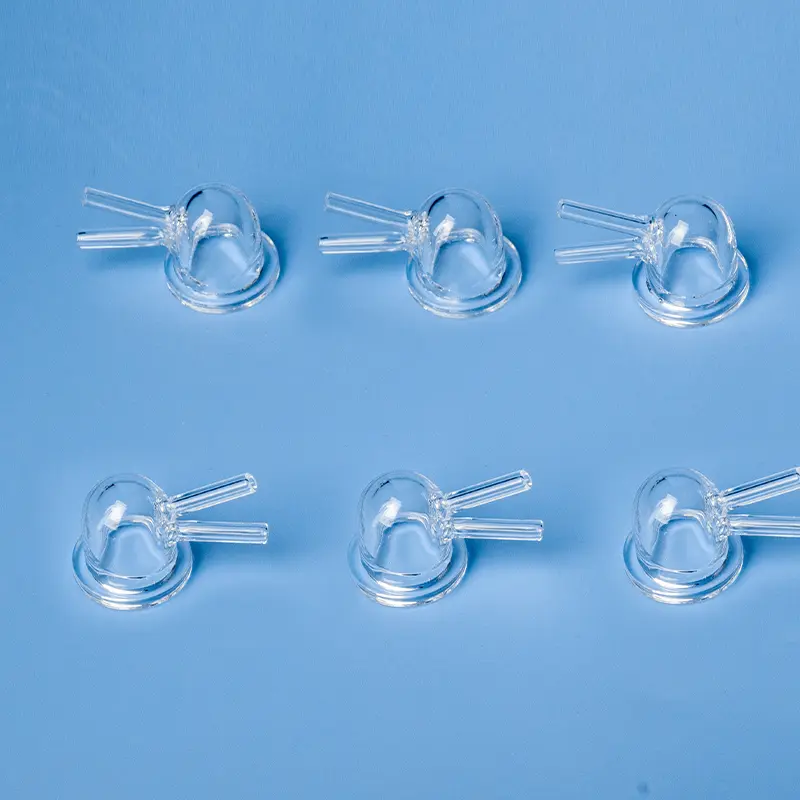
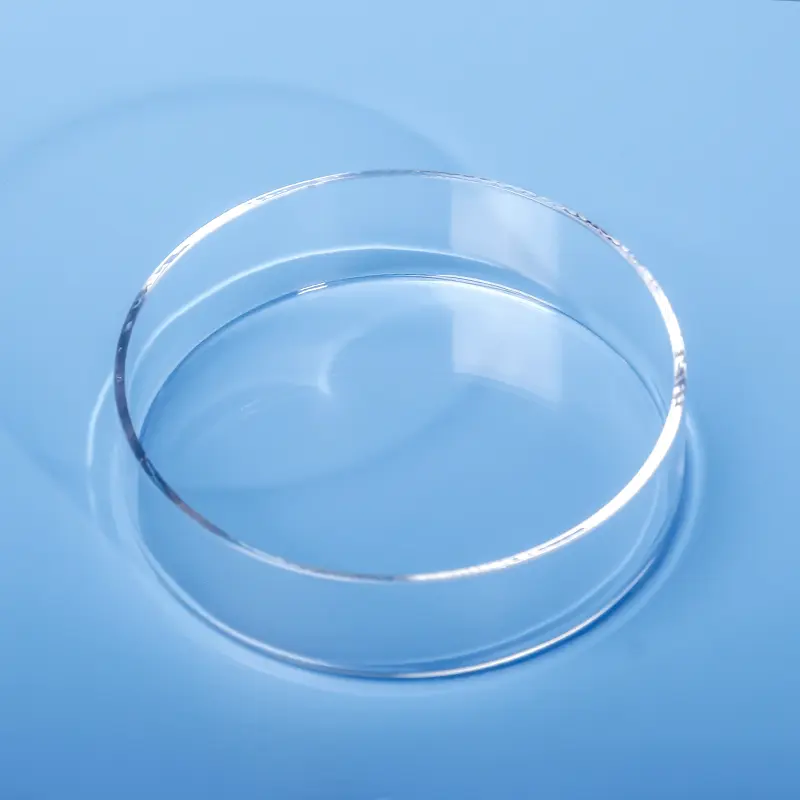
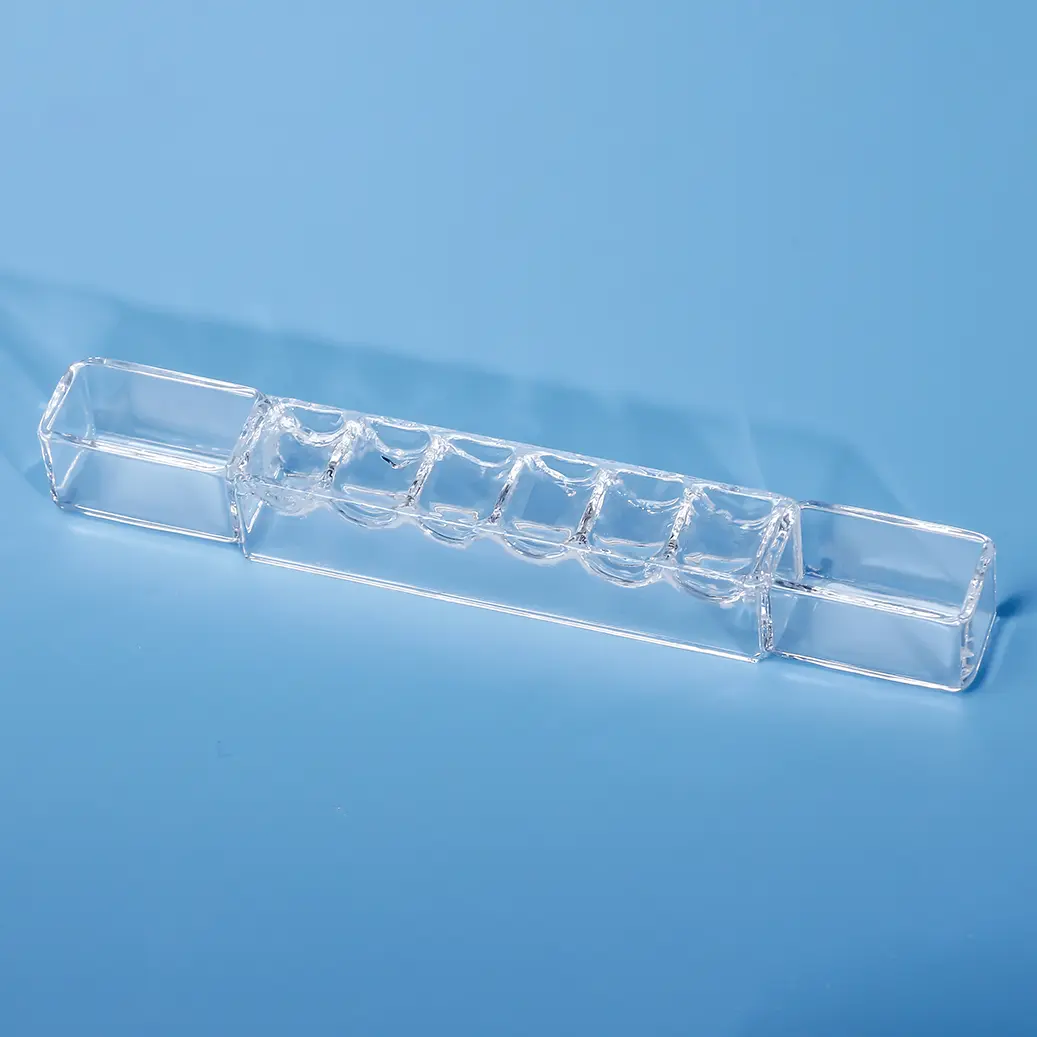
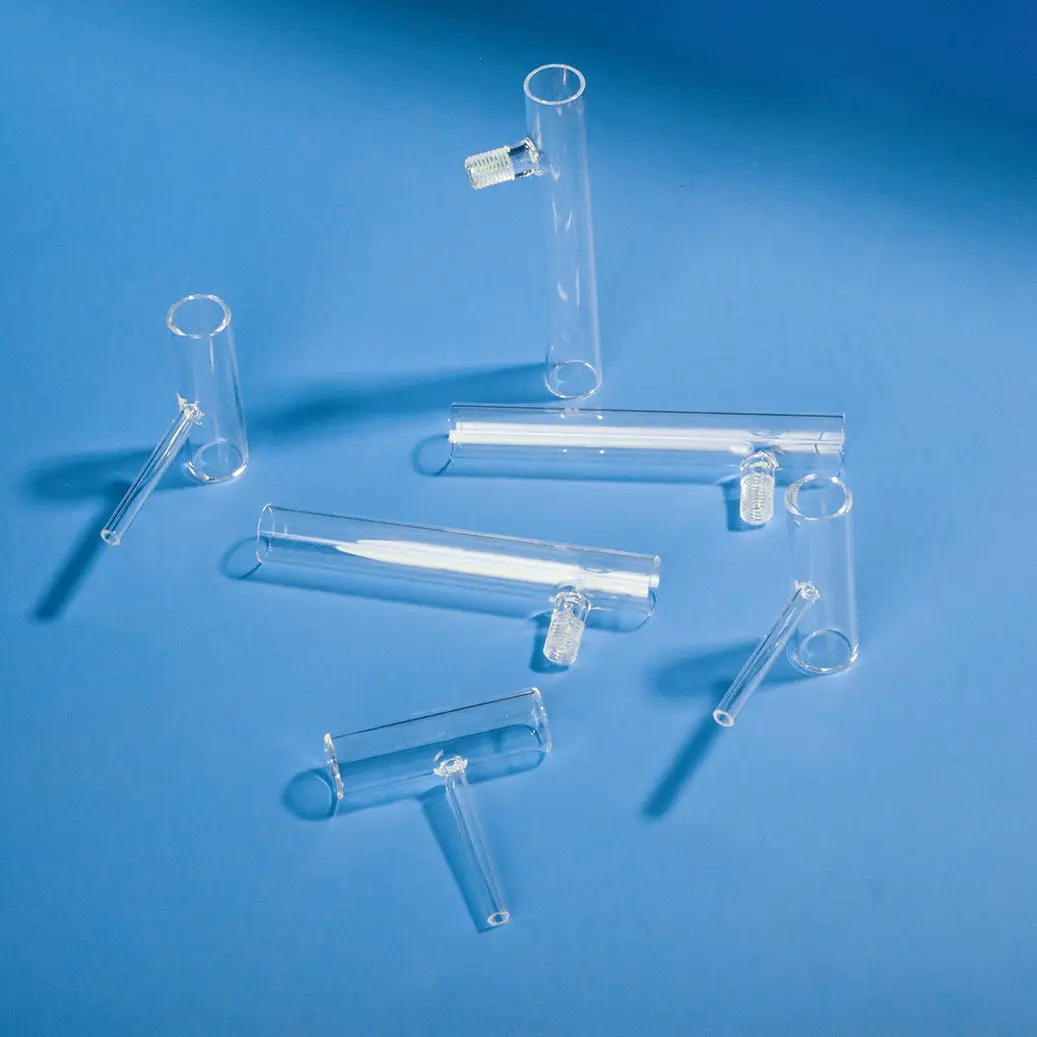
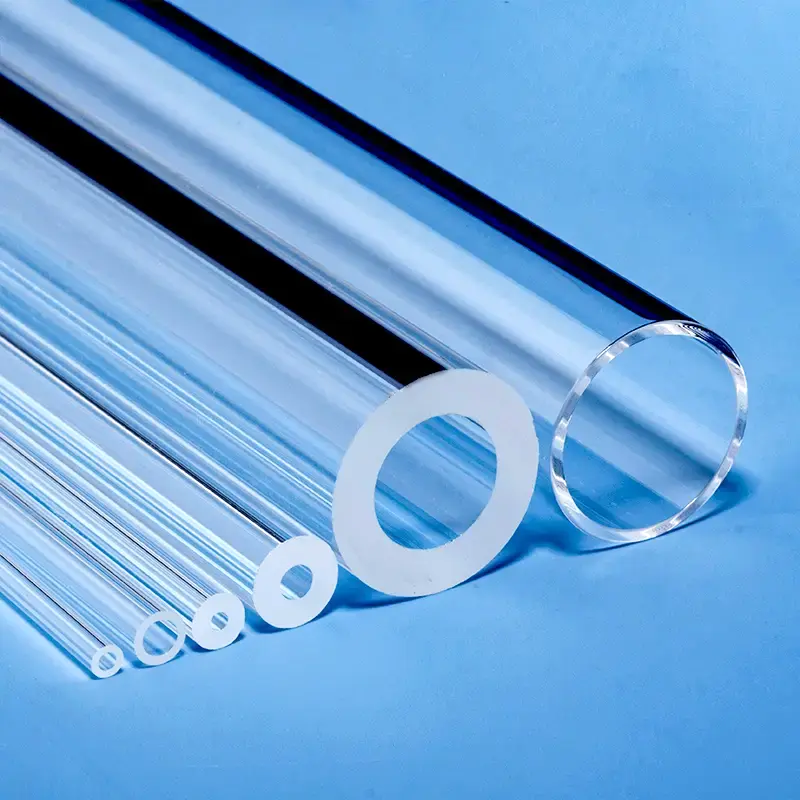
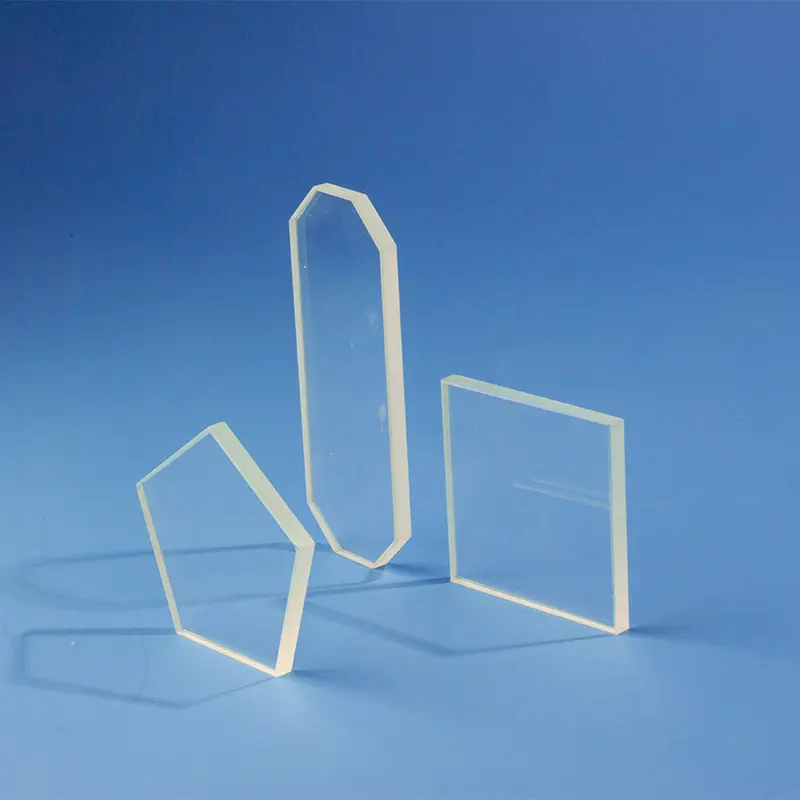
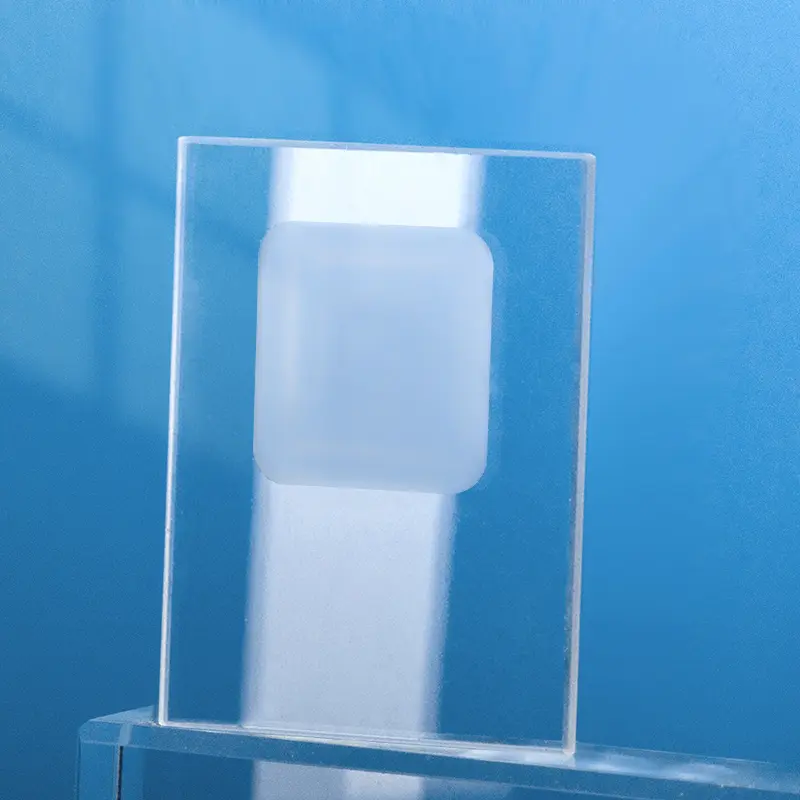
Nos porte-échantillons quartz DRX sont méticuleusement fabriqués à partir de silice fondue de haute pureté, offrant une structure amorphe qui garantit une interférence de fond minimale dans l'analyse par diffraction des rayons X. Le design transparent, avec un puits d'échantillon rectangulaire central dépoli, est chimiquement inerte et très résistant aux températures