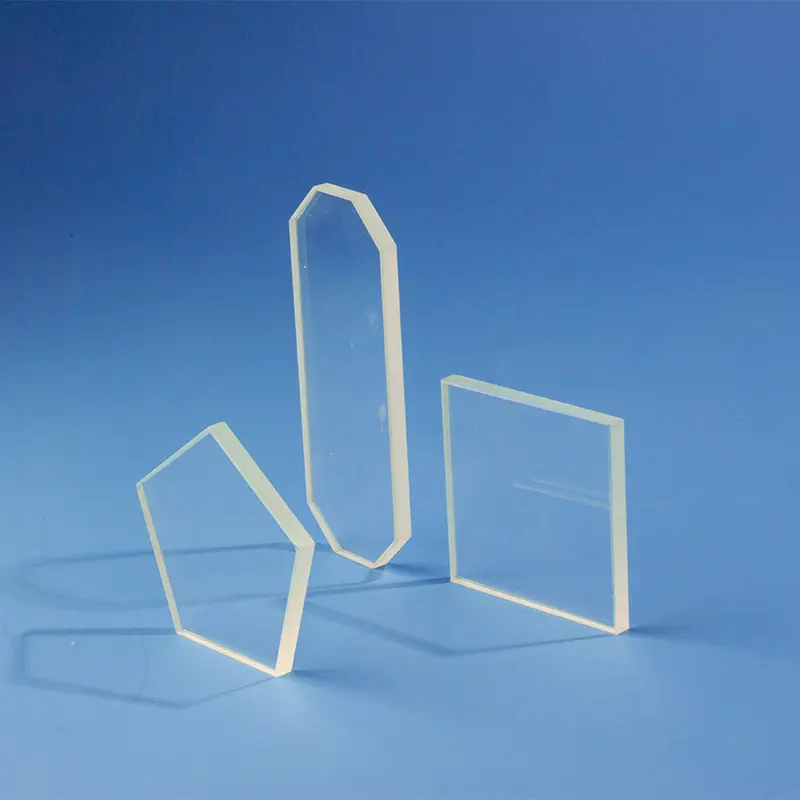
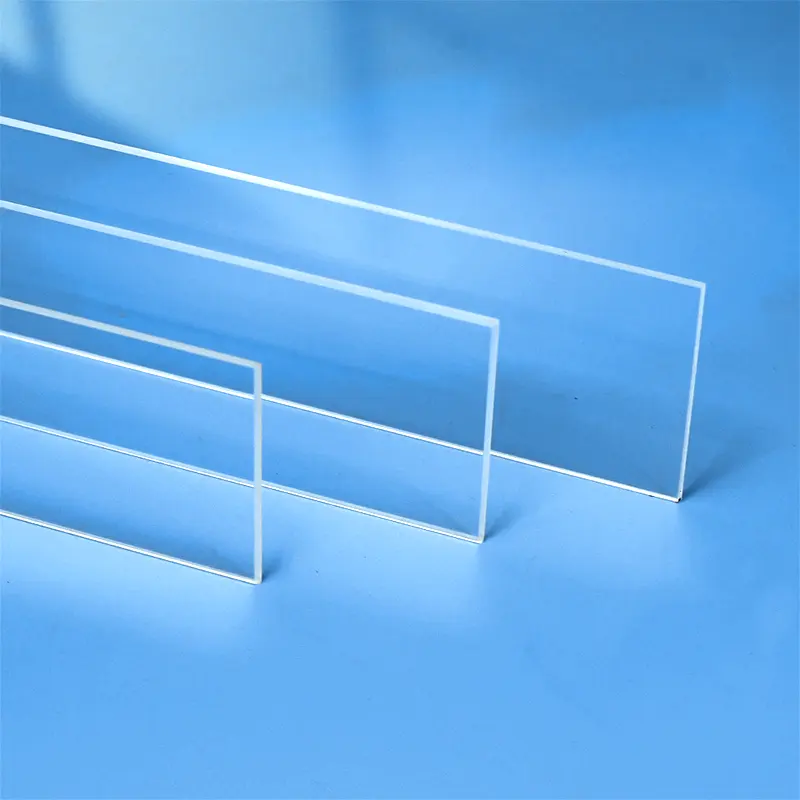
Наши крупногабаритные кварцевые пластины, также известные как листы из плавленого кварца увеличенного размера, разработаны для применений, требующих исключительной чистоты и превосходных оптических, термических и химических свойств. Идеально подходят в качестве окон, подложек или защитных покрытий в высокотемпературных печах, полупроводниковых камерах и передовых оптических системах. Мы предлагаем изготовление на заказ для точного соответствия размерам и конкретным эксплуатационным требованиям.
