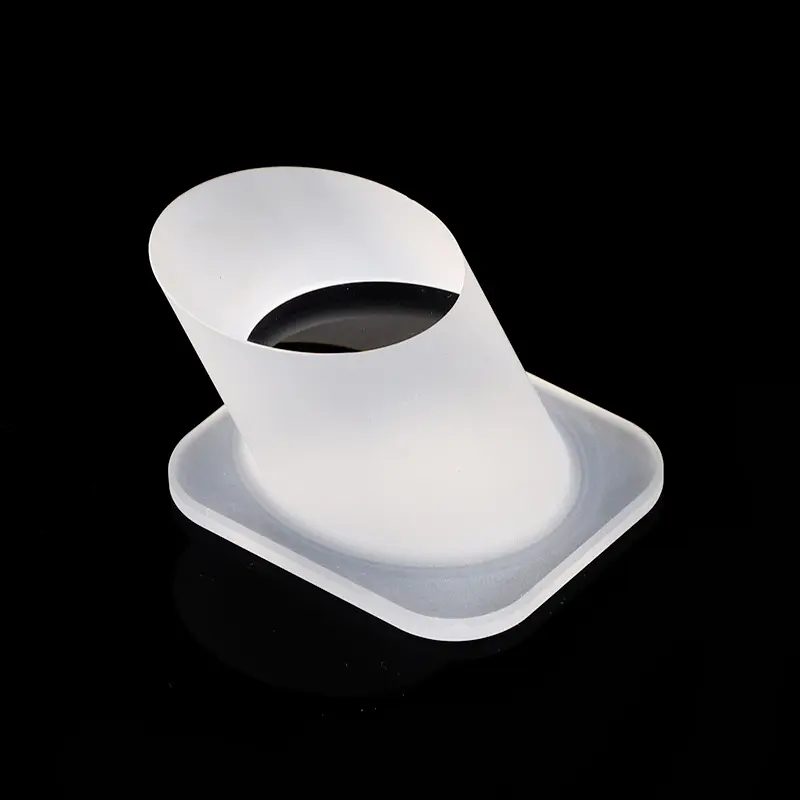
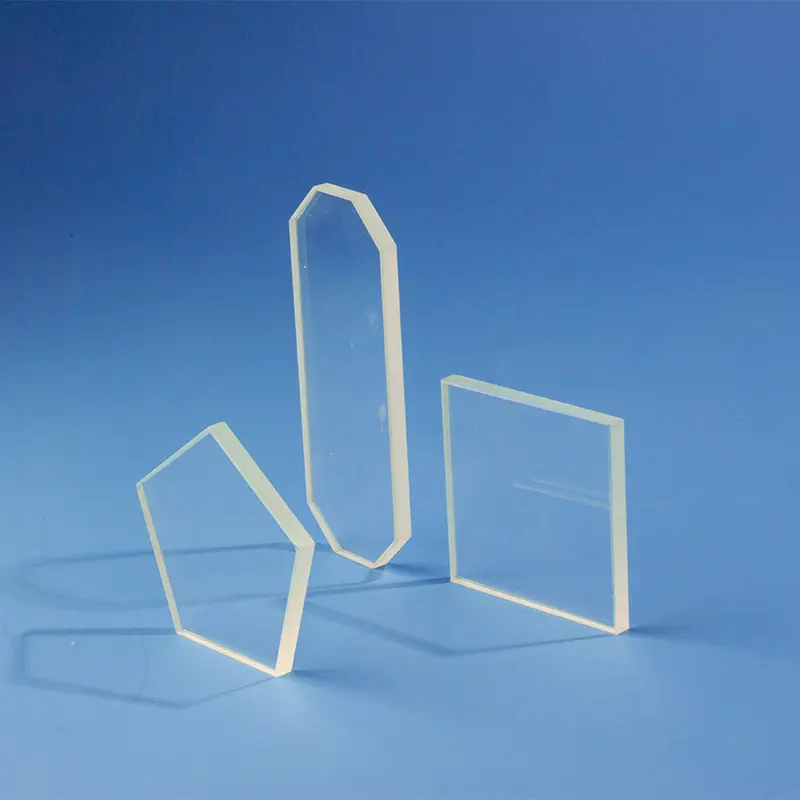
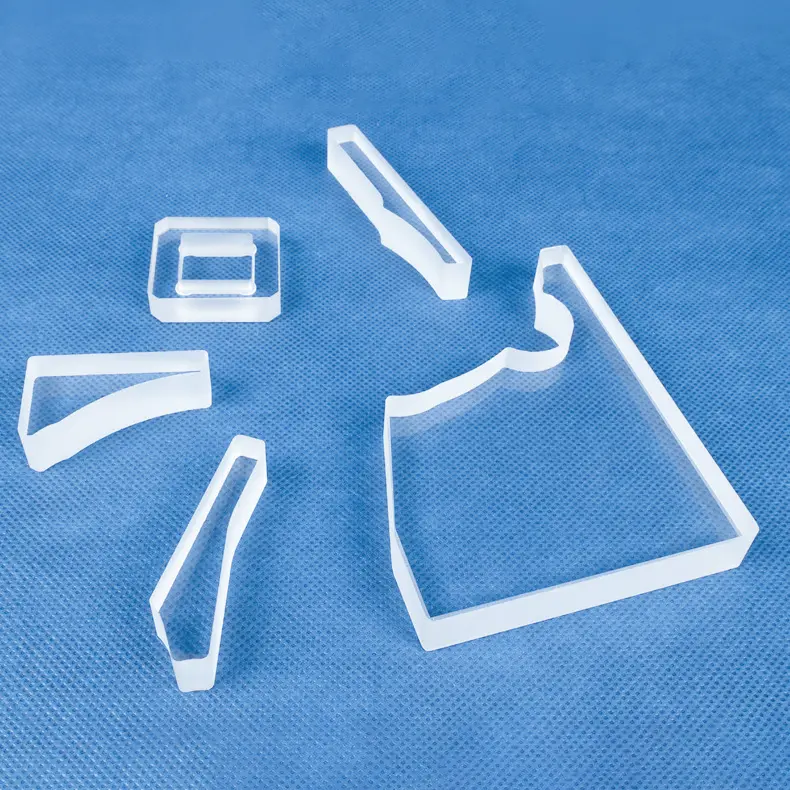
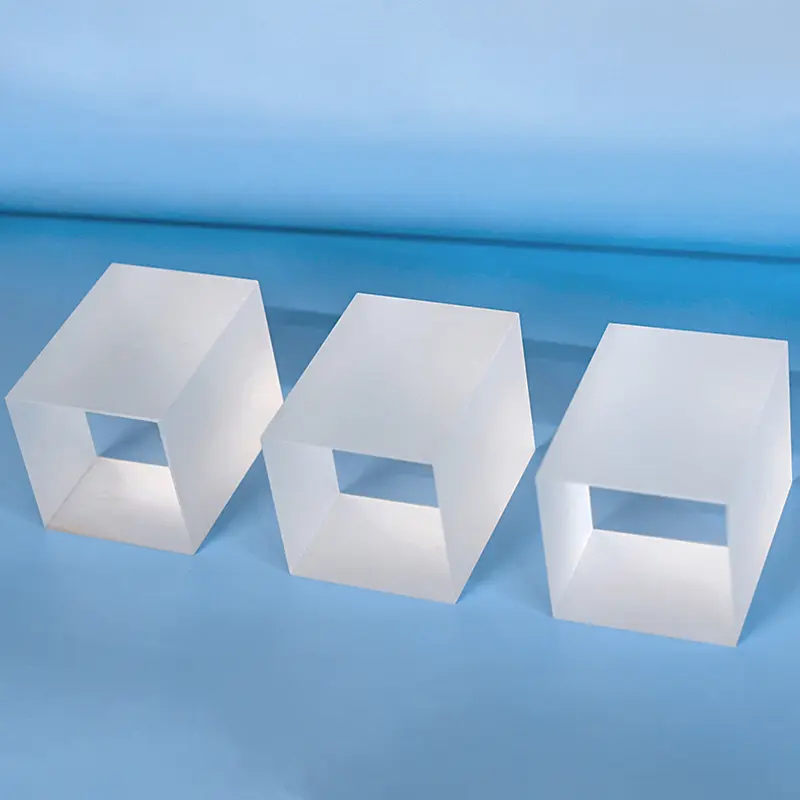
Unsere kundenspezifischen Spezialgeformten Quarzfenster, wie das abgebildete einzigartige abgeschrägte zylindrische Design mit flacher quadratischer Basis, werden präzise aus hochreinem Quarzglas gefertigt. Diese maßgeschneiderten Komponenten bieten außergewöhnliche chemische Beständigkeit, hohe Temperaturstabilität und überlegene UV-Transparenz und sind ideal für anspruchsvolle Beobachtungsanwendungen in der Halbleiter-, Medizin-, Chemie- und Hochvakuumumgebung, wo maßgeschneiderte Designs und komplexe Geometrien entscheidend sind.
| Eigenschaftsinhalt | Eigenschaftswerte |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Dichte | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Härte | Mohs-Härte 5,5 - 6,5; Knoop-Härte 570 (bei 100 g Prüflast) |
| Zugfestigkeit | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² bzw. 48 MPa); 7.000 psi |
| Druckfestigkeit | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Spezifische Wärme | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Erweichungspunkt | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Transformationspunkt | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Spannungspunkt | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Arbeitstemperatur | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Elektrischer Widerstand | 7×10⁷ Ohm cm (350°C) |
| Größe | Kundenspezifisch |
| Logo | Personalisierung mit Logo |
Hohe Temperaturbeständigkeit
Kundenspezifische Quarzfenster können extrem hohen Temperaturen standhalten, mit einem Erweichungspunkt von etwa 1730°C. Sie können kontinuierlich bei 1100°C eingesetzt werden und kurzzeitig Temperaturen von bis zu 1450°C tolerieren.