extrêmes, ce qui le rend idéal pour divers types d'échantillons, y compris les poudres et les films minces. Nous proposons des solutions personnalisées pour répondre aux exigences spécifiques des différents diffractomètres de rayons X et des applications de recherche avancées.
| Contenu des propriétés | Valeurs des propriétés |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densité | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureté | Dureté Mohs de 5,5 à 6,5; Dureté Knoop 570 (sous une charge de 100g) |
| Résistance à la traction | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² ou 48 MPa); 7 000 psi |
| Résistance à la compression | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coefficient de dilatation thermique | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductivité thermique | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Chaleur spécifique | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Point de ramollissement | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Point de recuit | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Point de contrainte | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Température de travail | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Résistivité électrique | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Taille | Sur mesure |
| Logo | Personnalisation du logo disponible |
Haute résistance à la température
Les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz sont fabriqués en verre de quartz, qui a un point de ramollissement d'environ 1730°C. Ils peuvent être utilisés pendant de longues périodes à 1100°C et pour de courtes durées à des températures allant jusqu'à 1450°C.
Stabilité chimique
Le verre de quartz est très résistant aux réactions chimiques avec la plupart des acides. Sa résistance aux acides est environ 30 fois supérieure à celle de la céramique et 150 fois supérieure à celle de l'acier inoxydable. Il présente une stabilité chimique exceptionnelle, particulièrement à haute température.
Faible coefficient d'expansion thermique
Le verre de quartz présente un coefficient de dilatation thermique extrêmement faible, ce qui lui permet de résister aux changements rapides de température sans se fracturer. Cela confère une excellente stabilité thermique.
Excellente transmission lumineuse
Le verre de quartz présente une excellente transmission optique sur l'ensemble du spectre, de l'ultraviolet à l'infrarouge. Sa transmission dans la lumière visible est supérieure à 93%, et dans la région spectrale ultraviolette, sa transmission peut dépasser 90%.
