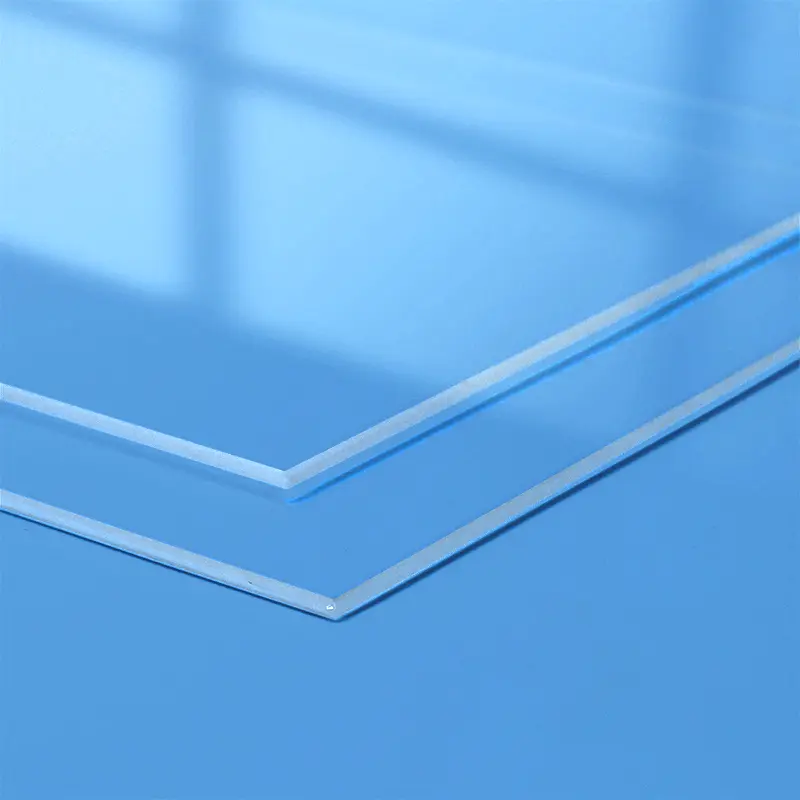
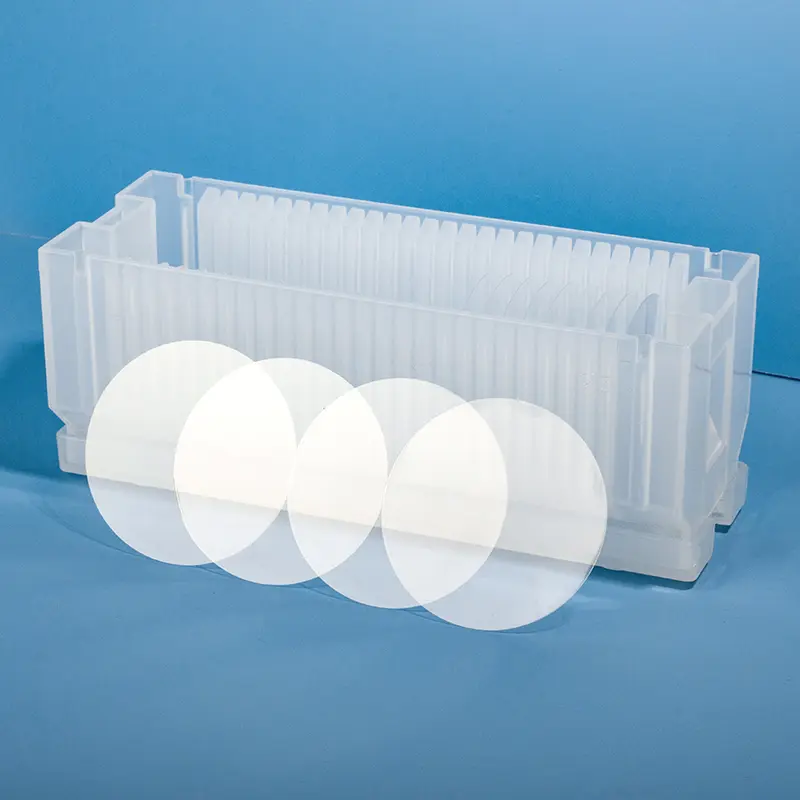
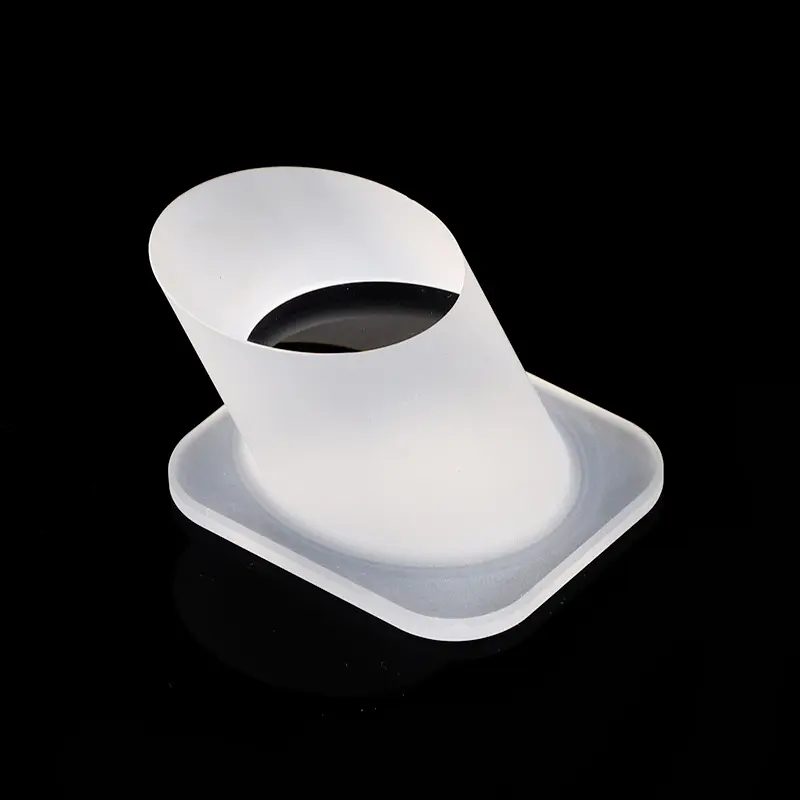
