vous pouvez vous attendre à une première réponse en quelques minutes et à une communication détaillée dans la demi-heure.
Conception & Proposition : Nous vous soumettrons une proposition de conception détaillée et un devis compétitif sous 24 heures.
Prototypage & Production : Dès approbation, nous passons rapidement du prototypage à la production à grande échelle afin de respecter vos délais.
Un partenariat avec Aoxin Quartz offre plusieurs avantages clés :
Expertise avérée : Avec plus de 10 ans d'expérience dans l'industrie, nous possédons les connaissances techniques nécessaires pour relever les défis complexes.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Valeur compétitive : Situés dans un pôle majeur de production de quartz, nous tirons parti d'une chaîne d'approvisionnement efficace et d'une fabrication avancée pour offrir une qualité exceptionnelle à un prix compétitif.</span
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.