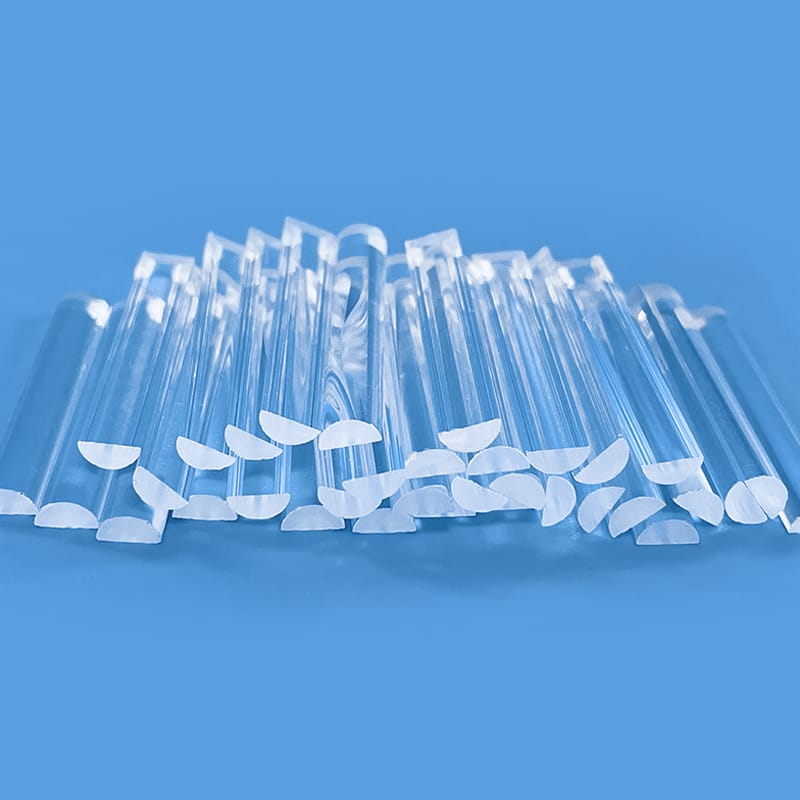
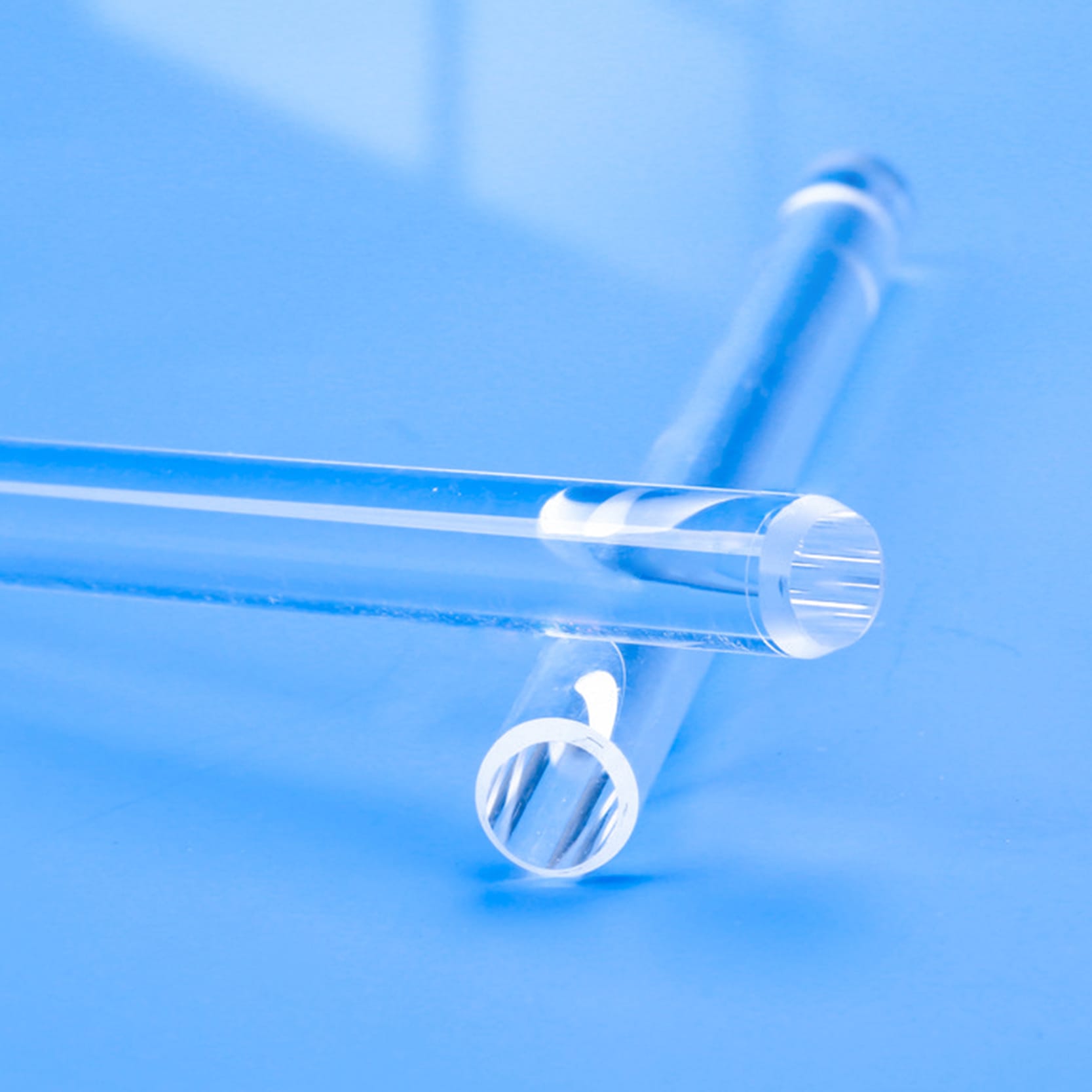
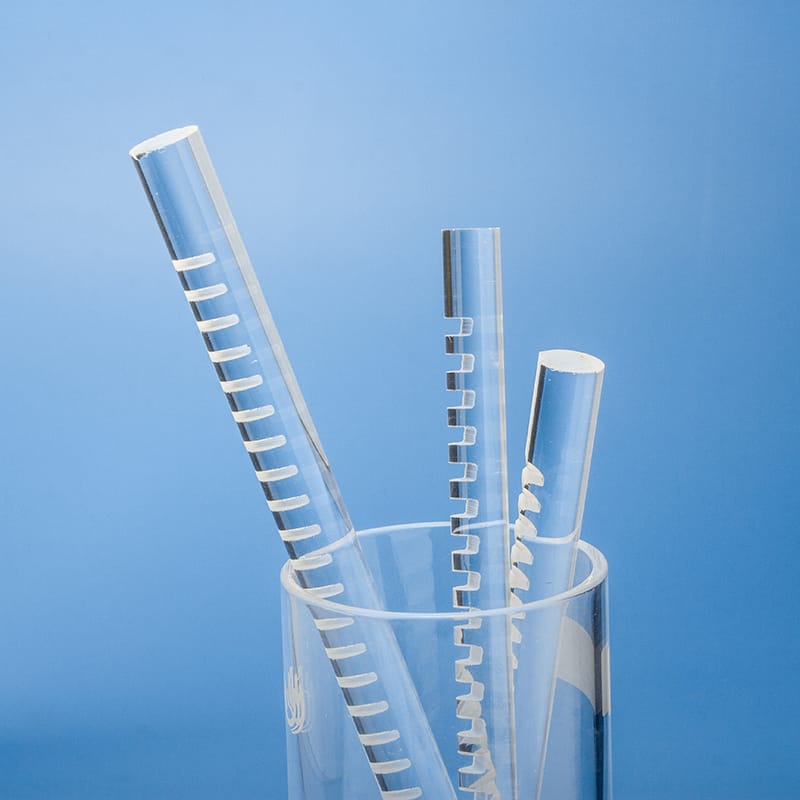
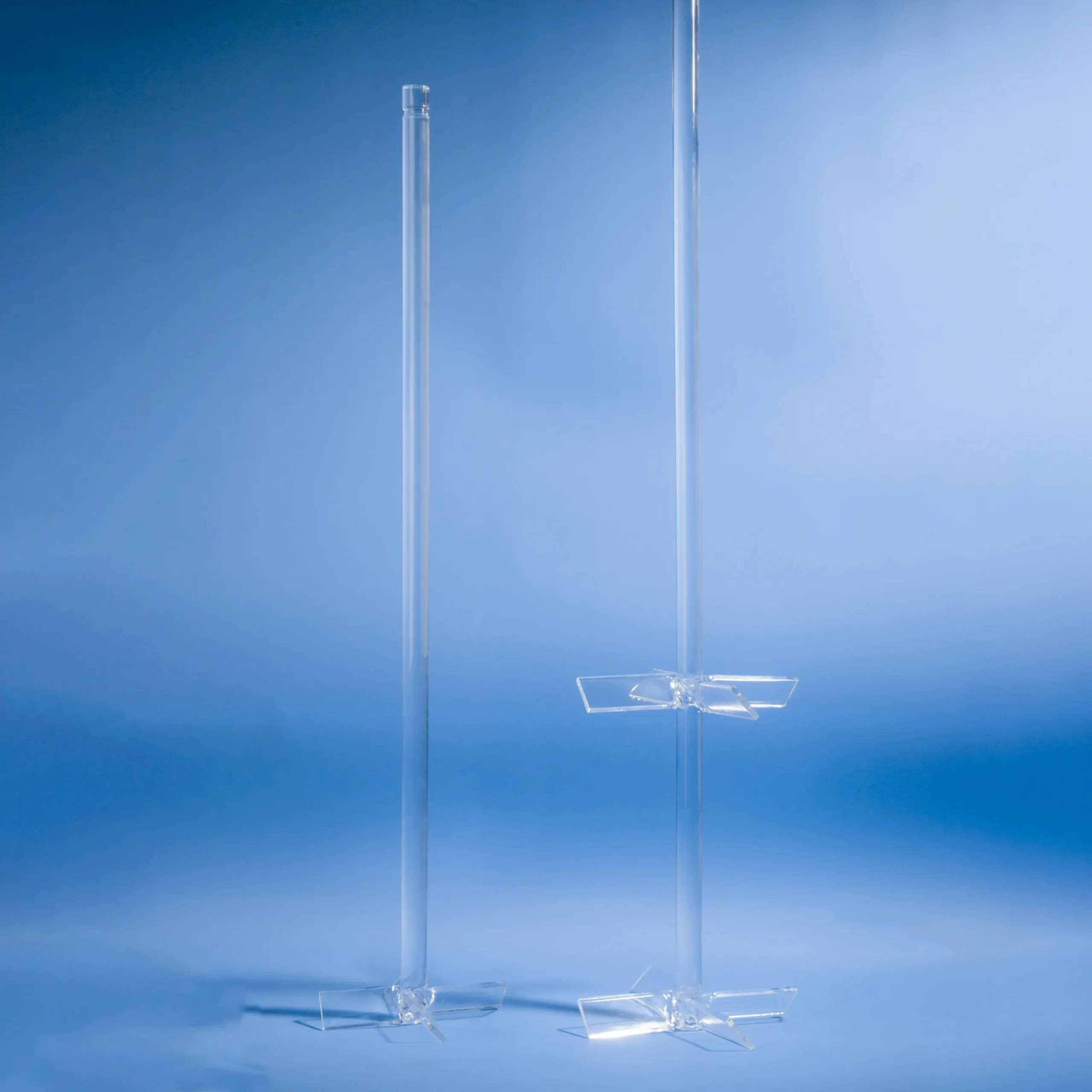
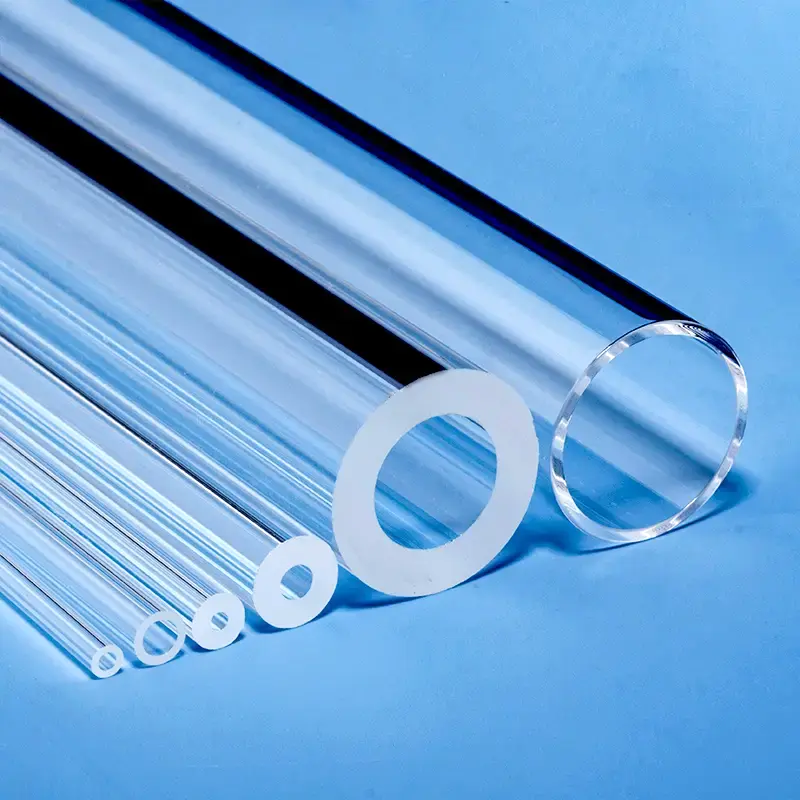
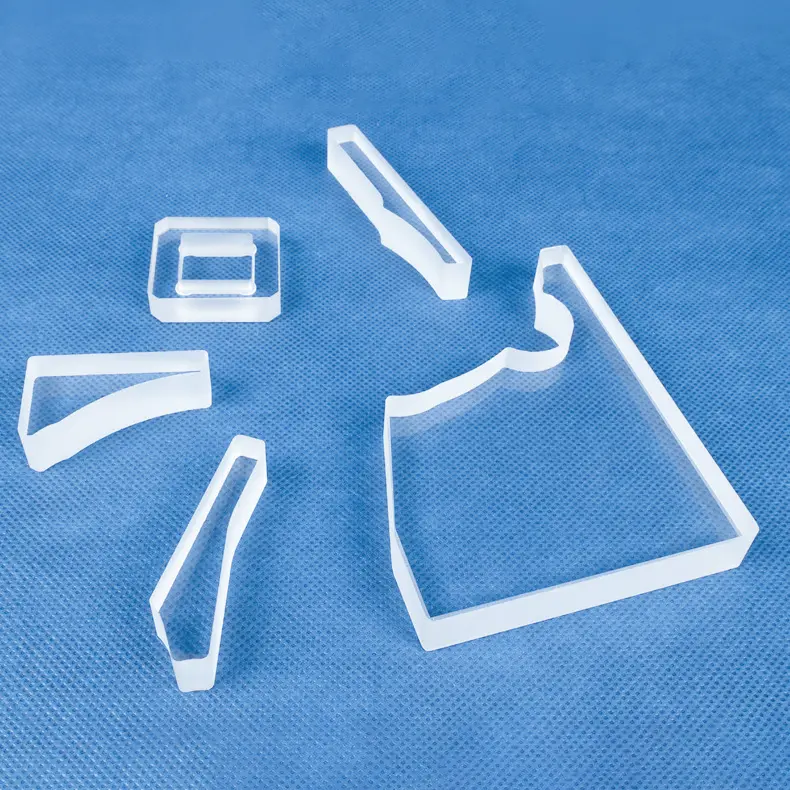
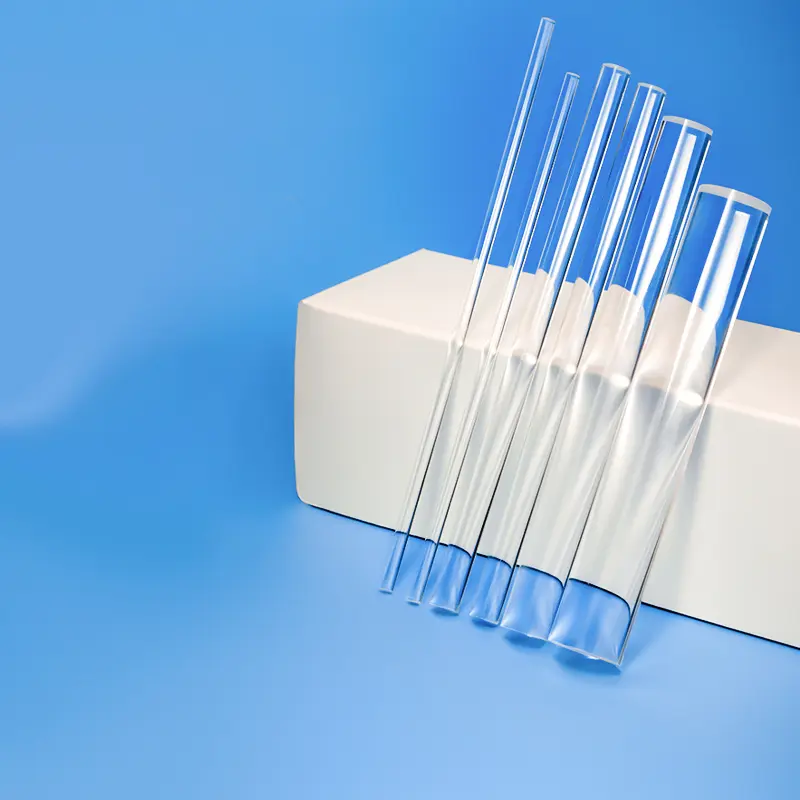
Quartz rods are rod-shaped materials primarily made from quartz sand, characterized by high purity, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance.
| diameter | length |
|---|---|
| 10mm | 300mm |
| 10mm | 600mm |
| 12mm | 300mm |
| 12mm | 600mm |
| 14mm | 300mm |
| 14mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 300mm |
| 15mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 300mm |
| 16mm | 600mm |