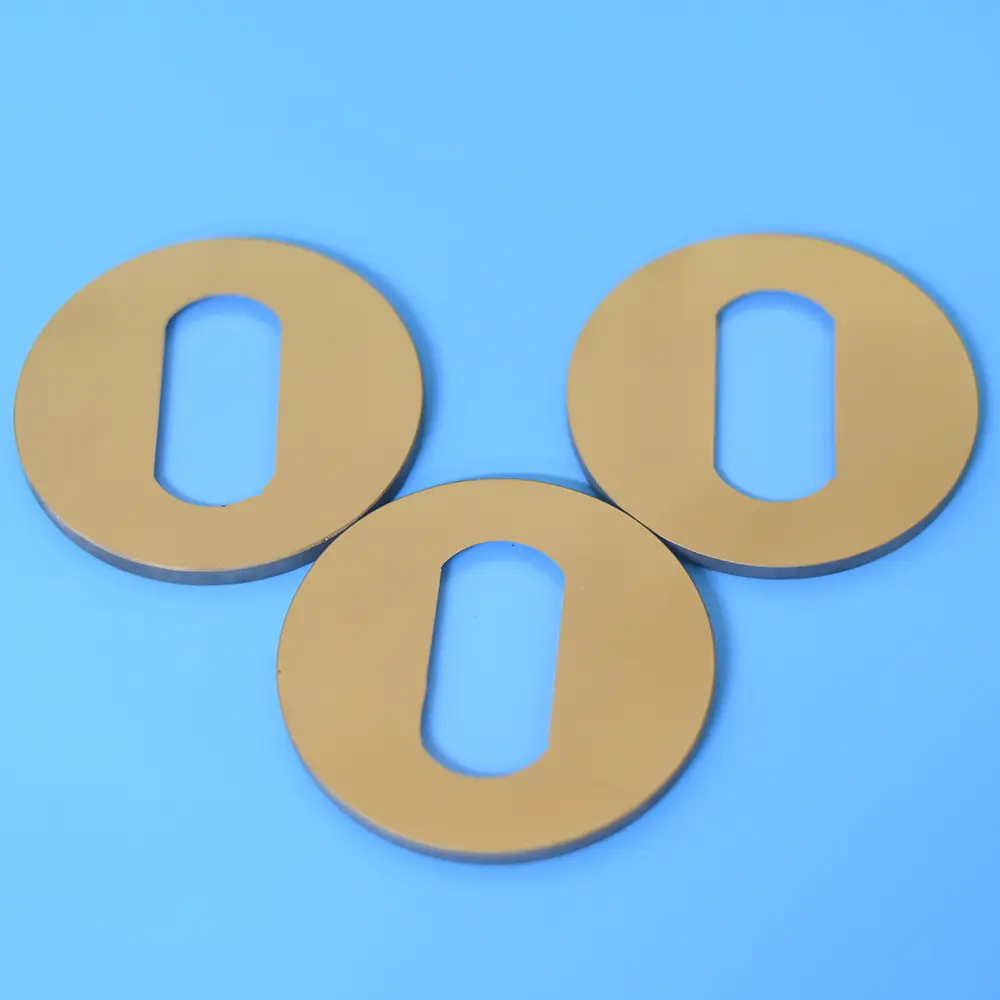
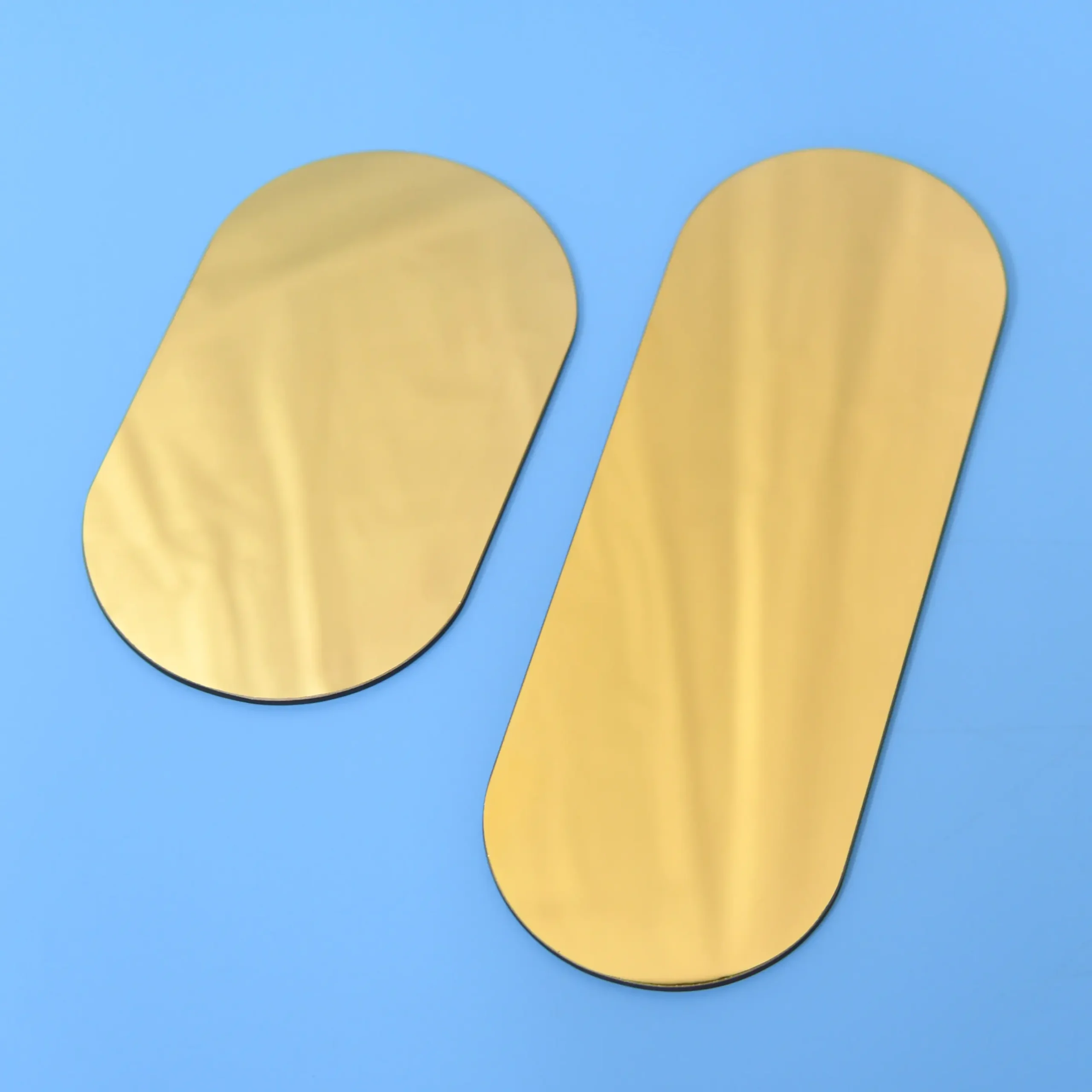
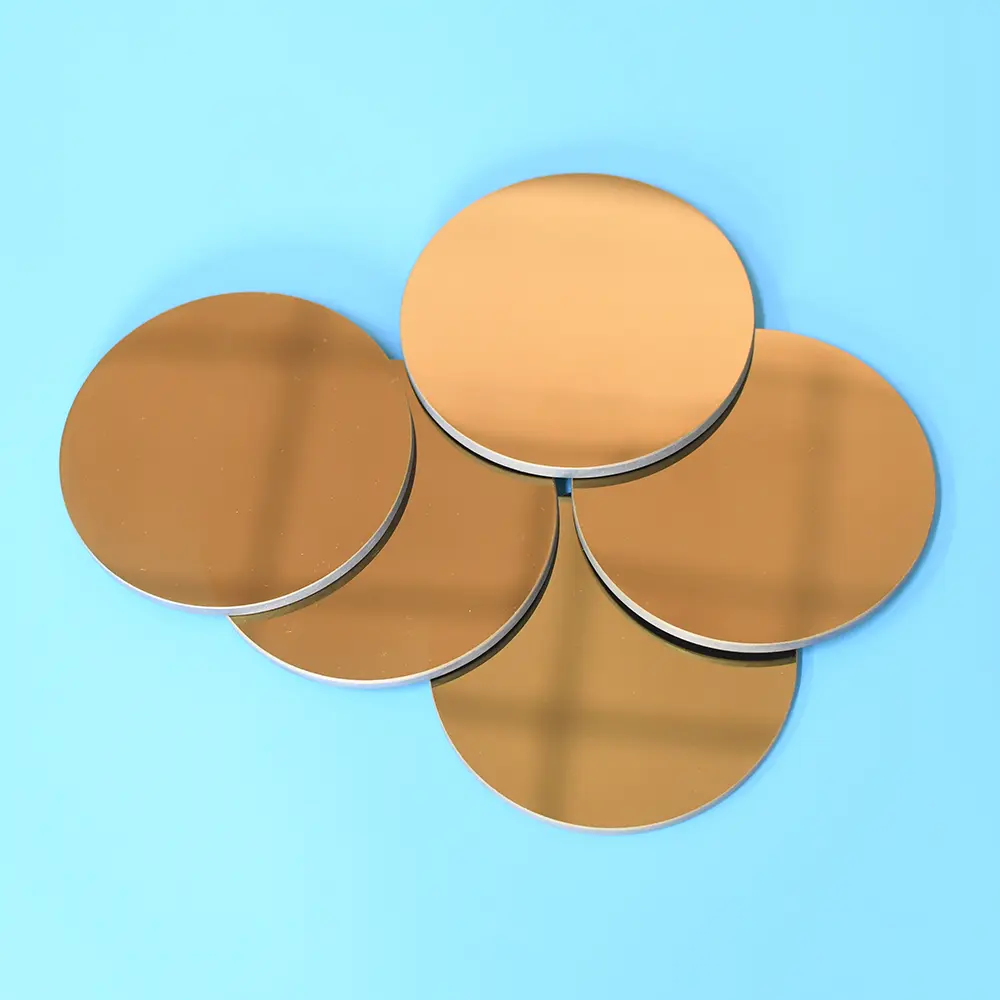
