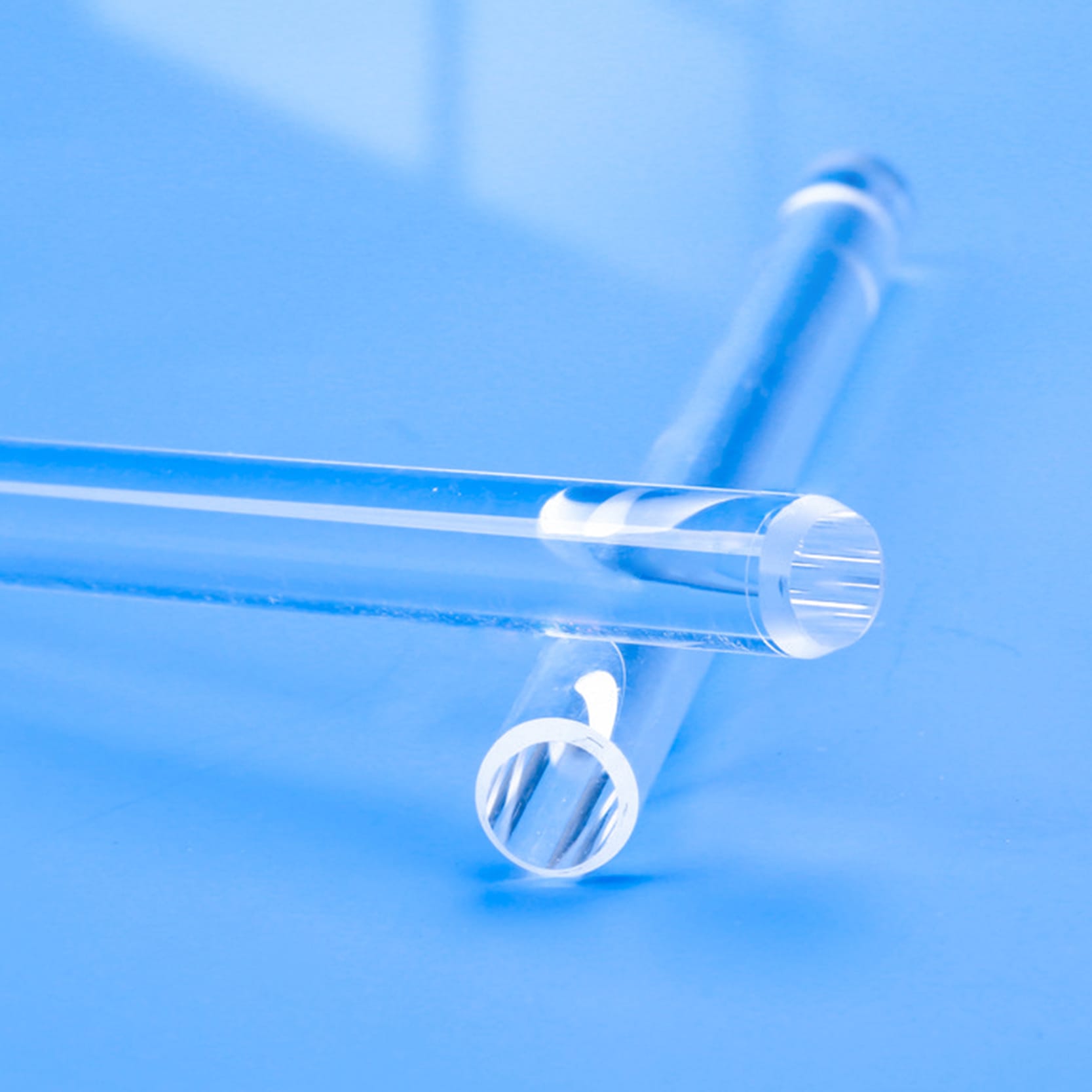
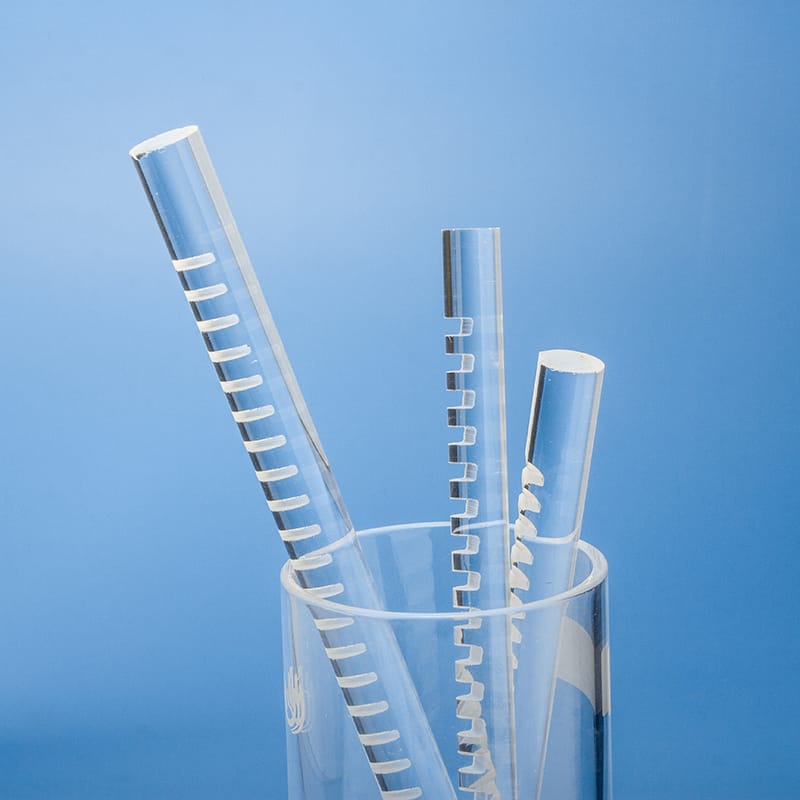
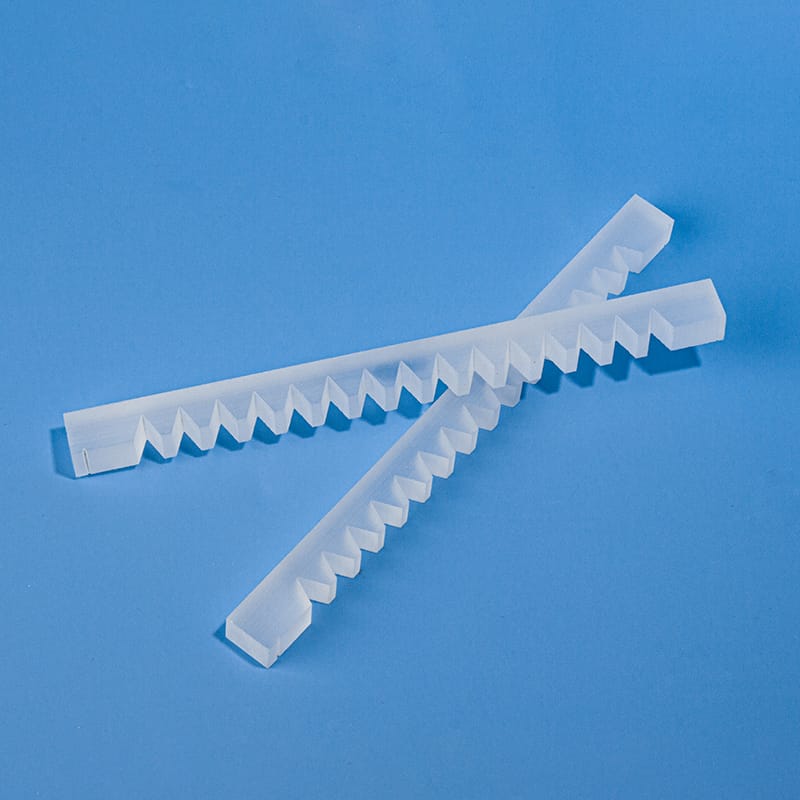
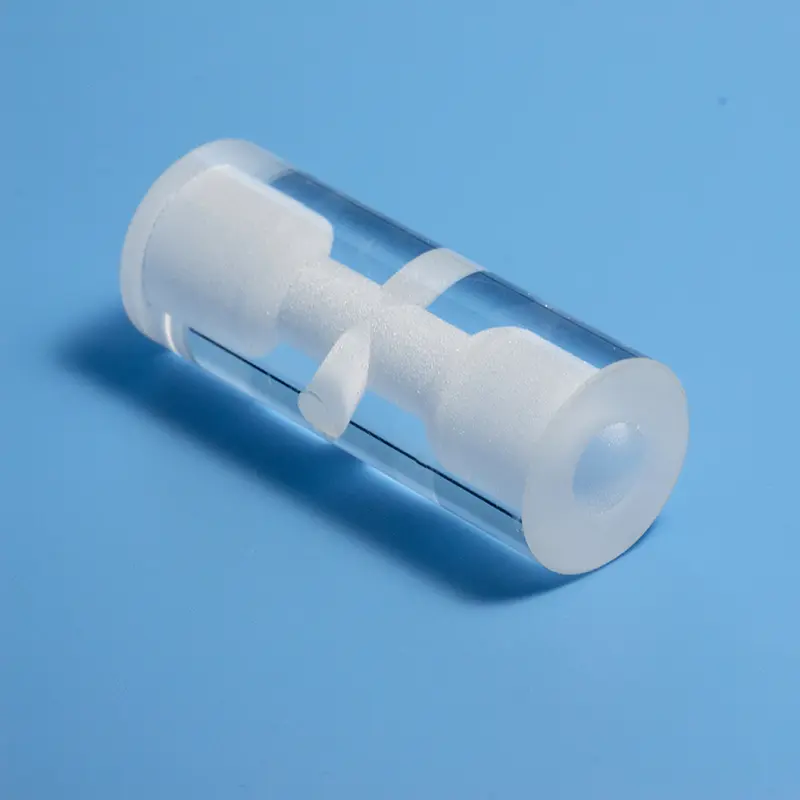
