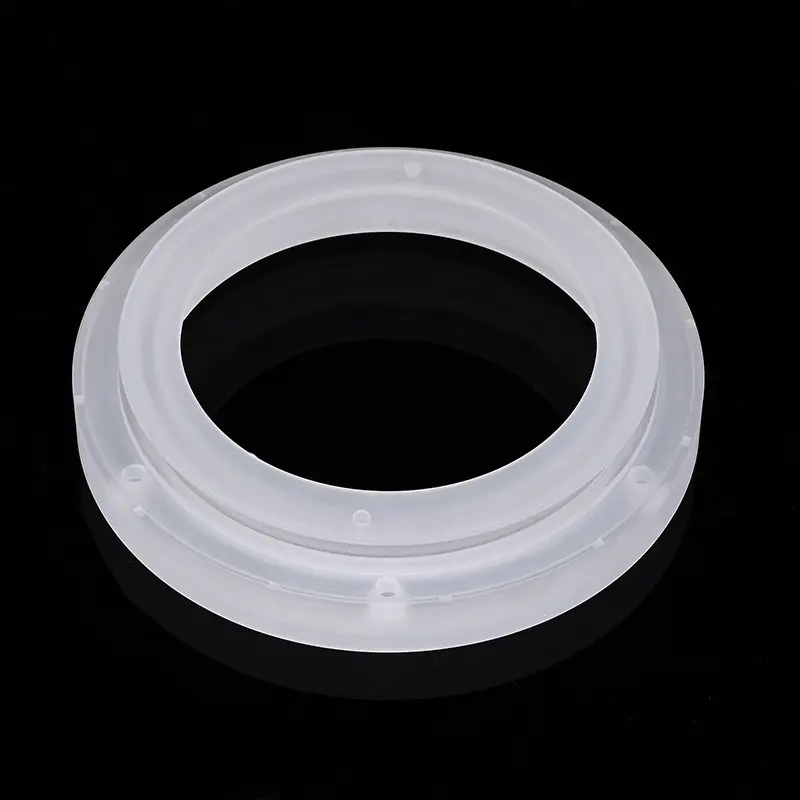
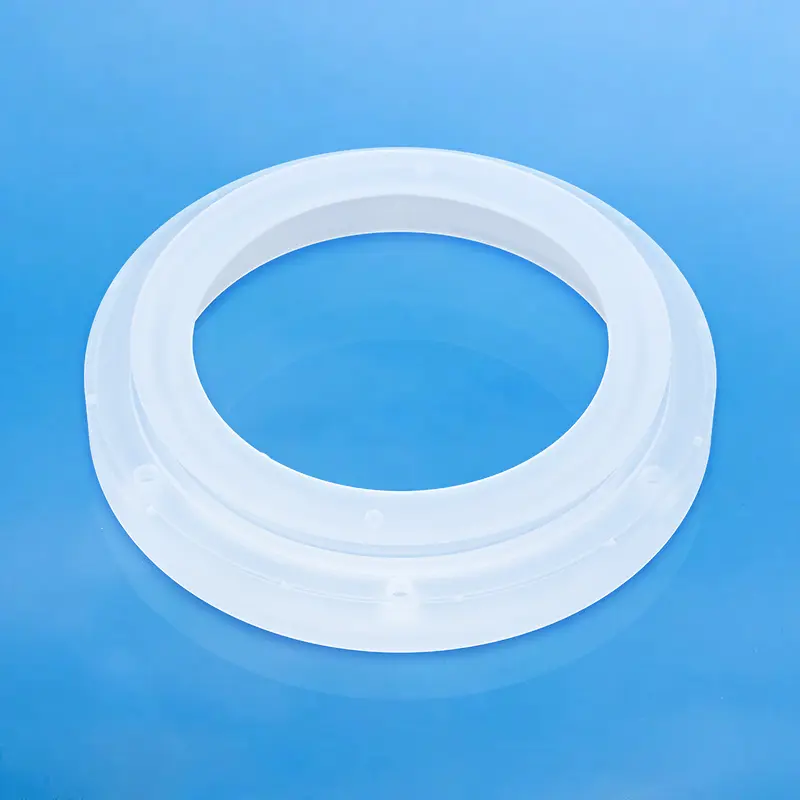
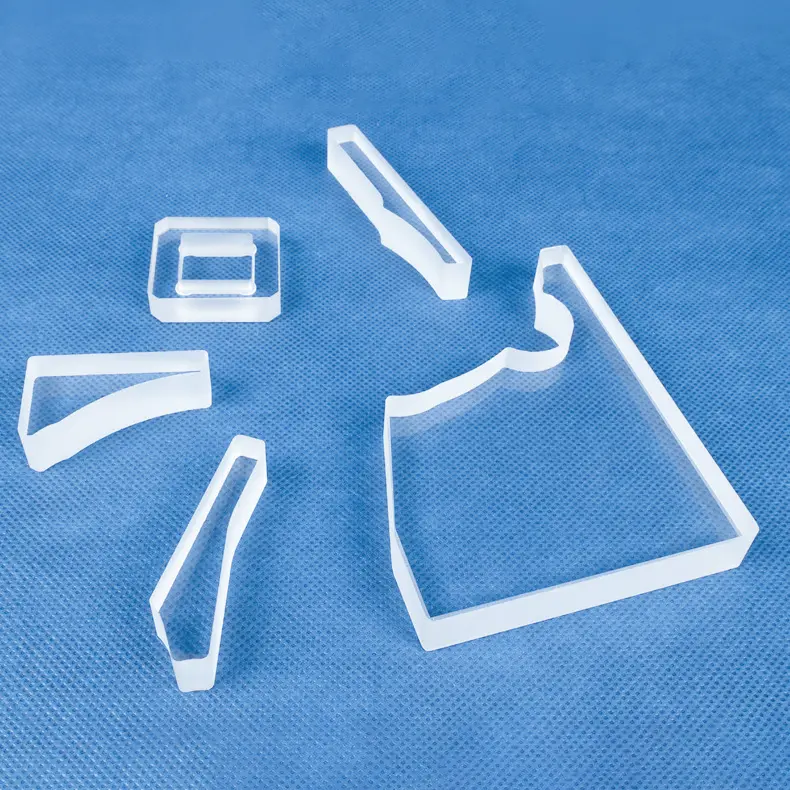
Nuestras bridas de cuarzo, también conocidas como bridas de sílice fundida, están diseñadas con precisión para aplicaciones críticas que requieren pureza extrema, resistencia a altas temperaturas y compatibilidad con el vacío. Ideales para equipos de semiconductores, ópticos y de laboratorio, estas bridas garantizan conexiones fiables y resistentes a la corrosión. Hay diseños personalizados disponibles para cumplir con sus especificaciones exactas.
| Contenido de la propiedad | Valores de la propiedad |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densidad | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureza | Dureza Mohs de 5,5 a 6,5; Dureza Knoop 570 (con una carga de 100g) |
| Resistencia a la tracción | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² o 48 MPa); 7.000 psi |
| Resistencia a la compresión | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coeficiente de dilatación térmica | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductividad térmica | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Calor específico | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Punto de ablandamiento | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Punto de recocido | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Punto de deformación | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Temperatura de trabajo | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Resistividad eléctrica | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Tamaño | Personalizado |
| Logotipo | Se acepta el logotipo personalizado |
Rendimiento a alta temperatura
Las bridas de cuarzo pueden soportar temperaturas extremadamente altas, típicamente superiores a 1000°C, lo que las hace adecuadas para entornos de alta temperatura, como tuberías de vapor de alta temperatura y sistemas de transporte de metales fundidos.