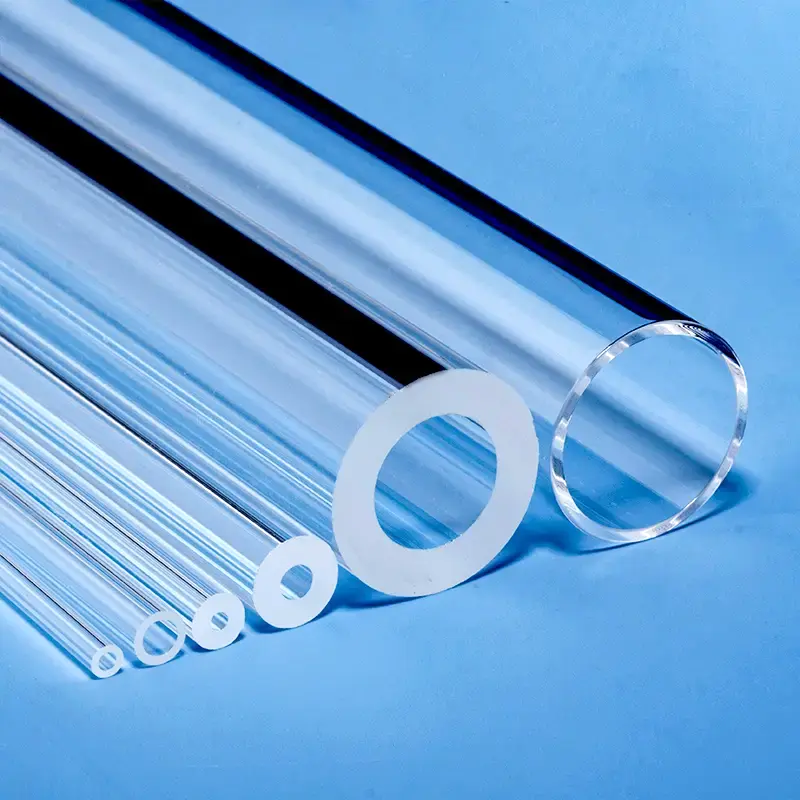
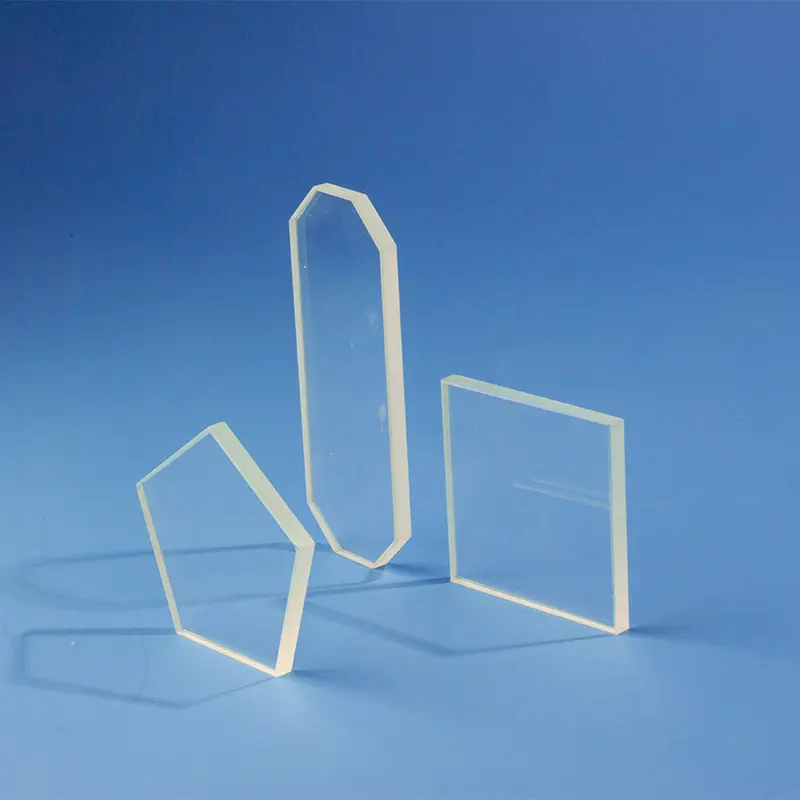
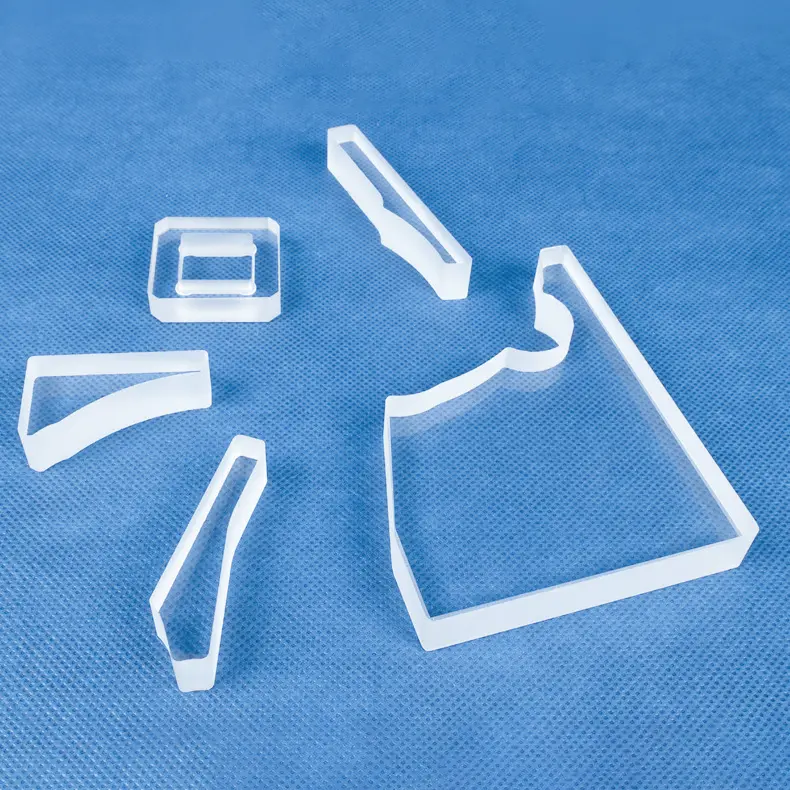
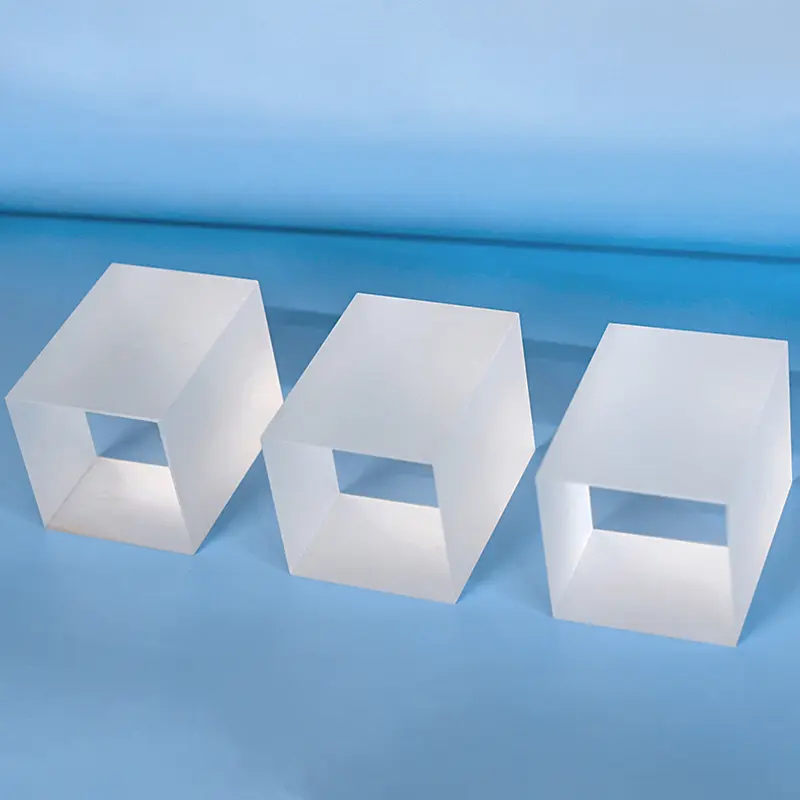
