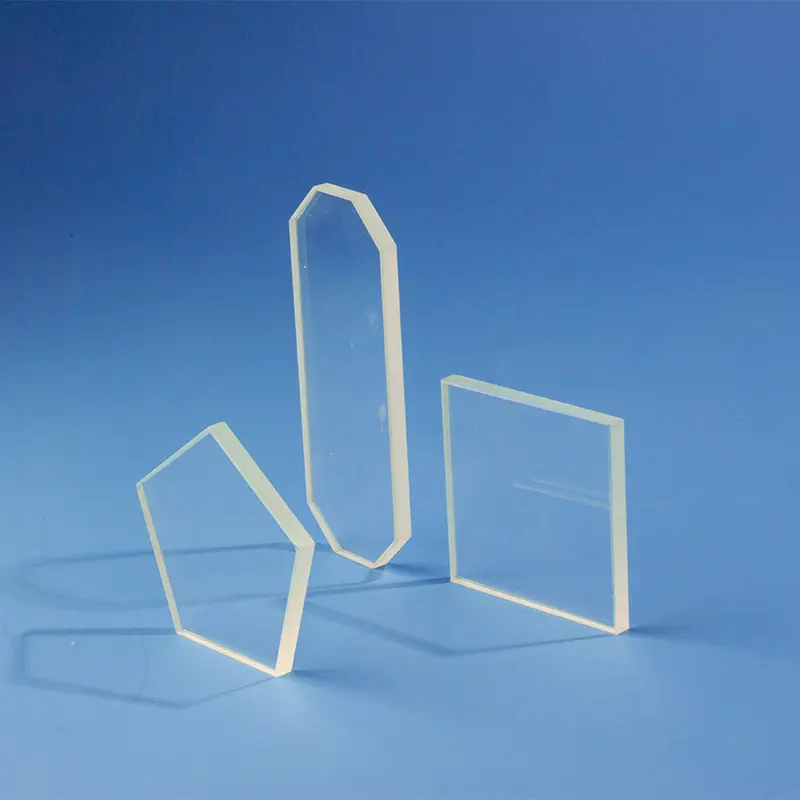
当社の大型石英ガラス板(大型溶融石英シートとも呼ばれる)は、極めて高い純度と優れた光学、熱、化学特性が要求される用途向けに設計されています。高温炉、半導体チャンバー、先進光学システムでの窓、基板、保護カバーとして理想的です。正確な寸法と特定の性能要件を満たすカスタム加工を提供しています
| 特性内容 | 特性値 |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| 密度 | 2.2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| 硬度 | モース硬度 5.5~6.5; ヌープ硬度 570 (荷重100g) |
| 引張強度 | 4.8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² または 48 MPa); 7,000 psi |
| 圧縮強度 | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| 熱膨張係数 | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| 熱伝導率 | 1.4 W/m-°C |
| 比熱 | 670 J/kg-°C |
| 軟化点 | 1730度C(3146度F) |
| 徐冷点 | 1210度C(2210度F) |
| 歪点 | 1120度C(2048度F) |
| 使用温度 | 1200°C |
| 電気抵抗率 | 7×10⁷Ωcm (350°C) |
| サイズ | カスタマイズ対応 |
| ロゴ | ロゴのカスタマイズ対応 |
高温耐性
石英ガラス板は、1100°Cから1250°Cまでの連続動作温度、および短期間であれば最大1450°Cに耐えることができる、卓越した耐熱性を示します
化学的安定性
フッ化水素酸を除き、石英ガラス板はほとんどの酸および化学試薬に対して不活性であり、化学産業および実験室環境での使用に非常に適しています
光学性能
石英ガラス板は、特に紫外線 (UV) 領域において優れた光透過率を有しており、光学部品や光学機器の製造に理想的な材料です。
寸法多様性
石英ガラス板は、様々な産業用途および顧客の要求を満たすために、多種多様なサイズと仕様で製造することができます。
アプリケーションシナリオ
大型石英ガラス板は、卓越した耐熱性を示し、1100°Cから1250°Cまでの連続動作温度、および短期間であれば最大1450°Cに耐えることができます。この特性により、半導体製造や高温実験など、高温環境が要求されるアプリケーションに非常に適しています
光学分野において、大型石英ガラス板は高い透明度、低い屈折率、および優れた紫外線(UV)透過率により広く利用されています。これらは光学ミラー、レンズ、光ファイバー通信部品、レーザー、光センサーの製造に使用できます。石英ガラス板の光学性能は、光学機器製造にとって理想的な材料となります
