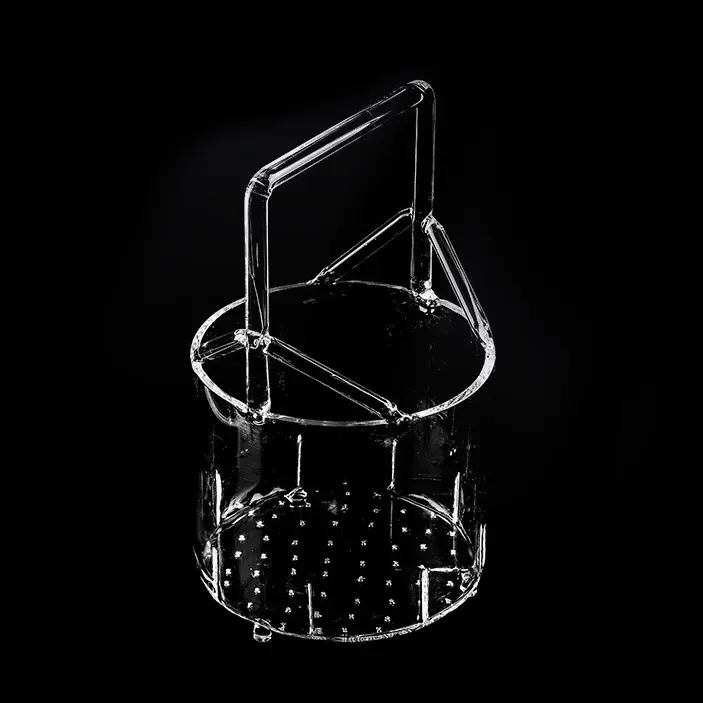
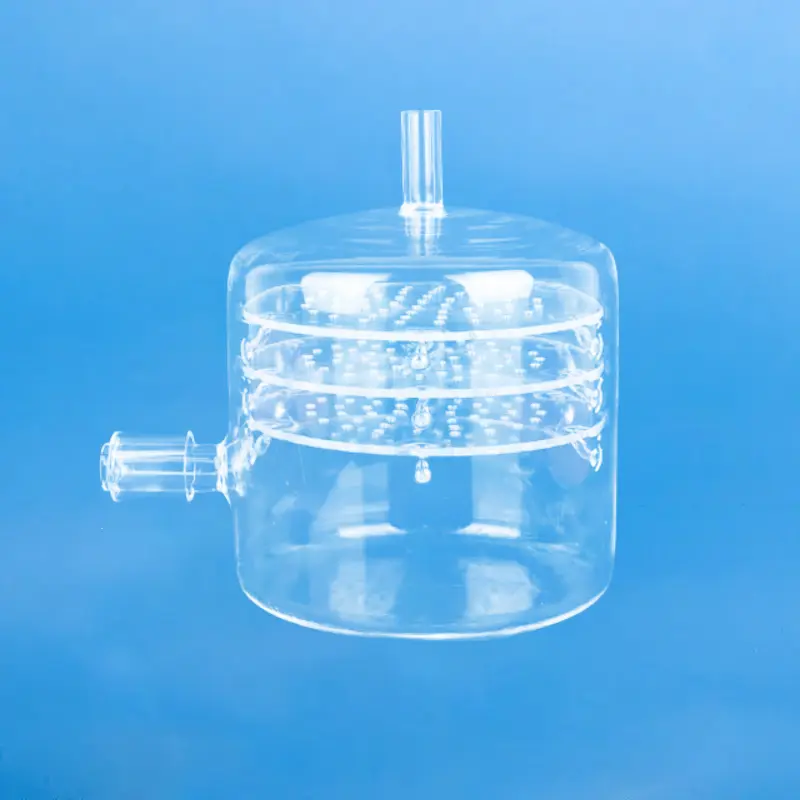
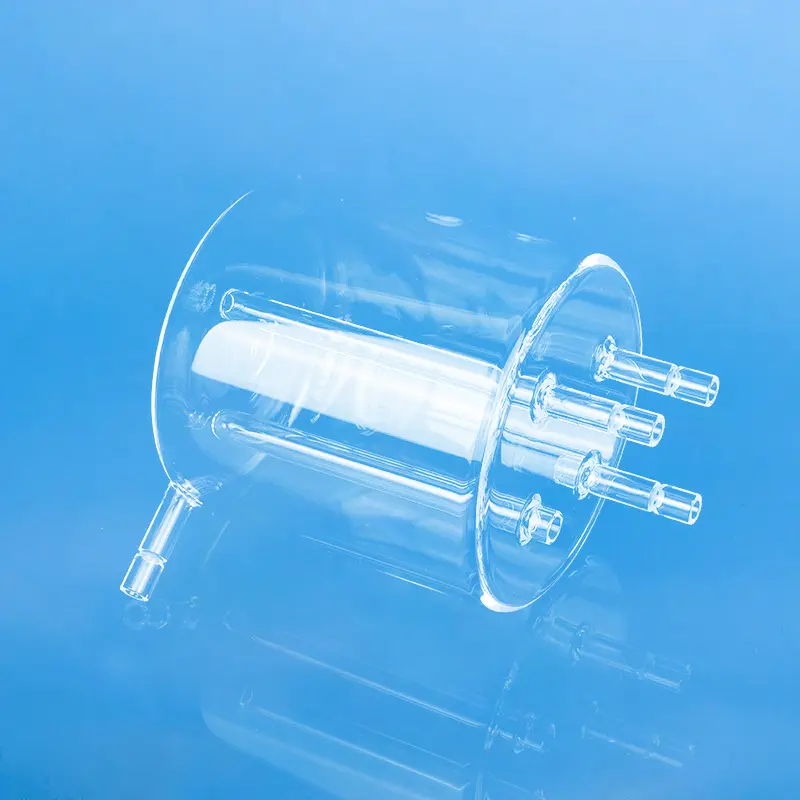
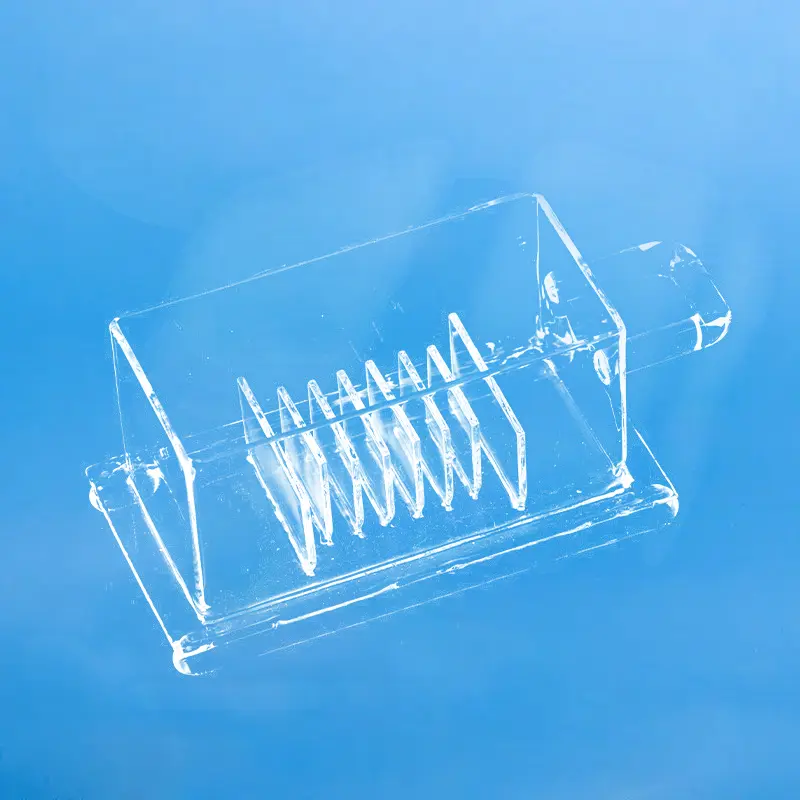
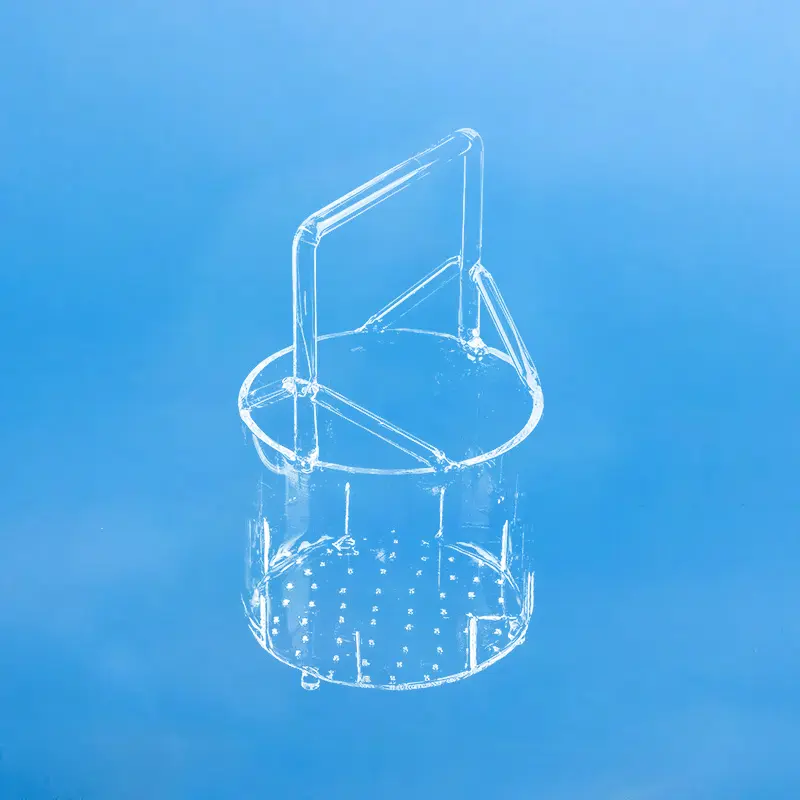
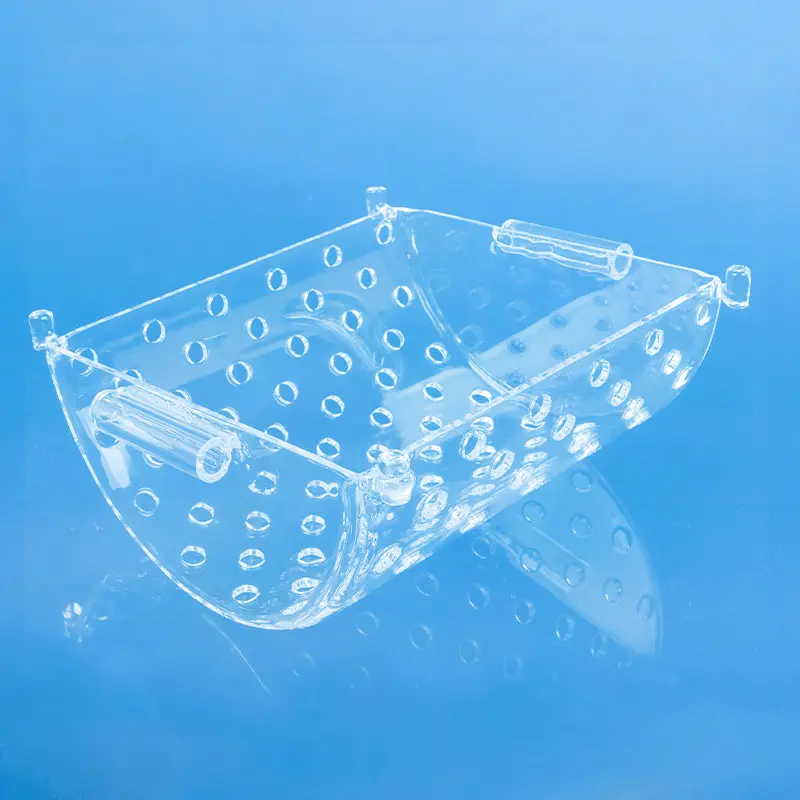
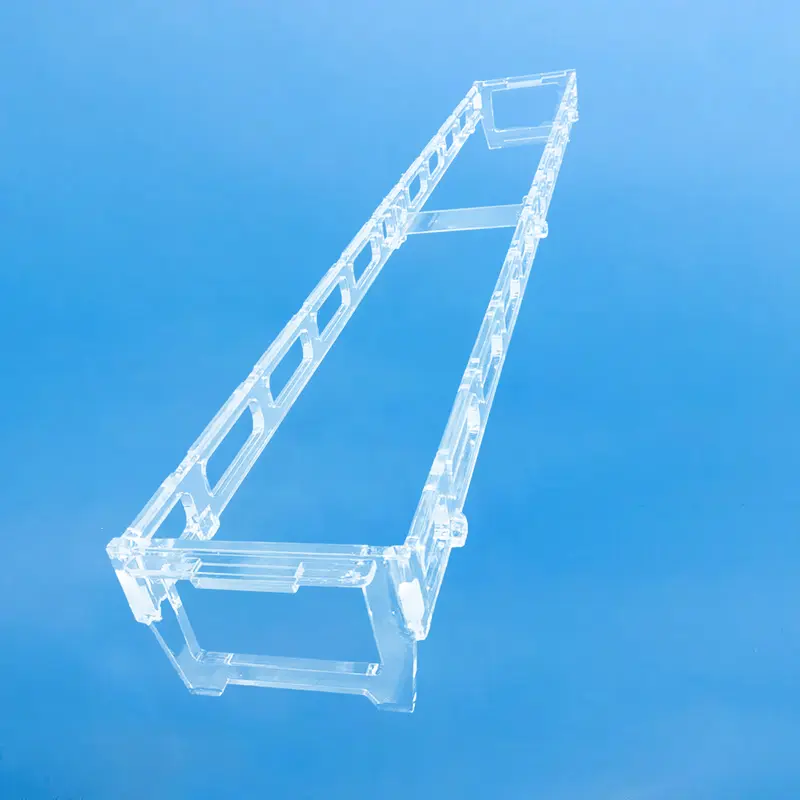
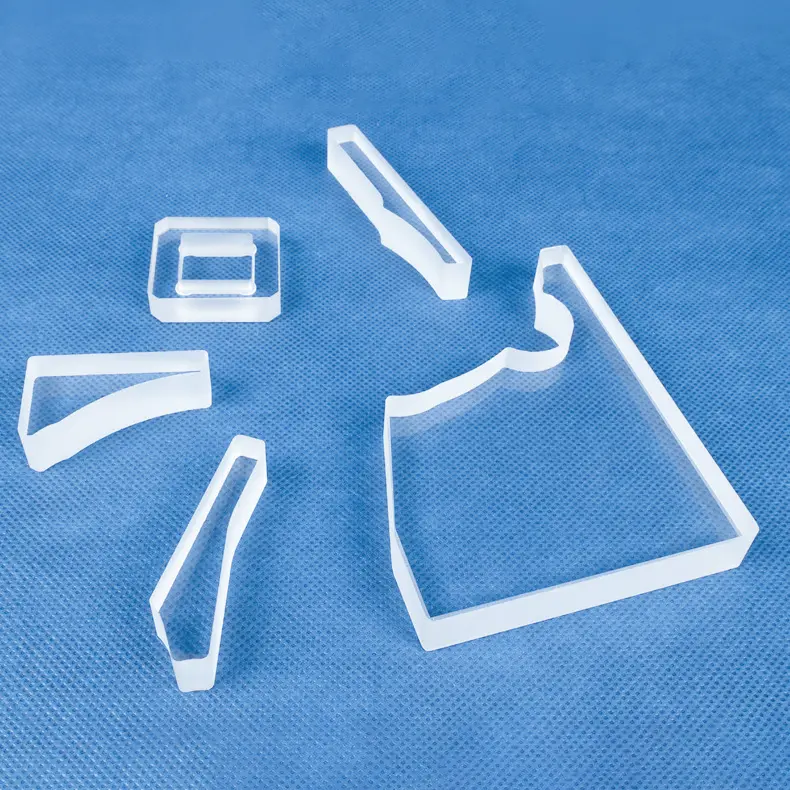
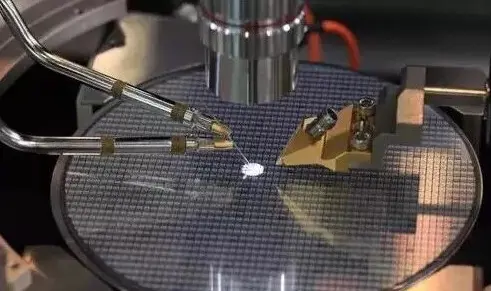
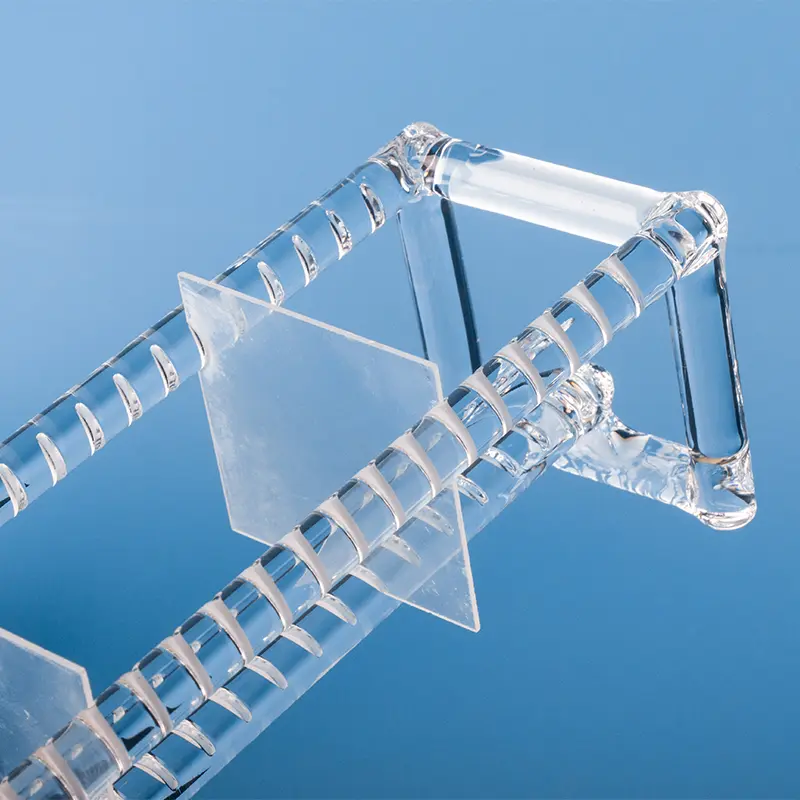
A quartz basket is a container or device made from quartz material, typically used in a variety of industrial and consumer applications.
| Property Content | Property Values |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Density | 2.2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Hardness | 5.5 - 6.5 Mohs' Scale 570 KHN 100 |
| Tensile Strength | 4.8×10⁷ Pa (N/mm2) (7000 psi) |
| Compression Strength | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.4 W/m·°C |
| Specific Heat | 670 J/kg·°C |