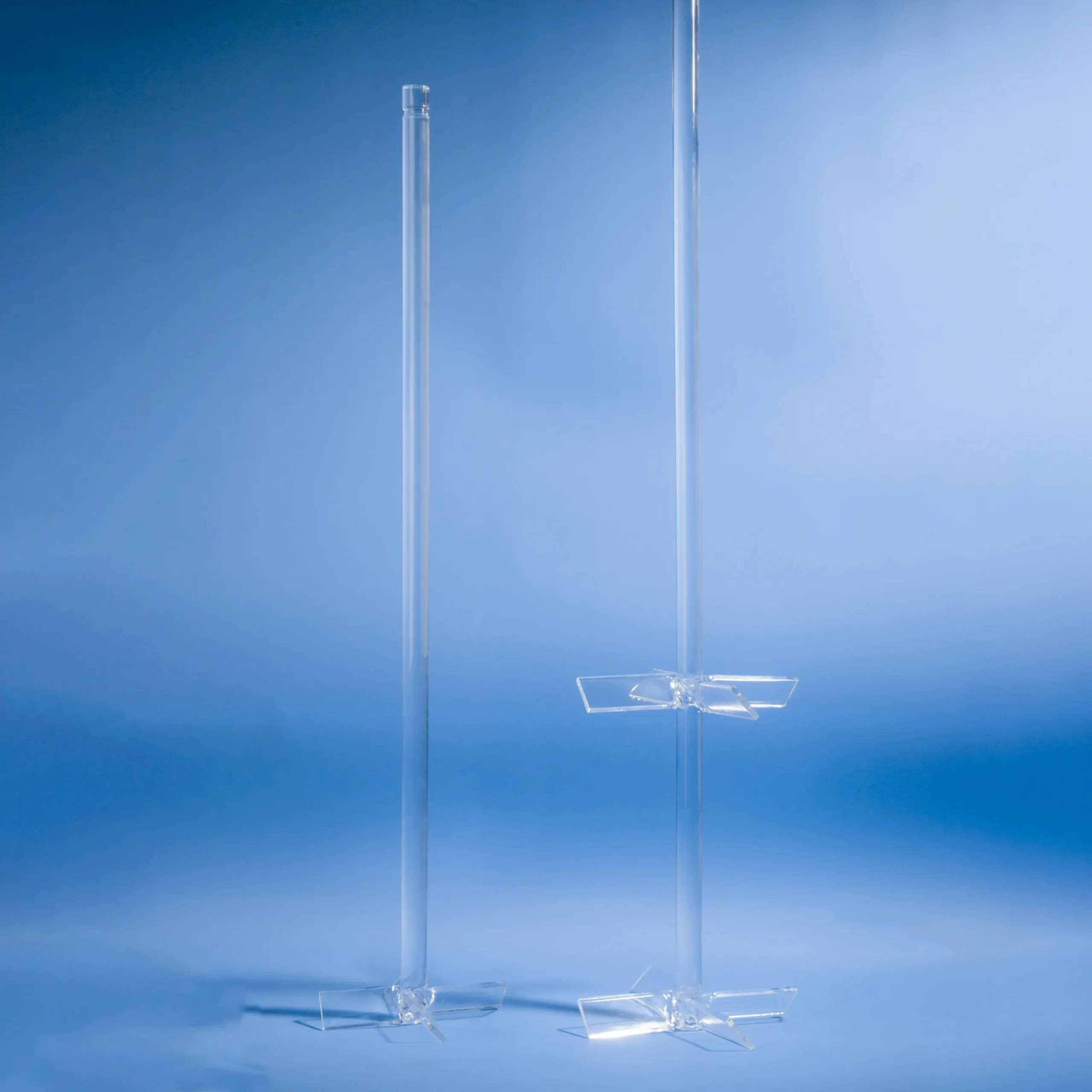
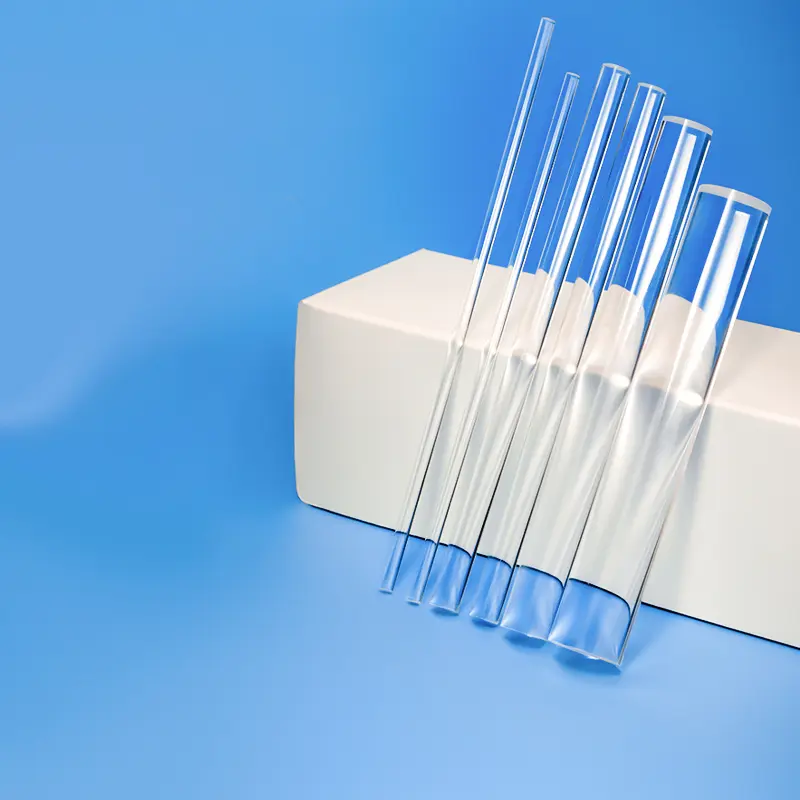
Our high-purity quartz mixing rods and fused silica stirrers are designed for demanding applications requiring superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability. Ideal for laboratories, chemical processing, and semiconductor industries, these rods ensure contamination-free mixing of corrosive liquids and high-purity substances. Custom dimensions and designs are available to meet your specific mixing needs.
