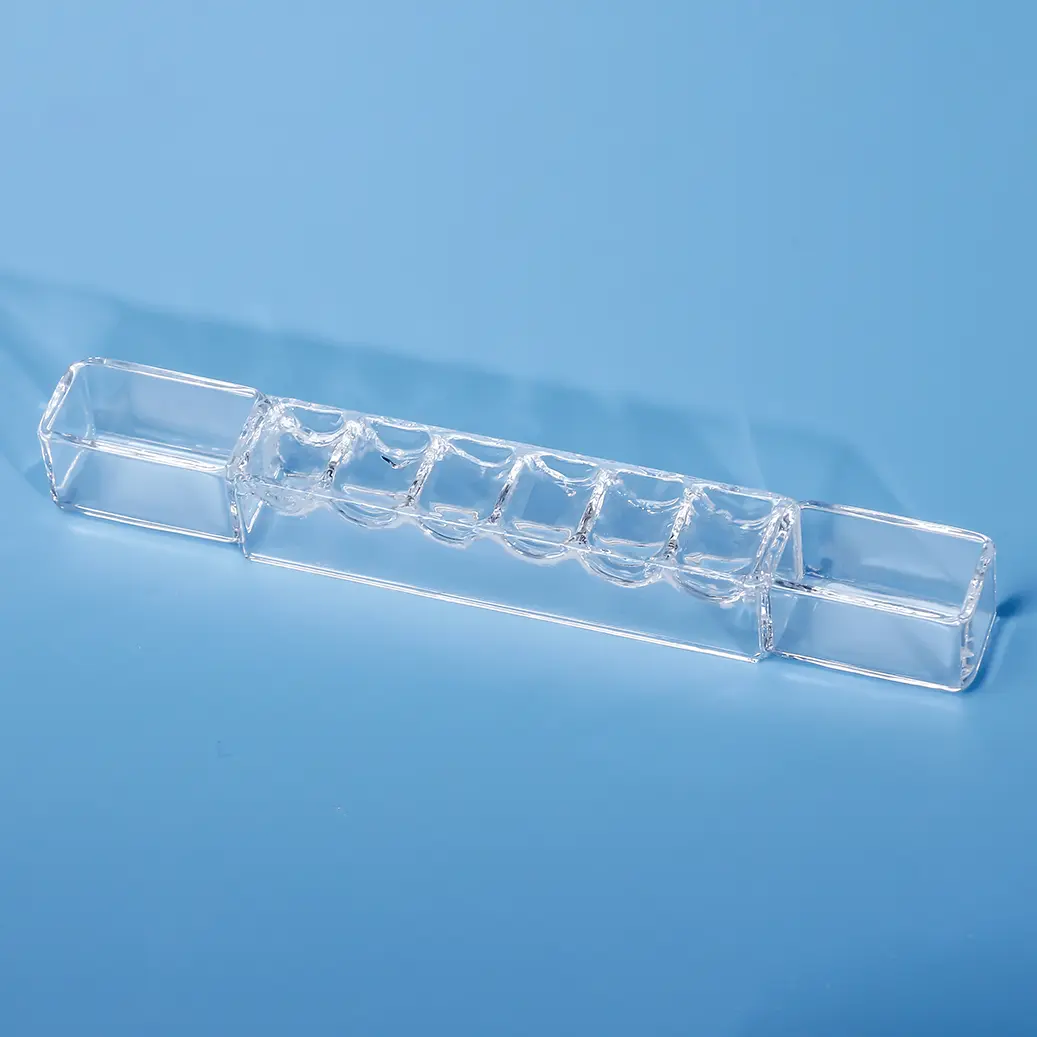
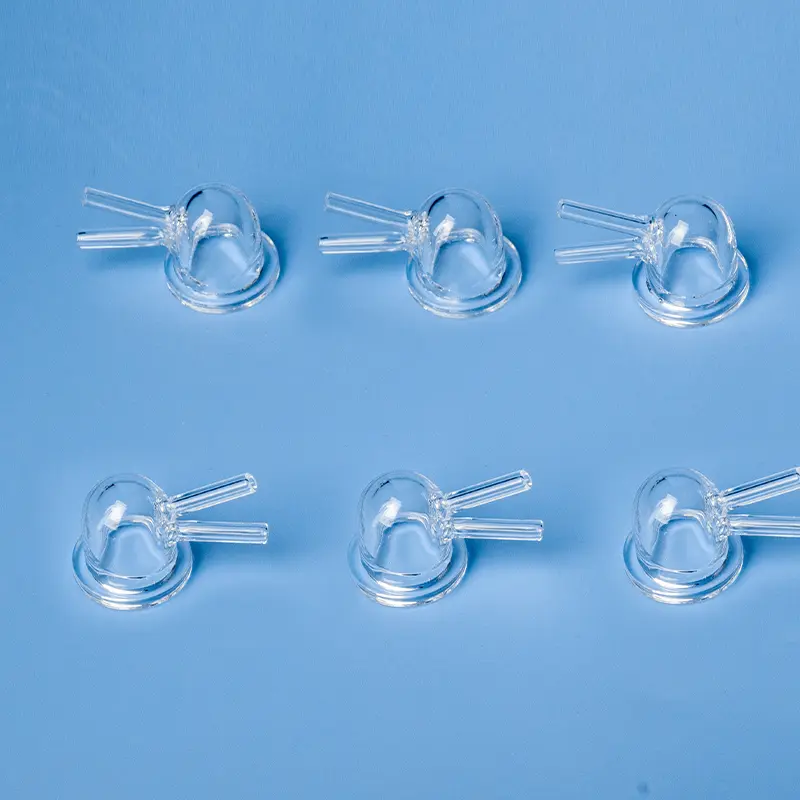
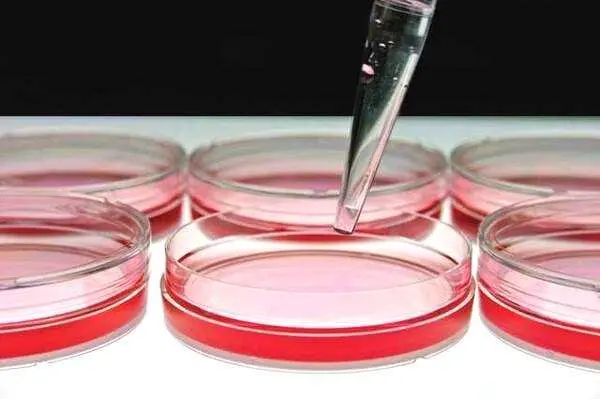
Nuestras placas multipocillo de cuarzo y celdas de reacción de sílice fundida personalizadas están diseñadas con precisión para diversas aplicaciones analíticas y de investigación. Fabricados con sílice fundida de alta pureza, estos componentes a medida ofrecen una transmisión UV-Vis excepcional, una resistencia química superior y una alta estabilidad térmica. Ideales para el procesamiento de múltiples muestras, espectroscopia y sistemas microfluídicos avanzados, ofrecemos soluciones adaptadas para cumplir con sus especificaciones exactas de diseño y rendimiento.
| Contenido de la propiedad | Valores de la propiedad |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densidad | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureza | Dureza Mohs de 5,5 a 6,5; Dureza Knoop 570 (con una carga de 100g) |
| Resistencia a la tracción | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² o 48 MPa); 7.000 psi |
| Resistencia a la compresión | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coeficiente de dilatación térmica | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductividad térmica | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Calor específico | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Punto de ablandamiento | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Punto de recocido | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Punto de deformación | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Temperatura de trabajo | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Resistividad eléctrica | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Tamaño | Personalizado |
| Logotipo | Se acepta el logotipo personalizado |
Alta resistencia a la temperatura
Las placas de Petri de cuarzo pueden soportar temperaturas extremadamente altas, con temperaturas de trabajo a largo plazo que oscilan entre 1100°C y 1250°C y una exposición a corto plazo a temperaturas de hasta 1450°C
Resistencia a la corrosión
El vidrio de cuarzo es inerte a casi todos los ácidos (excepto el ácido fluorhídrico), ofreciendo una resistencia superior a los ácidos que es 30 veces mayor que la de la cerámica y 150 veces mayor que la del acero inoxidable.
Alta transmitancia de luz
El vidrio de cuarzo exhibe una excelente transmitancia de luz en todo el espectro, desde el ultravioleta hasta el infrarrojo. Su transmitancia en la luz visible es superior al 95%, y su transmitancia máxima en el rango espectral ultravioleta supera el 85%.