| Softening Point | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Annealing Point | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Strain Point | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Work Temperature | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Size | Customized |
| Logo | Customized Logo Accept |
High-Temperature Resistance
Quartz material exhibits exceptional high-temperature resistance, enabling it to withstand various process requirements in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance
Quartz possesses excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of substances, making it suitable for the storage and processing of corrosive liquids.
Light Transmission
Some quartz baskets exhibit good light transmission, allowing them to be used in applications requiring light penetration.
Stability
Quartz material demonstrates high chemical stability, with low reactivity to other substances, ensuring long-term performance of quartz baskets.
Application Scenario
Laboratory and Research
Due to their excellent chemical stability and high-temperature resistance, quartz baskets are commonly used as experimental containers in laboratories, such as for chemical reactions and sample processing.
In research fields, quartz baskets are also utilized in the fabrication of various precision research equipment components.
A quartz basket is a cleaning carrier used in the fabrication of semiconductor chips. Its primary function is to clean raw silicon wafers. It is manufactured from high-purity quartz material, which exhibits resistance to acids, bases, and high temperatures, with a purity level reaching 99.98%.
The primary function of a quartz basket in the production of silicon transistors and integrated circuits is to hold silicon wafers during chemical cleaning to remove invisible contaminants, such as atoms and ions, from the wafer surface.