| Содержание свойств | Значения свойств |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Плотность | 2,2×10³ кг/см³ |
| Твердость | Твердость по шкале Мооса 5,5 - 6,5; Твердость по Кнупу 570 (при нагрузке 100 г) |
| Предел прочности при растяжении | 4,8 × 10⁷ Па (48 Н/мм² или 48 МПа); 7 000 фунтов на квадратный дюйм (psi) |
| Предел прочности при сжатии | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Коэффициент теплового расширения | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Теплопроводность | 1,4 Вт/м-°C |
| Удельная теплоемкость | 670 Дж/кг-°C |
| Температура размягчения | 1730 °C (3146 °F) |
| Точка отжига | 1210 °C (2210 °F) |
| Точка напряжения | 1120 °C (2048 °F) |
| Рабочая температура | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Удельное электрическое сопротивление | 7×10⁷ Ом см (350°C) |
| Размер | Индивидуальный заказ |
| Логотип | Нанесение логотипа по заказу |
Высокая термостойкость
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины обладают исключительной термостойкостью, способностью непрерывно работать при температурах от 1100°C до 1250°C и выдерживать температуры до 1450°C в течение коротких периодов.
Химическая стабильность
За исключением плавиковой кислоты, кварцевые стеклянные пластины инертны к большинству кислот и химических реагентов, что делает их очень подходящими для использования в химической промышленности и лабораторных условиях.
Оптические характеристики
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины обладают превосходным оптическим пропусканием, особенно в ультрафиолетовом (УФ) диапазоне, что делает их идеальным материалом для производства оптических компонентов и приборов.
Разнообразие размеров
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины могут быть произведены в широком диапазоне размеров и спецификаций для удовлетворения различных промышленных применений и требований заказчиков.
Сценарий применения
Производство полупроводников
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины используются в полупроводниковой промышленности в качестве подложек благодаря их исключительной термической стабильности и химической инертности. Они служат основами для выращивания полупроводниковых кристаллов, в качестве фотошаблонов в фотолитографии, а также как компоненты в процессах травления и осаждения.
Производство оптических устройств
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины играют решающую роль в производстве оптических устройств, включая волоконно-оптическую связь, лазеры и оптические датчики. Их высокий показатель преломления, превосходная прозрачность и высокая термическая стабильность делают их широко используемым материалом в оптической промышленности.
Химическая промышленность
Благодаря своей отличной коррозионной стойкости и химической стабильности кварцевые стеклянные пластины широко используются в химической промышленности для производства химических лабораторных инструментов, химических трубопроводов, реакционных сосудов и различного другого оборудования.
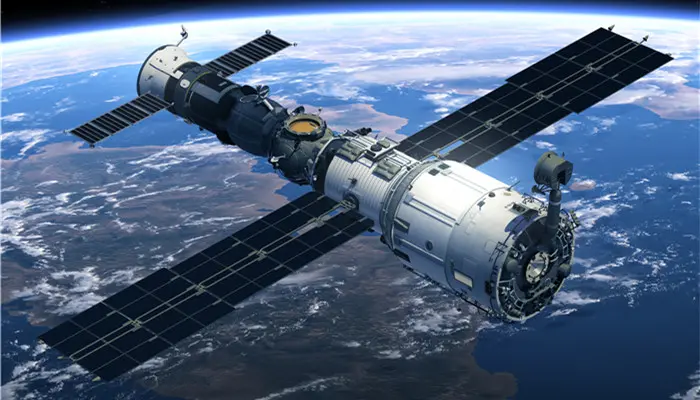
Аэрокосмическая отрасль
В аэрокосмической отрасли кварцевое стекло является ключевым компонентом космических аппаратов и космических кораблей благодаря своей высокой прочности, низким диэлектрическим потерям, высокой термостойкости и коррозионной стойкости. Например, радиационно-стойкие кварцевые стеклянные защитные покрытия эффективно защищают энергетические системы солнечных батарей космических аппаратов.
Кварцевые стеклянные пластины большого размера обладают исключительной термостойкостью, способностью непрерывно работать при температурах от 1100°C до 1250°C и выдерживать температуры до 1450°C в течение коротких периодов. Это делает их очень подходящими для применений, требующих высокотемпературных сред, таких как производство полупроводников и высокотемпературные эксперименты
В области оптики крупногабаритные кварцевые стеклянные пластины широко используются благодаря своей высокой прозрачности, низкому показателю преломления и отличному пропусканию ультрафиолета (УФ). Их можно применять для производства оптических зеркал, линз, компонентов волоконно-оптической связи, лазеров и оптических датчиков. Оптические характеристики кварцевых стеклянных пластин делают их идеальным материалом для производства оптических приборов.