Scénario d'application
Analyse de la structure cristalline en science des matériaux
Les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz sont cruciaux dans divers domaines de la science des matériaux, en particulier pour l'analyse de la structure cristalline. En analysant les figures de diffraction produites par l'interaction des rayons X avec un matériau, des informations vitales sur la structure cristalline, la taille des grains, la composition de phase et l'état de contrainte du matériau peuvent être obtenues.
Composition de phase et analyse des matériaux multiphasiques
Les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz sont utilisés pour identifier les composants et leurs proportions relatives au sein des matériaux polycristallins tels que les alliages, les céramiques et les composites. Ils sont également importants pour l'étude des caractéristiques structurales locales des matériaux amorphes, tels que le verre et les alliages amorphes.
Études sur la transition de phase et la stabilité thermique
Les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz permettent l'étude du comportement de transition de phase des matériaux sous des conditions de température ou de pression variables. En chauffant ou refroidissant les échantillons et en surveillant leurs figures de diffraction, les chercheurs peuvent déterminer si des transitions de phase se produisent dans des conditions spécifiques.
Applications de matériaux critiques dans la fabrication de semi-conducteurs
Dans l'industrie des semi-conducteurs, les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz jouent un rôle important en raison de leurs propriétés de résistance aux températures élevées et à la corrosion. Ils sont utilisés dans les dispositifs à haute température, tels que les tubes de four et les nacelles en verre (ou en quartz) pour les processus de diffusion et d'oxydation, ainsi que dans les dispositifs à basse température, tels que les anneaux en quartz pour les processus de gravure
Lors de l'utilisation de porte-échantillons XRD en quartz pour les expériences, les points suivants doivent être observés:
Assurez-vous que le porte-échantillon est propre et exempt de poussière pour éviter de contaminer l'échantillon et d'affecter les résultats de diffraction.
L'échantillon doit être réparti uniformément dans le porte-échantillon afin d'obtenir des signaux de diffraction optimaux.
Évitez d'exposer le porte-échantillon à des changements de température drastiques pour éviter que le verre de quartz ne se fissure en raison de différentiels de température excessifs.
Lors de l'utilisation du porte-échantillon à haute température ou dans des conditions spécifiques, suivez les directives du fabricant et les réglementations de sécurité.
Les étapes suivantes peuvent être utilisées pour nettoyer et entretenir les porte-échantillons XRD en quartz:
Retirez délicatement la poussière et les résidus de la surface du porte-échantillons à l'aide d'un chiffon doux ou d'une brosse.
Pour les taches tenaces, utilisez un détergent doux et de l'eau pour le nettoyage, mais assurez un rinçage et un séchage minutieux pour éviter tout résidu chimique.
Vérifiez régulièrement le porte-échantillons pour détecter les fissures ou les dommages, en particulier après des expériences à haute température ou haute pression.
Rangez-le dans un endroit sec et propre, à l'abri de la lumière directe du soleil et des environnements humides.
La durée de vie d'un porte-échantillons XRD en quartz dépend de plusieurs facteurs, notamment:
La fréquence d'utilisation et les conditions expérimentales; une utilisation fréquente ou dans des conditions extrêmes peut réduire sa durée de vie.
L'entretien et la propreté du porte-échantillons; un bon entretien peut prolonger sa durée de vie.
La qualité du matériau et de fabrication du porte-échantillons; le verre de quartz de haute qualité est généralement plus durable.
Questions fréquemment posées
Nous sommes spécialisés dans la fabrication intégrée de composants en verre de quartz de haute pureté. Nos principales gammes de produits comprennent :
Tubes et barres de quartz: Une large gamme de diamètres et de spécifications.
Plaques et disques de quartz: Découpés et polis avec précision pour usages optiques et industriels.
Verrerie de laboratoire en quartz: Une gamme complète de verrerie standard et sur mesure, incluant béchers, fioles et nacelles.
Quartz de qualité semi-conducteur: Composants de haute pureté tels que les tubes de traitement et les porteurs pour la fabrication de semi-conducteurs.