| 16mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 1200mm |
| 18mm | 300mm |
| 18mm | 600mm |
| 18mm | 1000mm |
| 18mm | 1200mm |
| 20mm | 300mm |
| 20mm | 600mm |
| 20mm | 1000mm |
| 20mm | 1200mm |
| 22mm | 300mm |
| 22mm | 600mm |
| 22mm | 1000mm |
| 22mm | 1200mm |
| 25mm | 300mm |
| 25mm | 600mm |
| 25mm | 1000mm |
| 25mm | 1200mm |
| 28mm | 300mm |
| 28mm | 600mm |
| 28mm | 1000mm |
| 28mm | 1200mm |
| 30mm | 300mm |
| 30mm | 600mm |
| 30mm | 1000mm |
| 30mm | 1200mm |
| 32mm | 300mm |
| 32mm | 600mm |
| 32mm | 1000mm |
| 32mm | 1200mm |
| 35mm | 300mm |
| 35mm | 600mm |
| 35mm | 1000mm |
| 35mm | 1200mm |
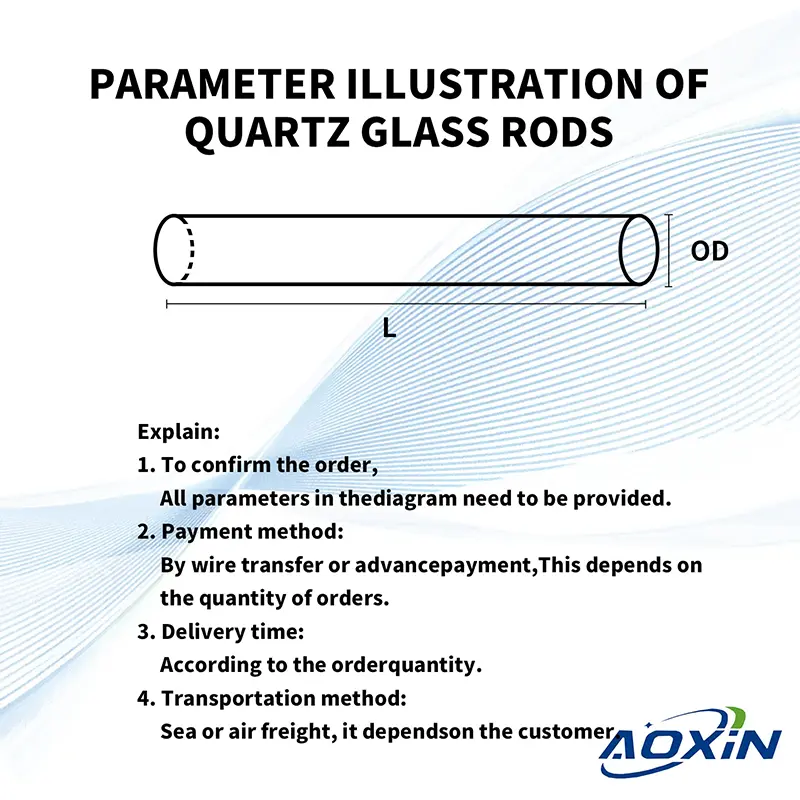
- Payment method:
By T/T or prepayment,
It depends on the quantity of the order. - Delivery time:
According to the order quantity. - Shipping method:
By sea or by air,
It depends on the customer.
Remarks:
To confirm the order,
the following parameters are required:
① outer diameter ② length ③ quantity
Error: Formulario de contacto no encontrado.
| Contenido de la propiedad | Valores inmobiliarios |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Densidad | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Dureza | 5,5 - 6,5 Escala de Mohs 570 KHN 100 |
| Resistencia a la tracción | 4,8×10⁷ Pa (N/mm2) (7000 psi) |
| Resistencia a la compresión | >1,1×10⁹ Pa (160.000 psi) |
| Coeficiente de dilatación térmica | 5,5×10-⁷ cm/cm-°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Conductividad térmica | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Calor específico | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Punto de ablandamiento | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Punto de recocido | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Punto de deformación | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Temperatura de trabajo | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Resistividad eléctrica | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Talla | Personalizado |
| Logotipo | Logotipo personalizado Aceptar |

There are two primary methods for producing quartz rods: the continuous method and the flame fusion method (also known as the gas fusion method).
Continuous Method: In this method, quartz sand is fed from the top into a furnace, which comprises a metallic quartz crucible surrounded by electric heating elements. The quartz sand melts at high temperatures. The molten material then passes through a shaping orifice at the bottom of the crucible, producing rods, tubes, sheets, or other various specified product forms.
Flame Fusion Method: This method involves using hydrogen and oxygen to melt colorless quartz crystal. The molten material is formed into quartz glass through the melting and congealing of crystalline particles in the flame. The quartz glass is then removed from the flame through different methods and processed into quartz rods of the desired shape.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Quartz rods are made from pure natural quartz stone, which provides exceptional resistance to corrosion, enabling long-term use in harsh environments such as acids and alkalis without being easily damaged.
High-Temperature Stability
The quartz composition of these rods provides excellent resistance to high temperatures, allowing them to withstand hot water, steam, and similar conditions without deformation or embrittlement.
Smooth and Flat Surface
Through precise processing, the quartz rod surfaces are smooth and flat, making them less prone to accumulating dirt, and thus are easy to clean and maintain.
igh Hardness and Compressive Strength
Quartz rods are resistant to external impacts and wear, resulting in a long service life.