大型石英ガラス板は、極めて高い化学的安定性を示し、フッ化水素酸を除き、ほとんどすべての酸および化学試薬に対して不活性です。この特性により、大型石英ガラス板は、化学産業や化学実験装置、化学配管、反応容器などの実験室環境での使用に非常に適しており、性能を損なうことなく使用できます
よくある質問
当社は、高純度石英ガラス部品の一貫製造を専門としております。主な製品ラインナップは以下の通りです:
石英管・石英棒: 幅広い直径と仕様。
石英プレート・ディスク: 光学および工業用途向けに精密に切断・研磨。
石英実験器具: ビーカー、フラスコ、ボートなど、標準品から特注品まで幅広い種類のガラス器具。
半導体グレード石英: 半導体製造用のプロセスチューブやキャリアなどの高純度部品。
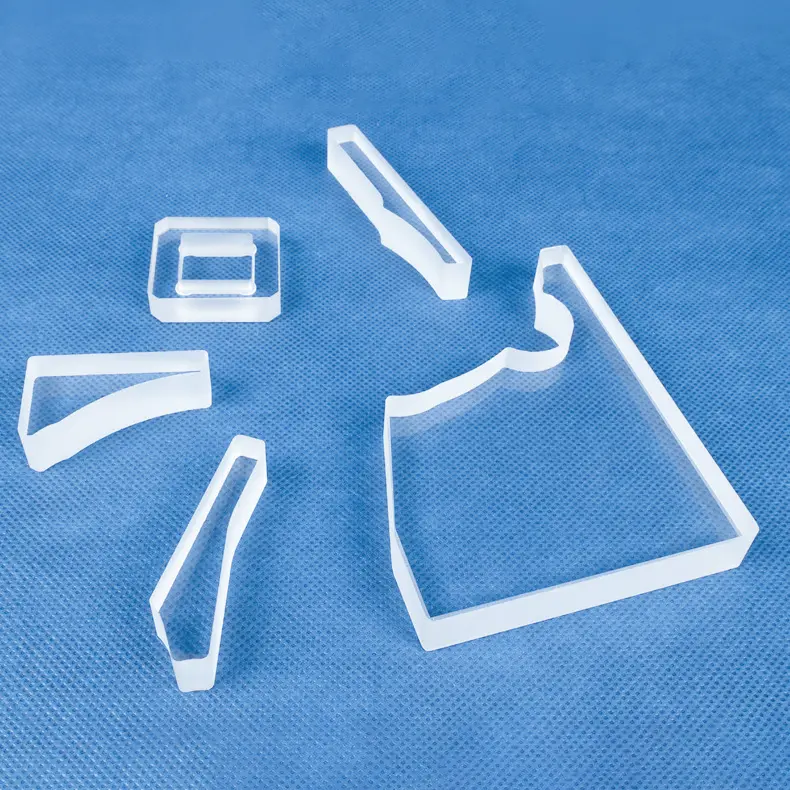
特注加工部品: お客様固有の設計および仕様に合わせて、複雑な部品を製造できます。
はい。特注加工(カスタム加工)は、当社の事業の中核です。10年以上にわたる専門的な経験を活かし、お客様企業と提携し、専門的なOEM/ODMサービスを提供しております。当社の加工技術には、溶接、研削、穴あけ、研磨、曲げ加工、その他さまざまな精密加工技術が含まれており、お客様の厳密なご要望にお応えする部品を製造いたします。
品質は当社の製造プロセスにおいて最も重要です。当社はISO 9001:2015認証取得メーカーであり、当社のプロセスが国際的な品質管理基準を満たしていることを保証します。また、当社の製品は純度と性能に関して厳格なSGS試験を受けています。当社は高純度原材料(SiO2 99.998%まで)を使用し、優れた熱安定性、高温耐性、化学的不活性を持つ溶融石英および溶融シリカ製品を製造しています。
当社はプロセスを最大限に効率化しました:
RFQ(見積依頼)を提出:ウェブサイトのお問い合わせフォームまたはEメールで、技術図面、仕様、要件をお送りください。
迅速な対応: 数分以内に初回返信を、30分以内に詳細なご連絡を差し上げます。
設計・提案:24時間以内に詳細な設計提案と競争力のある見積もりをお届けします。
試作・生産:承認後、お客様の納期に間に合わせるため、迅速に試作から本格的な量産へと移行いたします。
Aoxin Quartzとの提携には、いくつかの重要なメリットがあります:
実証された専門知識:業界で10年以上の経験を持つ当社には、複雑な課題に取り組むための技術的知見があります。
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
競争力のある価値:主要な石英生産拠点に位置することで、効率的なサプライチェーンと先進的な製造技術を活用し、競争力のある価格で卓越した品質を提供しています。
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.