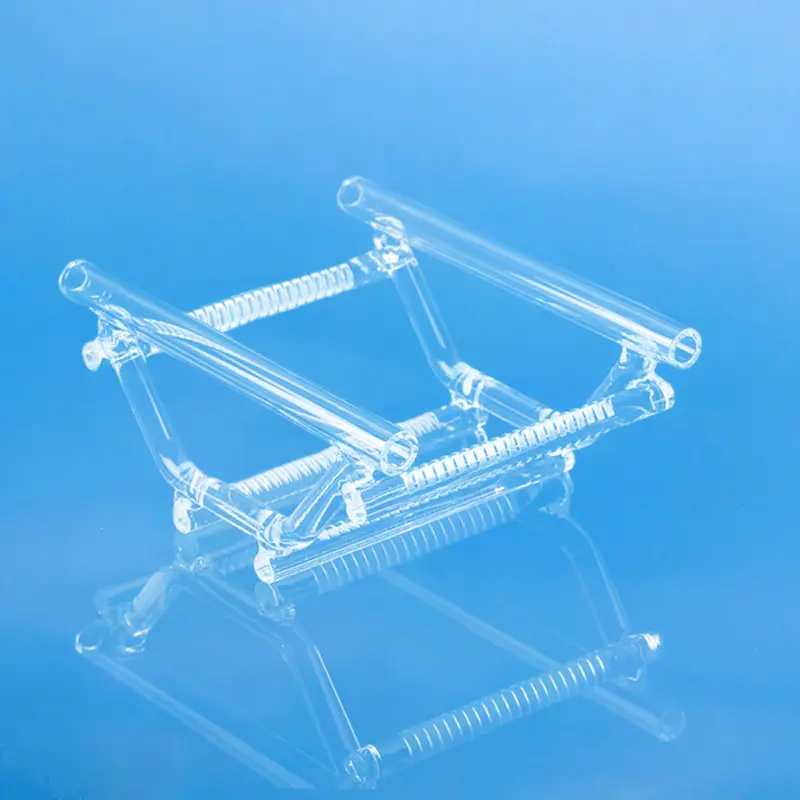
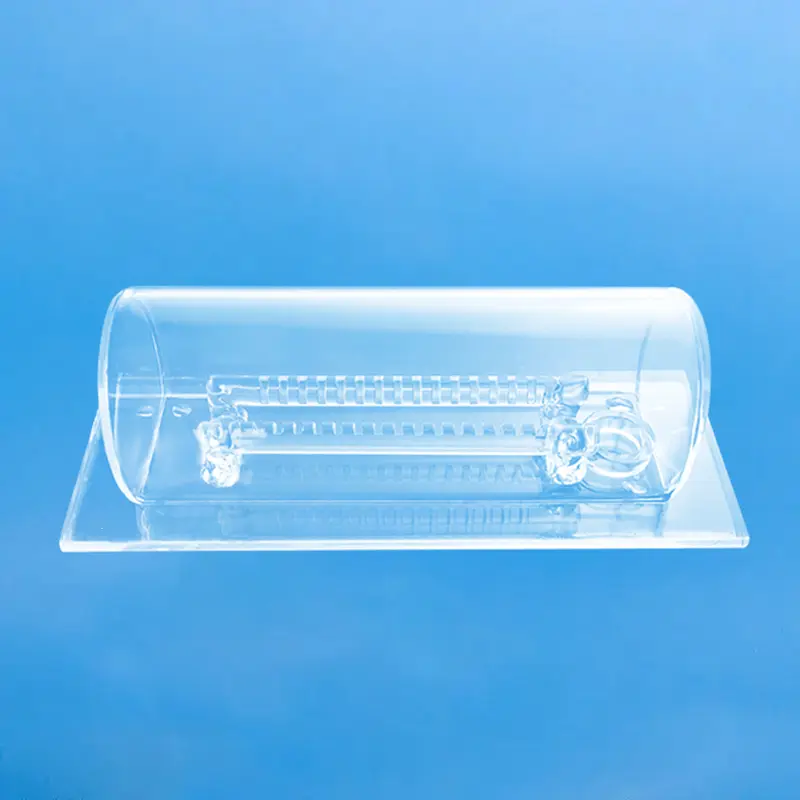
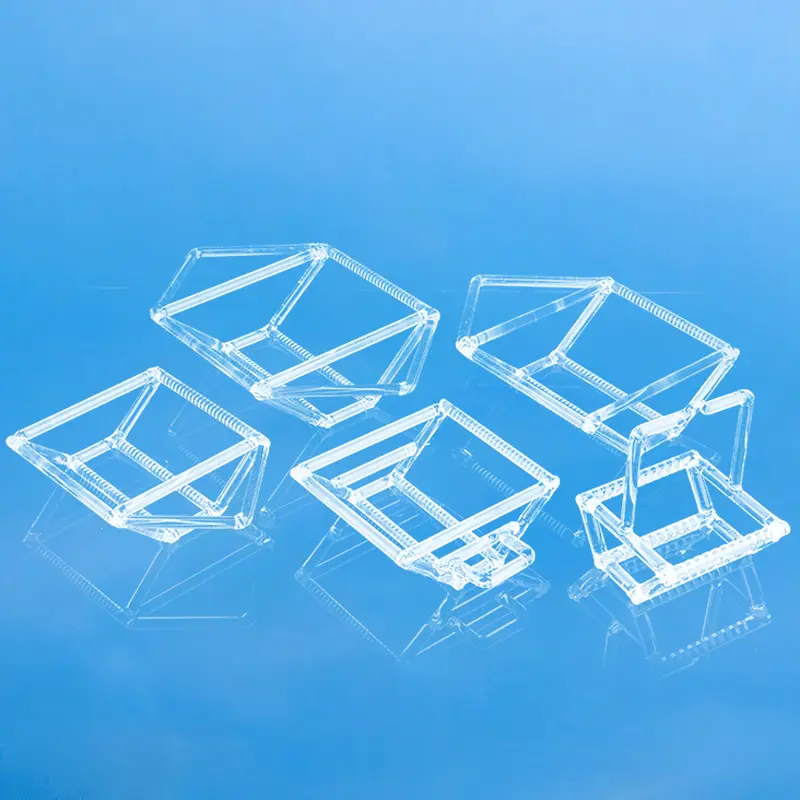
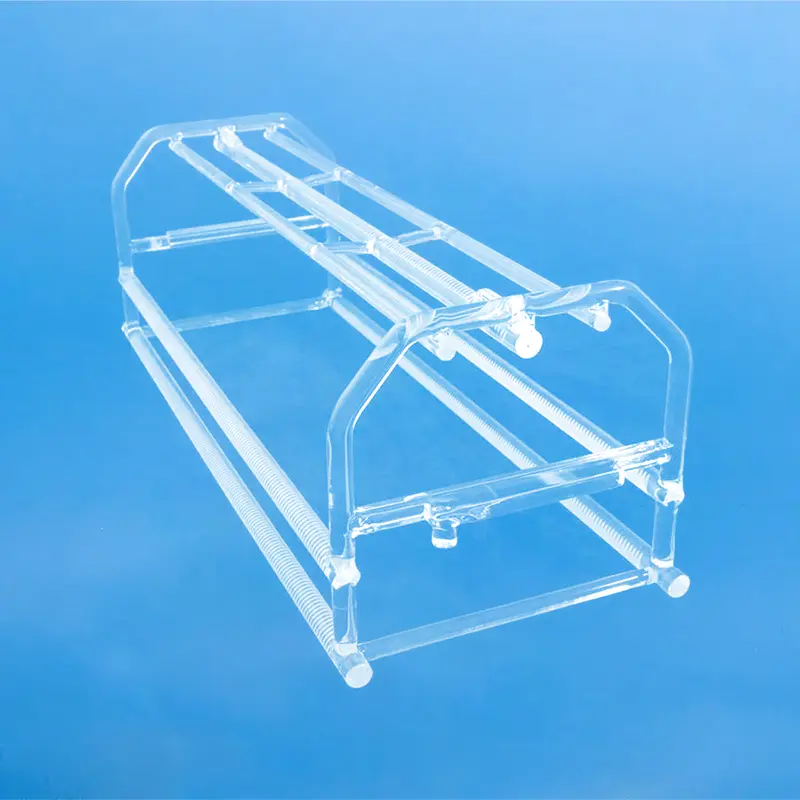
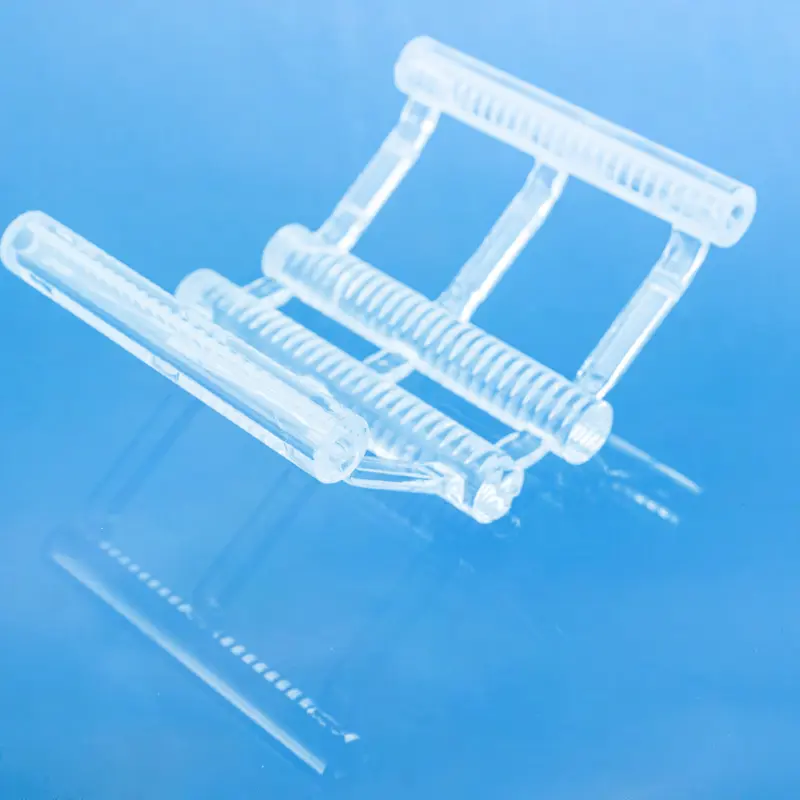
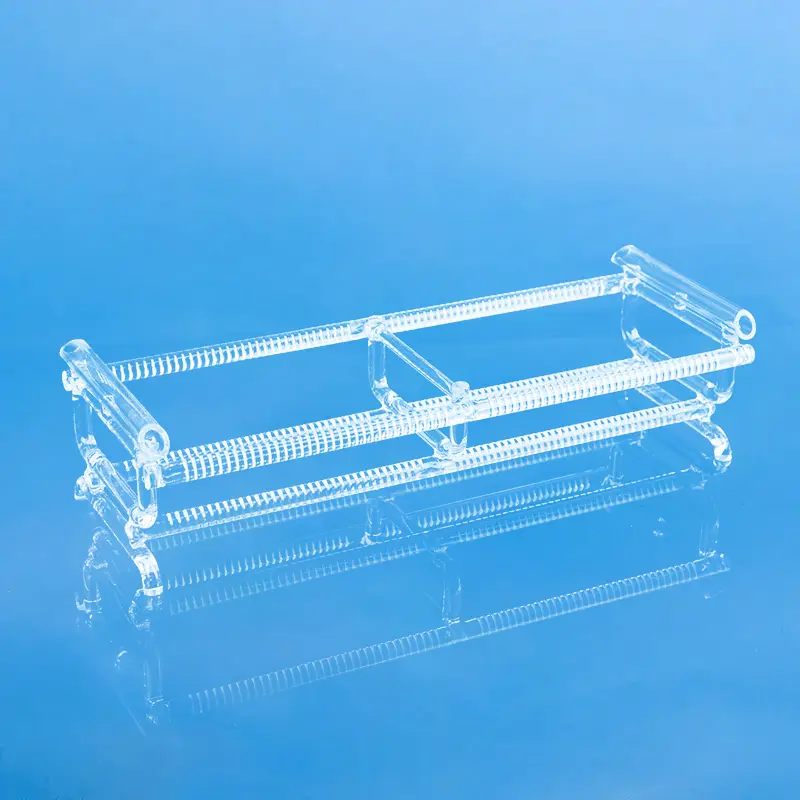
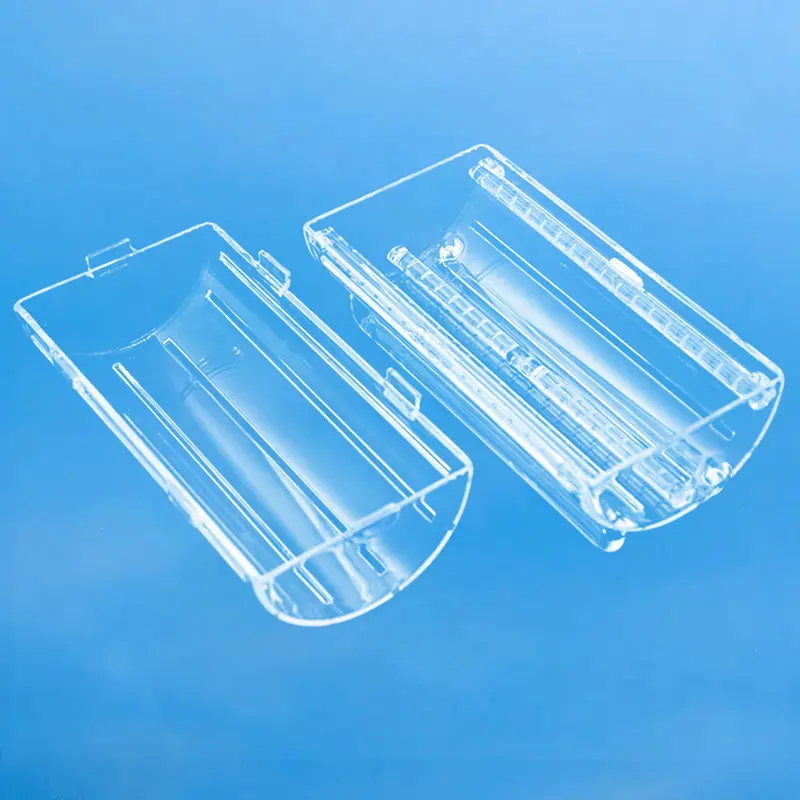
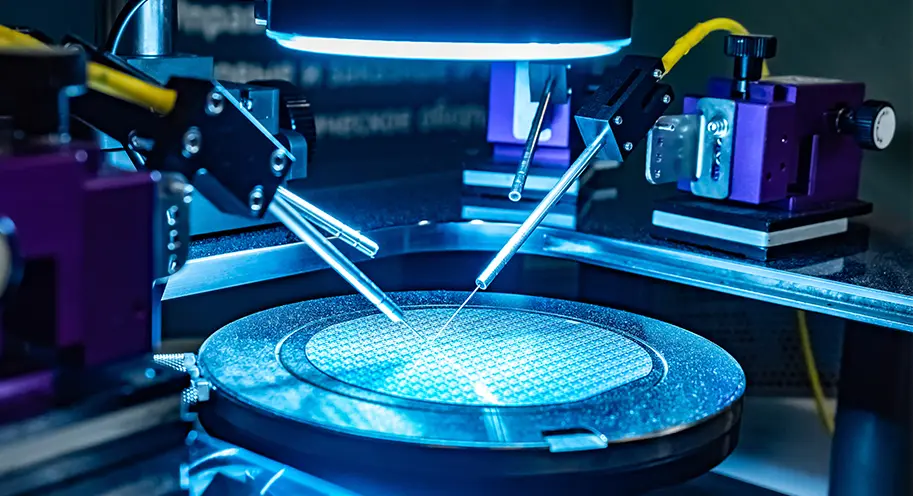
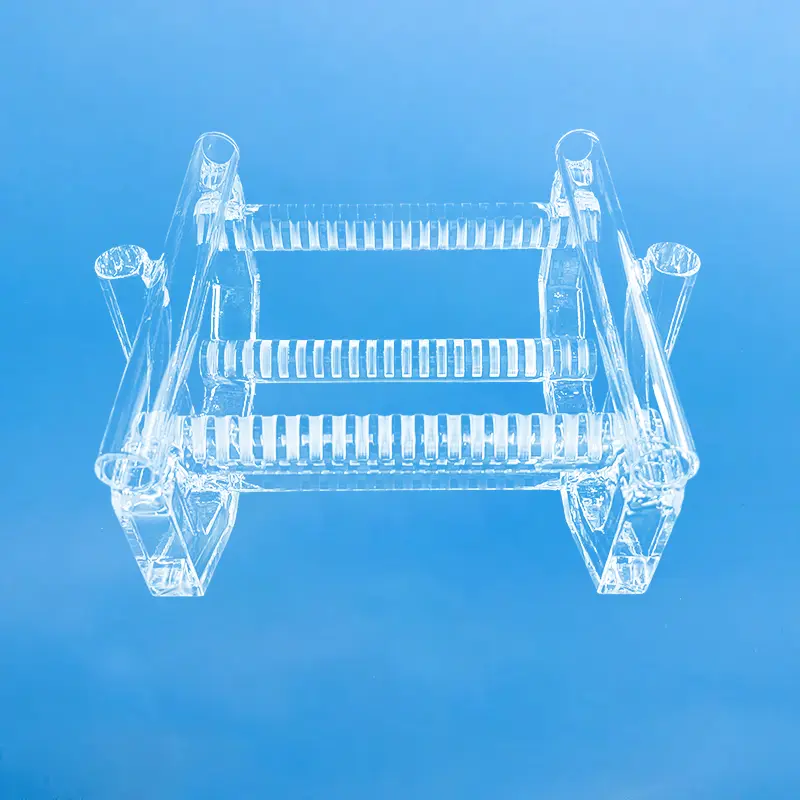
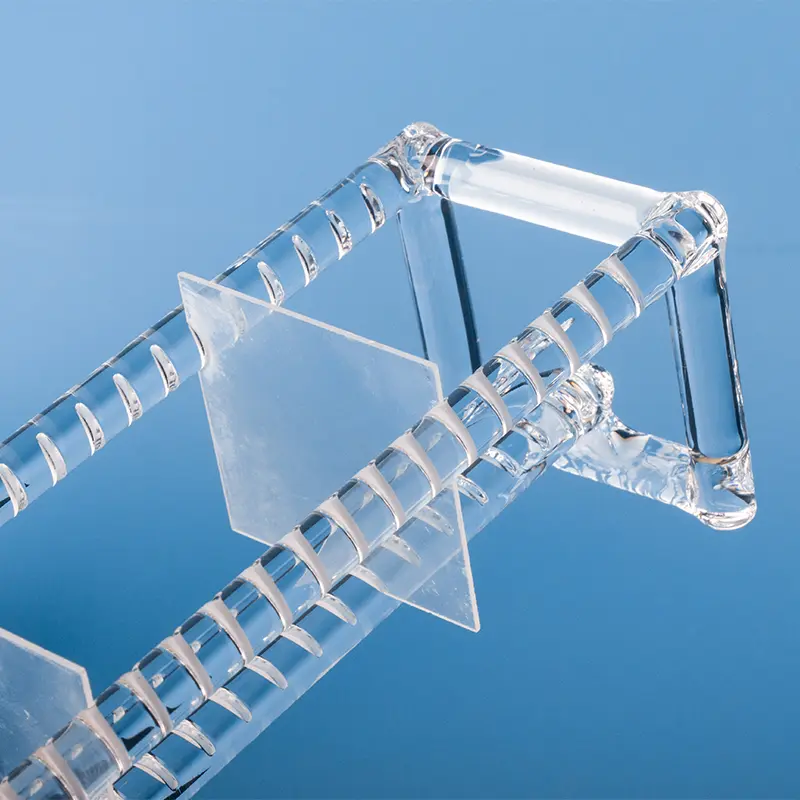
Quartz wafer boats are manufactured from high-purity quartz glass and are characterized by their high-temperature resistance and excellent chemical stability. They are primarily used in semiconductor manufacturing for carrying and processing silicon wafers. Quartz wafer boats play a critical role in semiconductor processes, ensuring the safety and stability of wafers during manufacturing while also influencing the quality and performance of the final chip products.
| Contenido de la propiedad | Valores inmobiliarios |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densidad | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureza | 5,5 - 6,5 Escala de Mohs 570 KHN 100 |
| Resistencia a la tracción | 4,8×10⁷ Pa (N/mm2) (7000 psi) |
| Resistencia a la compresión | >1,1×10⁹ Pa (160.000 psi) |
| Coeficiente de dilatación térmica | 5,5×10-⁷ cm/cm-°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductividad térmica | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Calor específico | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Punto de ablandamiento | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Punto de recocido | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Punto de deformación | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Temperatura de trabajo | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Resistividad eléctrica | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Talla | Personalizado |
| Logotipo | Logotipo personalizado Aceptar |
Resistencia a altas temperaturas
Quartz wafer boats can withstand the high-temperature environments encountered in semiconductor manufacturing, typically tolerating temperatures up to 1100 degrees Celsius and above.