Escenario de aplicación
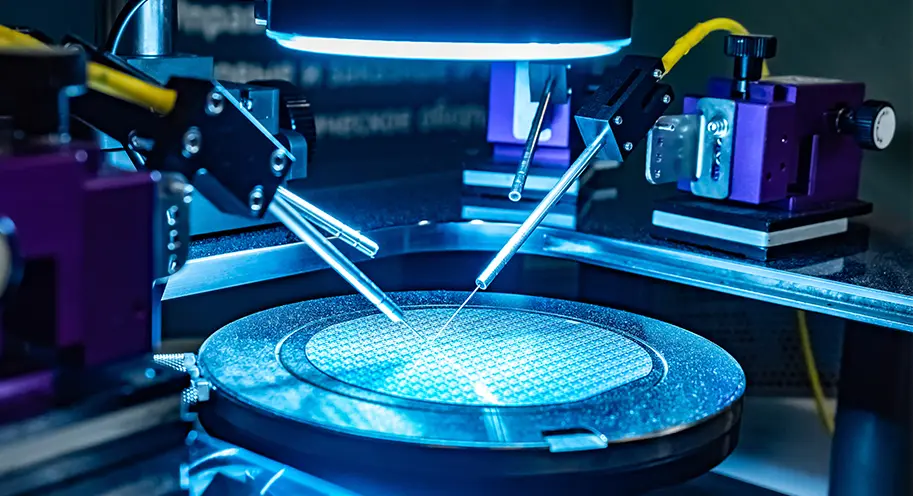
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Quartz rods are used in the semiconductor industry for manufacturing wafer processing equipment, photolithography equipment, and other semiconductor process tools. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and chemical corrosion is critical in semiconductor manufacturing processes.
The manufacturing process of quartz rods primarily involves melting quartz sand into hollow quartz preforms using a plasma flame. These preforms are then mechanically cold-worked into thick-walled quartz tubes. Finally, a medium-frequency induction heating non-contact secondary shaping technology is used to produce the quartz rods. This meticulous process ensures the quartz rods possess high purity, low hydroxyl content, high dimensional accuracy, and a superior surface finish free of defects.
In the electronics industry, quartz rods are primarily utilized as substrates for semiconductor materials and as bases for electronic components. Their excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability make them ideal for use in high-frequency circuits and sensors, as well as other high-precision electronic devices. Quartz rods are also crucial for the production of photomasks and glass chips, which are vital for enhancing electronic device performance.
Quartz rods exhibit an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion and excellent resistance to thermal shock.
Preguntas más frecuentes
El vidrio de cuarzo es un material duro y quebradizo con excelentes propiedades físicas y químicas, dureza mecánica extremadamente alta, buen aislamiento eléctrico, resistencia a altas temperaturas y a la corrosión, rendimiento de retardo bajo y estable, buena transmitancia luminosa, etc. Se utiliza ampliamente en semiconductores, óptica, electricidad, química, aeroespacial, automoción y otros campos. Los materiales duros y quebradizos son difíciles de procesar, y muchos campos necesitan urgentemente procesos de corte con un pequeño colapso del borde, menos pérdida de material, baja rugosidad de la sección transversal y un amplio rango de grosor de corte. El método de corte tradicional del vidrio de cuarzo es el corte mecánico, es decir, el corte por disco. Los métodos de corte no tradicionales incluyen el corte por chorro de agua, el corte por hilo de descarga electroquímica, el corte por láser continuo, etc. El corte mecánico tiene un bajo coste, pero el contacto entre la rueda y el material causa un gran desgaste de la herramienta, y el material es fácilmente contaminado por la herramienta. El vidrio de cuarzo es propenso al colapso de los bordes, las microfisuras y la tensión residual, lo que afecta a la resistencia y el rendimiento del material. Es difícil conseguir un corte curvo y requiere un tratamiento posterior, como esmerilado y pulido. El corte por láser no entra en contacto directo con el material, no tiene tensión de contacto y puede realizar cortes curvos complejos. El láser de picosegundos tiene las ventajas de un diámetro de punto pequeño, alta precisión, tiempo de acción corto con el material y área de acción pequeña, y es adecuado para el procesamiento de materiales duros y quebradizos.
。