| diameter | length |
|---|---|
| 10mm | 300mm |
| 10mm | 600mm |
| 12mm | 300mm |
| 12mm | 600mm |
| 14mm | 300mm |
| 14mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 300mm |
| 15mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 300mm |
| 16mm | 600mm |
| 16mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 1200mm |
| 18mm | 300mm |
| 18mm | 600mm |
| 18mm | 1000mm |
| 18mm | 1200mm |
| 20mm | 300mm |
| 20mm | 600mm |
| 20mm | 1000mm |
| 20mm | 1200mm |
| 22mm | 300mm |
| 22mm | 600mm |
| 22mm | 1000mm |
| 22mm | 1200mm |
| 25mm | 300mm |
| 25mm | 600mm |
| 25mm | 1000mm |
| 25mm | 1200mm |
| 28mm | 300mm |
| 28mm | 600mm |
| 28mm | 1000mm |
| 28mm | 1200mm |
| 30mm | 300mm |
| 30mm | 600mm |
| 30mm | 1000mm |
| 30mm | 1200mm |
| 32mm | 300mm |
| 32mm | 600mm |
| 32mm | 1000mm |
| 32mm | 1200mm |
| 35mm | 300mm |
| 35mm | 600mm |
| 35mm | 1000mm |
| 35mm | 1200mm |
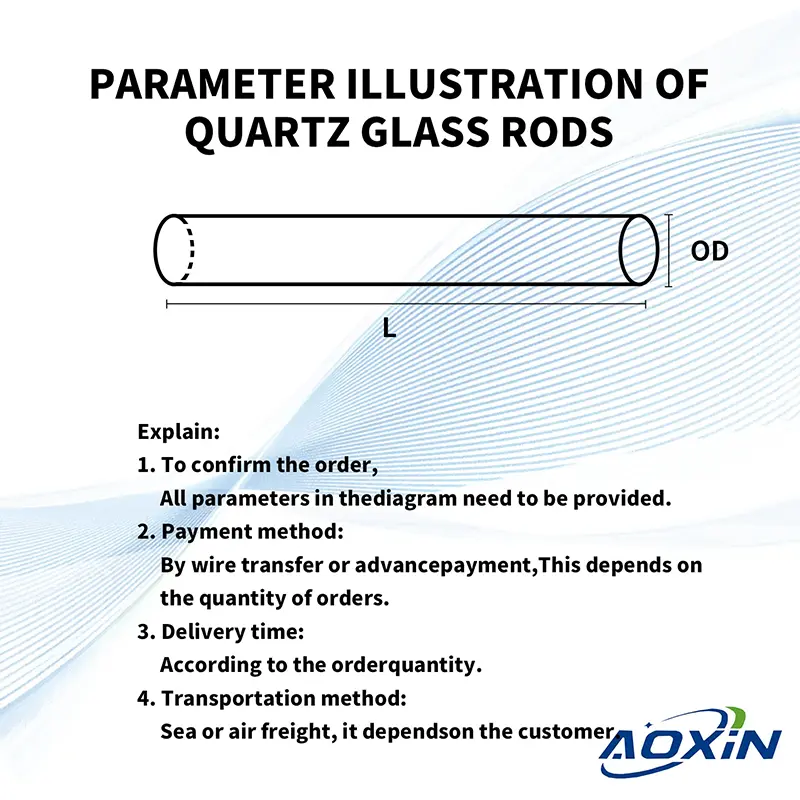
Remarks:
To confirm the order,
the following parameters are required:
① outer diameter ② length ③ quantity
- Payment method:
By T/T or prepayment,
It depends on the quantity of the order. - Delivery time:
According to the order quantity. - Shipping method:
By sea or by air,
It depends on the customer.
| Property Content | Property Values |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Density | 2.2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Hardness | 5.5 - 6.5 Mohs' Scale 570 KHN 100 |
| Tensile Strength | 4.8×10⁷ Pa (N/mm2) (7000 psi) |
| Compression Strength | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.4 W/m·°C |
| Specific Heat | 670 J/kg·°C |
| Softening Point | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Annealing Point | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Strain Point | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Work Temperature | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Size | Customized |
| Logo | Customized Logo Accept |

There are two primary methods for producing quartz rods: the continuous method and the flame fusion method (also known as the gas fusion method).
Continuous Method: In this method, quartz sand is fed from the top into a furnace, which comprises a metallic quartz crucible surrounded by electric heating elements. The quartz sand melts at high temperatures. The molten material then passes through a shaping orifice at the bottom of the crucible, producing rods, tubes, sheets, or other various specified product forms.