Estabilidad química
El vidrio de cuarzo posee una estabilidad química excepcional y no reacciona fácilmente con otras sustancias químicas. Esto lo convierte en una opción popular en laboratorios, especialmente para experimentos donde mantener la pureza del recipiente es crítico.
Escenario de aplicación
Investigación en microbiología
Se utilizan para el aislamiento, cultivo e identificación de microorganismos como bacterias y hongos. Las placas de Petri de cuarzo son adecuadas para una variedad de experimentos microbiológicos debido a sus propiedades de alta resistencia a la temperatura y a la corrosión.
Las placas de Petri de cuarzo pueden soportar temperaturas extremadamente altas, con temperaturas de trabajo a largo plazo que oscilan entre 1100°C y 1250°C y una exposición a corto plazo a temperaturas de hasta 1450°C.
El vidrio de cuarzo es inerte a casi todos los ácidos (excepto el ácido fluorhídrico), ofreciendo una resistencia superior a los ácidos que es 30 veces mayor que la de la cerámica y 150 veces mayor que la del acero inoxidable.
Las placas de Petri de cuarzo poseen una excelente transmitancia en todo el espectro, desde el ultravioleta hasta el infrarrojo. Su transmitancia en la luz visible es superior al 95%, y su transmitancia máxima en el rango espectral ultravioleta es superior al 85%, lo que las hace muy adecuadas para experimentos que requieren una alta transmisión de luz.
Preguntas más frecuentes
Nos especializamos en la fabricación integral de componentes de vidrio de cuarzo de alta pureza. Nuestras principales líneas de productos incluyen:
Tubos y varillas de cuarzo: Una amplia gama de diámetros y especificaciones.
Placas y discos de cuarzo: Corte de precisión y pulido para uso óptico e industrial.
Cristalería de laboratorio de cuarzo: Una suite completa de cristalería estándar y personalizada, incluyendo vasos de precipitados, matraces y barcas.
Cuarzo de grado semiconductor: Componentes de alta pureza como tubos de proceso y portadores para la fabricación de semiconductores.
Componentes fabricados a medida: Podemos producir piezas complejas adaptadas a sus diseños y especificaciones únicas.
Sí. La fabricación personalizada es el pilar central de nuestro negocio. Con más de una década de experiencia especializada, nos asociamos con empresas para ofrecerles servicios expertos de OEM/ODM. Nuestras capacidades incluyen soldadura, rectificado, perforación, pulido, doblado y otras técnicas de mecanizado de precisión para crear componentes que cumplan con sus requisitos exactos.
La calidad es primordial en nuestro proceso de fabricación. Somos un fabricante certificado ISO 9001:2015, lo que garantiza que nuestros procesos cumplen con los estándares internacionales de gestión de calidad.Nuestros productos también se someten a rigurosas pruebas SGS de pureza y rendimiento. Utilizamos materias primas de alta pureza (hasta 99,998% de SiO2) para producir productos de cuarzo fundido y sílice fundida con una estabilidad térmica excepcional, alta resistencia a la temperatura e inercia química.
Hemos optimizado nuestro proceso para que sea lo más eficiente posible:
Envíe su Solicitud de Cotización (RFQ): Envíenos sus dibujos técnicos, especificaciones y requisitos a través de nuestro formulario de contacto en el sitio web o por correo electrónico.
Respuesta rápida: Puede esperar una respuesta inicial en cuestión de minutos y una comunicación detallada en media hora.
Diseño y Propuesta: Le entregaremos una propuesta de diseño detallada y un presupuesto competitivo en 24 horas.
Prototipado y Producción: Tras la aprobación, pasamos rápidamente del prototipado a la producción a gran escala para cumplir con sus plazos de entrega.
Asociarse con Aoxin Quartz ofrece varias ventajas clave:
Experiencia comprobada: Con más de 10 años en la industria, poseemos el conocimiento técnico para abordar desafíos complejos.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Valor competitivo: Ubicados en un importante centro de producción de cuarzo, aprovechamos una cadena de suministro eficiente y una fabricación avanzada para ofrecer una calidad excepcional a un precio competitivo.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.