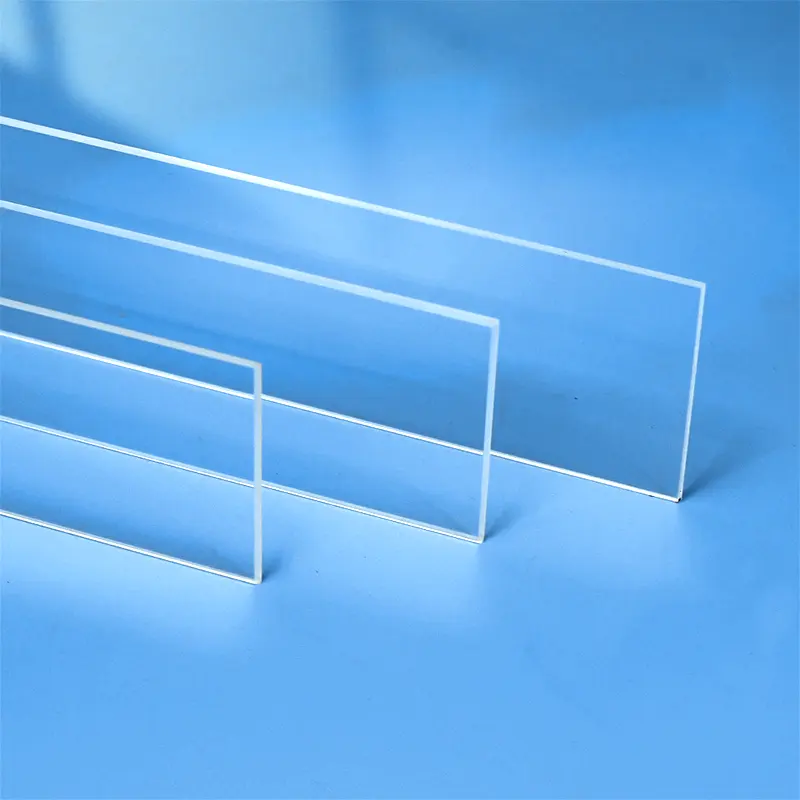
Our custom Quartz Sight Glass solutions, like the hollow square (or rectangular) and frosted quartz blocks shown, are precision-machined from high-purity fused silica. These components offer exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature stability, and superior UV transparency, making them ideal for observation windows in semiconductor, medical, chemical, and high-vacuum applications where tailored designs, precise dimensions, and specific finishes are crucial.