Flame Fusion Method: This method involves using hydrogen and oxygen to melt colorless quartz crystal. The molten material is formed into quartz glass through the melting and congealing of crystalline particles in the flame. The quartz glass is then removed from the flame through different methods and processed into quartz rods of the desired shape.
High Heat Resistance
Quartz material exhibits outstanding heat resistance, allowing for use in various temperature environments, including high-temperature cooking or experimental conditions.
Hardness and Durability
The hardness of quartz makes it resistant to wear and tear, effectively protecting the original shape and texture of ingredients while prolonging the service life of the stirring rod.
Good Light Transmission
Quartz stirring rods typically have good light transmission, making it easier to observe ingredient changes during the stirring process.
Diverse Designs
The structure of a quartz stirring rod generally includes the rod body, head, and connecting rod. Heads are designed in various shapes, such as disks or cones, to meet different stirring needs. Connecting rods are typically equipped with adjustment knobs for easy adjustment of the stirring rod length.
Application Scenario
Chemical Experiments
In chemical experiments, quartz stirring rods are commonly used for stirring solutions and mixing reagents to ensure uniformity and accuracy throughout the experimental process. Their high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance make them particularly suitable for experiments requiring high temperatures or strong corrosive reagents.
Quartz stirring rods offer several advantages over plastic stirring rods, including higher temperature resistance, greater chemical stability, superior structural strength, reduced risk of breakage, and a longer service life.
Quartz stirring rods are suitable for the following experimental environments:
1. High-Temperature Environments: Quartz stirring rods can be used for extended periods at temperatures up to 1100°C, with short-term use at temperatures up to 1730°C, making them ideal for high-temperature heating experiments.
2. Chemically Demanding Environments: Quartz stirring rods exhibit excellent chemical stability, with almost no reactivity with acids or bases, except for hydrofluoric acid and hot phosphoric acid. This makes them suitable for use in corrosive heating applications.
Quartz stirring rods demonstrate excellent stability in high-temperature experiments and do not deform easily. Quartz glass has a low thermal expansion coefficient, enabling it to withstand rapid temperature changes without shattering. Even when quartz glass is heated to around 1100°C and then placed in room-temperature water, it will not crack. Furthermore, quartz stirring rods possess strong heat resistance, with a short-term use temperature of up to 1300°C and a long-term use temperature of 1100°C.
Frequently asked questions
We specialize in the end-to-end manufacturing of high-purity quartz glass components. Our core product lines include:
Quartz Tubing & Rods: A wide range of diameters and specifications.
Quartz Plates & Discs: Precision-cut and polished for optical and industrial use.
Quartz Labware: A full suite of standard and custom glassware, including beakers, flasks, and boats.
Semiconductor-Grade Quartz: High-purity components like process tubes and carriers for semiconductor fabrication.
Custom Fabricated Components: We can produce complex parts tailored to your unique designs and specifications.
Yes. Custom fabrication is at the core of our business. With over a decade of specialized experience, we partner with companies to provide expert OEM/ODM services. Our capabilities include welding, grinding, drilling, polishing, bending, and other precision processing techniques to create components that meet your exact requirements.
Quality is paramount in our manufacturing process. We are an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer, ensuring that our processes meet international quality management standards.Our products also undergo rigorous SGS testing for purity and performance. We use high-purity raw materials (up to 99.998% SiO2) to produce fused quartz and fused silica products with exceptional thermal stability, high-temperature resistance, and chemical inertness.
We've streamlined our process to be as efficient as possible:
Submit Your RFQ: Send us your technical drawings, specifications, and requirements via our website contact form or email.
Rapid Response: You can expect an initial response within minutes and detailed communication within half an hour.
Design & Proposal: We will deliver a detailed design proposal and a competitive quote within 24 hours.
Prototyping & Production: Upon approval, we move swiftly from prototyping to full-scale production to meet your deadlines.
Partnering with Aoxin Quartz offers several key advantages:
Proven Expertise: With 10+ years in the industry, we have the technical knowledge to tackle complex challenges.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Competitive Value: Located in a major quartz production hub, we leverage an efficient supply chain and advanced manufacturing to offer exceptional quality at a competitive price point.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.