Крупногабаритные кварцевые стеклянные пластины обладают исключительной химической стабильностью, проявляя инертность к большинству кислот и химических реагентов, за исключением плавиковой кислоты. Это делает кварцевые стеклянные пластины очень подходящими для использования в химической промышленности и лабораторных условиях, таких как химические экспериментальные приборы, химические трубопроводы и реакционные сосуды, где они могут сохранять свою производительность без эрозии.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Мы специализируемся на комплексном производстве высокочистых кварцевых стекольных компонентов. Наши основные продуктовые линейки включают:
Кварцевые трубки и стержни: Широкий диапазон диаметров и спецификаций.
Кварцевые пластины и диски: Прецизионная резка и полировка для оптического и промышленного применения.
Кварцевая лабораторная посуда: Полный ассортимент стандартной и индивидуальной стеклянной посуды, включая стаканы, колбы и лодочки.
Кварц полупроводникового класса: Высокочистые компоненты, такие как технологические трубки и носители, для производства полупроводников.
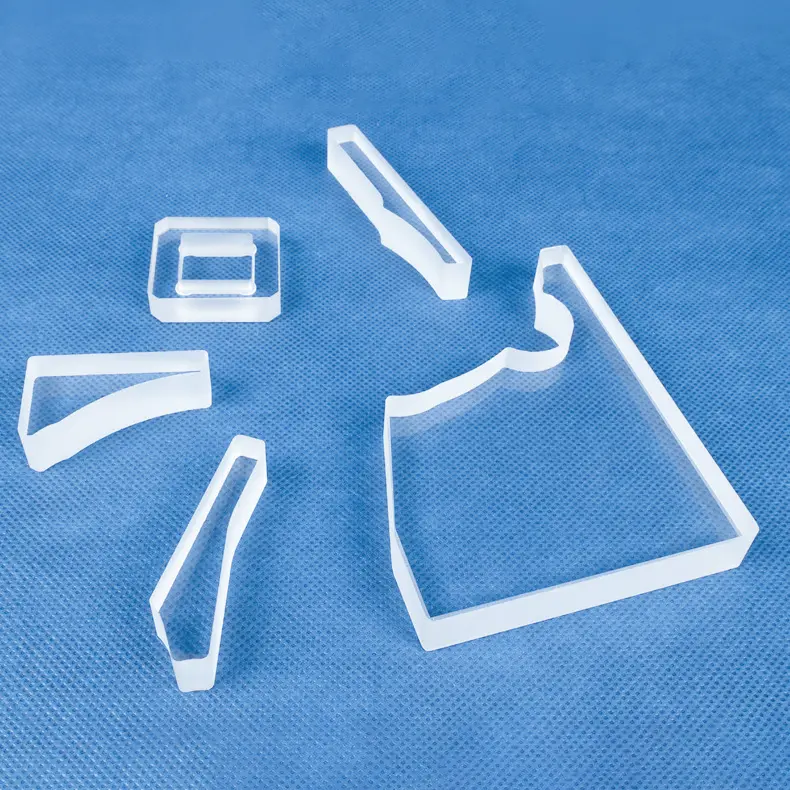
Компоненты индивидуального изготовления: Мы можем производить сложные детали, адаптированные под ваши уникальные чертежи и спецификации.
Да. Индивидуальное изготовление является основой нашей деятельности. Имея более чем десятилетний специализированный опыт, мы сотрудничаем с компаниями, предлагая высококлассные услуги OEM/ODM. Наши возможности включают сварку, шлифовку, сверление, полировку, гибку и другие методы прецизионной обработки для создания компонентов, точно соответствующих вашим требованиям.
Качество является первостепенным в нашем производственном процессе. Мы являемся производителем, сертифицированным по ISO 9001:2015, гарантируя, что наши процессы соответствуют международным стандартам управления качеством.Наша продукция также проходит строгие испытания SGS на чистоту и производительность. Мы используем высокочистое сырье (до 99,998% SiO2) для производства изделий из плавленого кварца и плавленого диоксида кремния с исключительной термической стабильностью, высокой термостойкостью и химической инертностью.
Мы максимально оптимизировали наш процесс для обеспечения эффективности:
Отправьте запрос коммерческого предложения (RFQ): Присылайте нам свои технические чертежи, спецификации и требования через контактную форму на нашем сайте или по электронной почте.
Быстрый ответ: Вы можете ожидать первоначальный ответ в течение нескольких минут и подробное общение в течение получаса.
Дизайн и Коммерческое предложение: Мы предоставим подробное проектное предложение и конкурентоспособное коммерческое предложение в течение 24 часов.
Прототипирование и производство: После утверждения мы оперативно переходим от прототипирования к полномасштабному производству, чтобы уложиться в ваши сроки.
Сотрудничество с Aoxin Quartz предоставляет несколько ключевых преимуществ:
Проверенный опыт: Имея более чем 10-летний опыт работы в отрасли, мы обладаем техническими знаниями для решения сложных задач.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Конкурентная ценность: Расположенные в крупном центре по производству кварца, мы используем эффективную цепочку поставок и передовое производство, чтобы предложить исключительное качество по конкурентоспособной цене.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.