| Property Content | Property Values |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Density | 2.2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Hardness | 5.5 - 6.5 Mohs' Scale 570 KHN 100 |
| Tensile Strength | 4.8×10⁷ Pa (N/mm2) (7000 psi) |
| Compression Strength | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.4 W/m·°C |
| Specific Heat | 670 J/kg·°C |
| Softening Point | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Annealing Point | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Strain Point | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Work Temperature | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 7×10⁷ ohm cm (350°C) |
| Size | Customized |
| Logo | Customized Logo Accept |
High Transparency
Quartz Square Windows offer excellent optical transmission, allowing for high-definition observation, which is crucial for applications requiring precise visual inspection.
High Heat Resistance
These windows are capable of withstanding high-temperature environments, possessing high heat resistance, making them suitable for equipment and instruments that require observation under high-temperature conditions.
High Chemical Stability
Quartz Square Windows exhibit high resistance to a variety of chemicals, including most acids and bases. This makes them highly stable in chemical laboratories and industrial applications.
Thermal Shock Resistance
SQuartz Square Windows possess good thermal shock resistance, maintaining their performance and resisting breakage even under rapid temperature changes, making them suitable for environments with significant temperature fluctuations.
Application Scenario
Quartz Square Windows are crucial in vacuum equipment because they provide a transparent window for observing internal processes while maintaining a vacuum seal. The high heat resistance and chemical stability of quartz glass allow it to withstand the extreme conditions of vacuum environments, while its high transparency ensures clarity of observation.
Quartz Square Windows exhibit superior heat resistance, able to withstand continuous use temperatures of up to 1100°C and short-term temperatures of up to 1450°C. This makes them highly suitable for applications that require observing high-temperature processes, such as high-temperature furnaces and chemical reactors.
The applications of Quartz Square Windows in optical instruments include their use as window plates in microscopes, entrance and exit windows in spectrometers, and other optical components requiring high light transmission and low dispersion. The superior optical properties of quartz glass make it an ideal material choice for these applications.
Frequently asked questions
We specialize in the end-to-end manufacturing of high-purity quartz glass components. Our core product lines include:
Quartz Tubing & Rods: A wide range of diameters and specifications.
Quartz Plates & Discs: Precision-cut and polished for optical and industrial use.
Quartz Labware: A full suite of standard and custom glassware, including beakers, flasks, and boats.
Semiconductor-Grade Quartz: High-purity components like process tubes and carriers for semiconductor fabrication.
Custom Fabricated Components: We can produce complex parts tailored to your unique designs and specifications.
Yes. Custom fabrication is at the core of our business. With over a decade of specialized experience, we partner with companies to provide expert OEM/ODM services. Our capabilities include welding, grinding, drilling, polishing, bending, and other precision processing techniques to create components that meet your exact requirements.
Quality is paramount in our manufacturing process. We are an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer, ensuring that our processes meet international quality management standards.Our products also undergo rigorous SGS testing for purity and performance. We use high-purity raw materials (up to 99.998% SiO2) to produce fused quartz and fused silica products with exceptional thermal stability, high-temperature resistance, and chemical inertness.
We've streamlined our process to be as efficient as possible:
Submit Your RFQ: Send us your technical drawings, specifications, and requirements via our website contact form or email.
Rapid Response: You can expect an initial response within minutes and detailed communication within half an hour.
Design & Proposal: We will deliver a detailed design proposal and a competitive quote within 24 hours.
Prototyping & Production: Upon approval, we move swiftly from prototyping to full-scale production to meet your deadlines.
Partnering with Aoxin Quartz offers several key advantages:
Proven Expertise: With 10+ years in the industry, we have the technical knowledge to tackle complex challenges.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Competitive Value: Located in a major quartz production hub, we leverage an efficient supply chain and advanced manufacturing to offer exceptional quality at a competitive price point.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.