High-Purity Material
Quartz wafer boats are made from high-purity quartz glass, generally exceeding 99.999% purity, ensuring that no impurities are introduced during semiconductor manufacturing.
Chemical Stability
Quartz wafer boats are inert to a variety of chemicals, maintaining stability in diverse chemical environments, and do not react with chemicals used in semiconductor processes.
Excellent Optical Properties
Quartz wafer boats possess excellent optical transmission, allowing light to pass through across the ultraviolet to infrared spectrum. This is crucial for semiconductor manufacturing processes that require optical inspection.
Escenario de aplicación
High-Temperature Processing
Quartz wafer boats play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes that require high-temperature treatment, such as diffusion and oxidation. They maintain stability at temperatures exceeding 300°C, preventing melting or deformation, thus ensuring the safety of the silicon wafers.
High-Temperature Zone Components
In the semiconductor field, quartz wafer boats are used as components in high-temperature zones, primarily for furnace tubes and boat frames used in processes like diffusion and oxidation. They come into direct or indirect contact with silicon wafers in high-temperature environments.
The primary material of quartz wafer boats is high-purity quartz glass, which contains an extremely high proportion of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), typically with a purity exceeding 99.999%. This high-purity quartz glass ensures that no impurities are introduced during semiconductor manufacturing, while also exhibiting excellent high-temperature resistance and chemical stability.
Quartz wafer boats primarily serve as tools for carrying and transporting silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing. They are used in critical process steps, such as high-temperature processing, cleaning, and chemical processing, ensuring the stability and safety of the silicon wafers. The high-temperature resistance and chemical stability of quartz wafer boats are crucial for ensuring product quality in semiconductor manufacturing.
The lifespan of quartz wafer boats is influenced by various factors, including frequency of use, temperature, and chemical environment. Generally, with proper usage and maintenance, quartz wafer boats can be reused multiple times. However, with increased use, they may gradually lose performance due to wear, contamination, or the formation of micro-cracks. It becomes necessary to replace the wafer boat to ensure process stability and product reliability. The specific lifespan needs to be determined based on actual use and maintenance conditions.
Preguntas más frecuentes
El vidrio de cuarzo es un material duro y quebradizo con excelentes propiedades físicas y químicas, dureza mecánica extremadamente alta, buen aislamiento eléctrico, resistencia a altas temperaturas y a la corrosión, rendimiento de retardo bajo y estable, buena transmitancia luminosa, etc. Se utiliza ampliamente en semiconductores, óptica, electricidad, química, aeroespacial, automoción y otros campos. Los materiales duros y quebradizos son difíciles de procesar, y muchos campos necesitan urgentemente procesos de corte con un pequeño colapso del borde, menos pérdida de material, baja rugosidad de la sección transversal y un amplio rango de grosor de corte. El método de corte tradicional del vidrio de cuarzo es el corte mecánico, es decir, el corte por disco. Los métodos de corte no tradicionales incluyen el corte por chorro de agua, el corte por hilo de descarga electroquímica, el corte por láser continuo, etc. El corte mecánico tiene un bajo coste, pero el contacto entre la rueda y el material causa un gran desgaste de la herramienta, y el material es fácilmente contaminado por la herramienta. El vidrio de cuarzo es propenso al colapso de los bordes, las microfisuras y la tensión residual, lo que afecta a la resistencia y el rendimiento del material. Es difícil conseguir un corte curvo y requiere un tratamiento posterior, como esmerilado y pulido. El corte por láser no entra en contacto directo con el material, no tiene tensión de contacto y puede realizar cortes curvos complejos. El láser de picosegundos tiene las ventajas de un diámetro de punto pequeño, alta precisión, tiempo de acción corto con el material y área de acción pequeña, y es adecuado para el procesamiento de materiales duros y quebradizos.
。