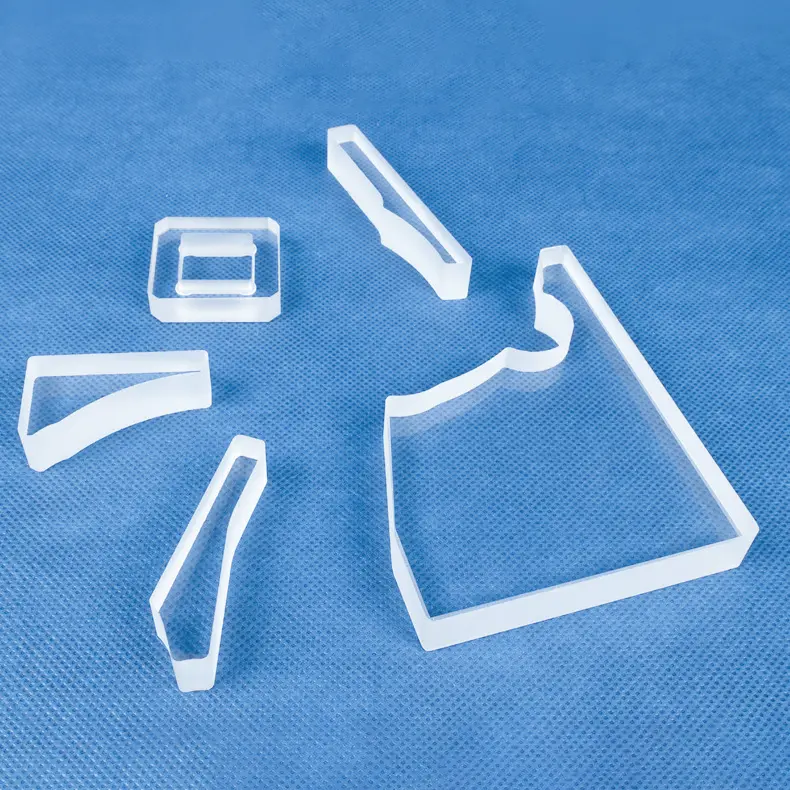
Composants fabriqués sur mesure: Nous pouvons produire des pièces complexes adaptées à vos conceptions et spécifications uniques.
Oui. La fabrication sur mesure est au cœur de notre activité. Forts de plus d'une décennie d'expérience spécialisée, nous nous associons à des entreprises pour leur offrir des services OEM/ODM experts. Nos capacités incluent le soudage, la rectification, le perçage, le polissage, le pliage et d'autres techniques d'usinage de précision, afin de créer des composants qui répondent précisément à vos exigences.
La qualité est primordiale dans notre processus de fabrication. Nous sommes un fabricant certifié ISO 9001:2015, garantissant que nos processus répondent aux normes internationales de gestion de la qualité.Nos produits subissent également des tests SGS rigoureux pour leur pureté et leurs performances. Nous utilisons des matières premières de haute pureté (jusqu'à 99,998% de SiO2) pour produire des articles en quartz fondu et en silice fondue dotés d'une stabilité thermique exceptionnelle, d'une résistance aux températures élevées et d'une inertie chimique.
Nous avons rationalisé notre processus pour qu'il soit le plus efficace possible :
Soumettez votre demande de devis (RFQ) : Envoyez-nous vos dessins techniques, spécifications et exigences via notre formulaire de contact sur le site web ou par e-mail.
Réponse rapide : Vous pouvez vous attendre à une première réponse en quelques minutes et à une communication détaillée dans la demi-heure.
Conception & Proposition : Nous vous soumettrons une proposition de conception détaillée et un devis compétitif sous 24 heures.
Prototypage & Production : Dès approbation, nous passons rapidement du prototypage à la production à grande échelle afin de respecter vos délais.
Un partenariat avec Aoxin Quartz offre plusieurs avantages clés :
Expertise avérée : Avec plus de 10 ans d'expérience dans l'industrie, nous possédons les connaissances techniques nécessaires pour relever les défis complexes.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Valeur compétitive : Situés dans un pôle majeur de production de quartz, nous tirons parti d'une chaîne d'approvisionnement efficace et d'une fabrication avancée pour offrir une qualité exceptionnelle à un prix compétitif.</span
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.