Excelente estabilidad química
Las bridas de cuarzo exhiben una resistencia excepcional a diversas sustancias químicas, incluyendo ácidos fuertes, bases fuertes y solventes orgánicos, lo que las hace muy valoradas en las industrias química y farmacéutica.
Material de alta pureza
Las bridas de cuarzo se fabrican con vidrio de cuarzo de alta pureza, lo que permite su uso en entornos de sala limpia dentro de las industrias de semiconductores y microelectrónica, ya que no liberan partículas ni productos químicos que puedan contaminar los productos.
Buena resistencia mecánica y durabilidad
Quartz flanges possess good mechanical strength and durability, maintaining their structural integrity even under repeated temperature and pressure fluctuations, thereby extending the lifespan of equipment.
Escenario de aplicación
Industria química
En la industria química, las bridas de cuarzo se utilizan para las conexiones de tuberías. Su resistencia a la corrosión y su rendimiento a alta temperatura las hacen particularmente adecuadas para el lavado ácido, el lavado alcalino y procesos similares, asegurando la operación estable a largo plazo de los sistemas de tuberías.
Industria petroquímica
En la industria petroquímica, las bridas de cuarzo sirven como componentes importantes para la conexión de tuberías. Cumplen con los requisitos de entornos hostiles caracterizados por altas temperaturas, alta presión y ácidos/bases fuertes. Su resistencia única al impacto las hace particularmente útiles para la conexión de bombas y válvulas.
Industria Electrónica y Eléctrica
Las bridas de cuarzo se aplican ampliamente en las industrias electrónica y eléctrica, como para la conexión de tuberías de precisión en la producción de chips LED y en reacciones de síntesis de óxidos en la fabricación de células solares. Su alta pureza y resistencia a la corrosión garantizan las conexiones de precisión y la pureza y continuidad de los procesos de reacción.