Quartz baskets improve cleaning efficiency by positioning wafers horizontally, which enhances the on-wafer uniformity of the product, reduces the amount of corrosive liquid used, and lowers heating time, leading to increased production efficiency.
Frequently asked questions
Quartz glass is a hard and brittle material with excellent physical and chemical properties, extremely high mechanical hardness, good electrical insulation, high temperature and corrosion resistance, low and stable delay performance, good light transmittance, etc. It is widely used in semiconductors, optics, electricity, chemistry, aerospace, automobiles and other fields. Hard and brittle materials are difficult to process, and many fields urgently need cutting processes with small edge collapse, less material loss, low cross-section roughness, and a wide cutting thickness range. The traditional cutting method of quartz glass is mechanical cutting, that is, wheel cutting. Non-traditional cutting methods include water jet cutting, electrochemical discharge wire cutting, continuous laser cutting, etc. Mechanical cutting has low cost, but the contact between the wheel and the material causes large tool wear, and the material is easily contaminated by the tool. Quartz glass is prone to edge collapse, microcracks, and residual stress, which affects the strength and performance of the material! It is difficult to achieve curve cutting and requires post-processing, such as grinding and polishing. Laser cutting does not directly contact the material, has no contact stress, and can perform complex curve cutting. Picosecond laser has the advantages of small spot diameter, high precision, short action time with the material, and small action area, and is suitable for the processing of hard and brittle materials.
。