Fabricación de Alimentos
En la industria de fabricación de alimentos, las bridas de cuarzo pueden utilizarse para el transporte de materiales ligeramente corrosivos como parte de las conexiones de tuberías en las líneas de producción de alimentos. No contaminan ni dañan los alimentos, lo que las convierte en una parte esencial del flujo de trabajo del procesamiento de alimentos.
El material principal de las bridas de cuarzo es el vidrio de cuarzo de alta pureza, que exhibe una resistencia excepcional a la corrosión y un rendimiento a alta temperatura. Puede resistir eficazmente la erosión de diversas sustancias químicas, incluyendo ácidos fuertes, bases fuertes y disolventes orgánicos, manteniendo la estabilidad en entornos de alta temperatura (típicamente superando los 1000°C), sin deformarse ni fundirse.
Las bridas de cuarzo se utilizan ampliamente en industrias como el procesamiento químico, la petroquímica, la electrónica y eléctrica, y la fabricación de alimentos. En las industrias química y petroquímica, se emplean para conexiones de tuberías que involucran medios a alta temperatura y corrosivos. En las industrias electrónica y eléctrica, se usan para conexiones precisas de tuberías en la producción de chips LED y la fabricación de células solares. En el sector de fabricación de alimentos, se utilizan para transportar materiales ligeramente corrosivos, garantizando la seguridad alimentaria.
Los ciclos de mantenimiento y reemplazo de las bridas de cuarzo dependen de múltiples factores, incluyendo el entorno operativo, la temperatura, la presión y el tipo de medios químicos involucrados. Generalmente, si las bridas de cuarzo se utilizan correctamente y se mantienen regularmente, su vida útil puede ser bastante larga. Sin embargo, con un uso intensificado, pueden perder rendimiento gradualmente debido al desgaste, la contaminación o la formación de microfisuras. Se hace necesario reemplazarlas cuando ocurren tales problemas. Los ciclos específicos de mantenimiento y reemplazo deben determinarse en función de las condiciones de uso reales y las recomendaciones del fabricante.
Preguntas más frecuentes
Nos especializamos en la fabricación integral de componentes de vidrio de cuarzo de alta pureza. Nuestras principales líneas de productos incluyen:
Tubos y varillas de cuarzo: Una amplia gama de diámetros y especificaciones.
Placas y discos de cuarzo: Corte de precisión y pulido para uso óptico e industrial.
Cristalería de laboratorio de cuarzo: Una suite completa de cristalería estándar y personalizada, incluyendo vasos de precipitados, matraces y barcas.
Cuarzo de grado semiconductor: Componentes de alta pureza como tubos de proceso y portadores para la fabricación de semiconductores.
Componentes fabricados a medida: Podemos producir piezas complejas adaptadas a sus diseños y especificaciones únicas.
Sí. La fabricación personalizada es el pilar central de nuestro negocio. Con más de una década de experiencia especializada, nos asociamos con empresas para ofrecerles servicios expertos de OEM/ODM. Nuestras capacidades incluyen soldadura, rectificado, perforación, pulido, doblado y otras técnicas de mecanizado de precisión para crear componentes que cumplan con sus requisitos exactos.
La calidad es primordial en nuestro proceso de fabricación. Somos un fabricante certificado ISO 9001:2015, lo que garantiza que nuestros procesos cumplen con los estándares internacionales de gestión de calidad.Nuestros productos también se someten a rigurosas pruebas SGS de pureza y rendimiento. Utilizamos materias primas de alta pureza (hasta 99,998% de SiO2) para producir productos de cuarzo fundido y sílice fundida con una estabilidad térmica excepcional, alta resistencia a la temperatura e inercia química.
Hemos optimizado nuestro proceso para que sea lo más eficiente posible:
Envíe su Solicitud de Cotización (RFQ): Envíenos sus dibujos técnicos, especificaciones y requisitos a través de nuestro formulario de contacto en el sitio web o por correo electrónico.
Respuesta rápida: Puede esperar una respuesta inicial en cuestión de minutos y una comunicación detallada en media hora.
Diseño y Propuesta: Le entregaremos una propuesta de diseño detallada y un presupuesto competitivo en 24 horas.
Prototipado y Producción: Tras la aprobación, pasamos rápidamente del prototipado a la producción a gran escala para cumplir con sus plazos de entrega.
Asociarse con Aoxin Quartz ofrece varias ventajas clave:
Experiencia comprobada: Con más de 10 años en la industria, poseemos el conocimiento técnico para abordar desafíos complejos.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Valor competitivo: Ubicados en un importante centro de producción de cuarzo, aprovechamos una cadena de suministro eficiente y una fabricación avanzada para ofrecer una calidad excepcional a un precio competitivo.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.