Chemische Stabilität
Mit Ausnahme von Flusssäure sind kundenspezifische Quarzfenster äußerst beständig gegenüber chemischen Reaktionen mit fast allen Säuren und weisen eine außergewöhnliche chemische Stabilität auf
Thermische Stabilität
Kundenspezifische Quarzfenster haben einen sehr niedrigen Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizienten, wodurch sie drastischen Temperaturwechseln standhalten können. Sie überstehen wiederholt große Temperaturunterschiede innerhalb kurzer Zeit ohne Rissbildung.
Optische Leistung
Kundenspezifische Quarzfenster zeigen eine gute Lichttransmission über das gesamte Spektrum von Ultraviolett bis Infrarot. Sie verfügen über eine sichtbare Lichttransmissionsrate von über 93 %, mit höheren Transmissionsraten von bis zu 80 % oder mehr, insbesondere im ultravioletten Bereich.
Anwendungsszenario
Optik- und Lichtquellenindustrie
Maßgeschneiderte Quarzfenster zeichnen sich durch hohe Wärmebeständigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und geringe thermische Ausdehnung aus und finden in der Optik breite Anwendung bei der Herstellung von Teleskoplinsen, Labor-optischen Geräten, Kommunikationsgeräten, Beugungslinsen, Projektionsdisplays, Scanneinrichtungen, Printer-optischen Komponenten sowie in Kameras und ultraschönen Fernsehbildschirmen
Glasfaser-Kommunikationsindustrie
Quarzglas ist ein Hauptrohstoff für optische Fasern, und seine Hochreinheit gewährleistet die Signalqualität von optischen Fasern. Quarzglas wird in der Herstellung von Faserverbänden und dem Ziehvorgang weitgehend eingesetzt, um die hohe Leistung und Stabilität von optischen Fasern zu gewährleisten
Photovoltaik-Industrie
Im Photovoltaik-Bereich wird Quarzglas als steifes Verschleißmaterial in Photovoltaik-Modulen verwendet, was die photoelektrische Wandlungseffizienz erheblich erhöht. Quarzkübel aus Quarzglas dienen als Behälter zum Schmelzen von polykristallinem Silizium für den nachfolgenden Prozess des Ziehens von Einkristallsiliziumstäben oder polykristallinen Siliziumingots
Das primäre Material von kundenspezifischen Quarzglasfenstern ist hochreines Quarzglas, das einzigartige physikalische Eigenschaften aufweist, darunter eine extrem hohe Temperaturbeständigkeit (kontinuierlich einsetzbar bis 1100°C und kurzzeitig bis 1450°C), eine exzellente optische Transmission (insbesondere im Ultraviolettbereich), einen extrem niedrigen Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizienten und eine herausragende chemische Beständigkeit. Diese Eigenschaften machen sie in einer Vielzahl von industriellen Anwendungen äußerst begehrt
Kundenspezifische Quarzglasfenster weisen eine außergewöhnlich hohe Beständigkeit gegenüber den meisten Chemikalien auf, mit Ausnahme von Flusssäure und heißer Phosphorsäure. Dies macht sie äußerst geeignet für chemische Labore, die chemische Produktion und andere Anwendungen, bei denen korrosionsbeständige Sichtfenster erforderlich sind.
Die Vorteile von kundenspezifischen Quarzglasfenstern in optischen Anwendungen ergeben sich aus ihrer hohen Transparenz und breiten spektralen Transmission, die eine exzellente Lichtdurchlässigkeit über das gesamte Spektrum vom Ultraviolett- bis in den Infrarotbereich ermöglichen. Diese Eigenschaft ist entscheidend für Anwendungen, die eine hohe Klarheit und präzise Lichtkontrolle erfordern, wie etwa in hochwertigen optischen Instrumenten, der Glasfaserkommunikation und Forschungsausrüstung.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wir sind auf die durchgängige Fertigung von hochreinen Quarzglaskomponenten spezialisiert. Unsere Kernproduktlinien umfassen:
Quarzrohre & -stäbe: Eine große Auswahl an Durchmessern und Spezifikationen.
Quarzplatten & -scheiben: Präzisionsgeschnitten und poliert für optische und industrielle Anwendungen.
Quarzlaborglas: Ein komplettes Sortiment an Standard- und kundenspezifischen Glasgeräten, einschließlich Bechergläsern, Kolben und Booten.
Halbleiterquarz: Hochreine Komponenten wie Prozessrohre und Träger für die Halbleiterfertigung.
Kundenspezifische Fertigungskomponenten: Wir können komplexe Teile nach Ihren einzigartigen Designs und Spezifikationen fertigen.
Ja. Kundenspezifische Fertigung ist das Herzstück unseres Geschäfts. Mit über einem Jahrzehnt spezialisierter Erfahrung arbeiten wir eng mit Unternehmen zusammen, um erstklassige OEM/ODM-Dienstleistungen anzubieten. Unsere Kompetenzen umfassen Schweißen, Schleifen, Bohren, Polieren, Biegen und weitere Präzisionsbearbeitungstechniken, um Komponenten zu fertigen, die exakt Ihren Anforderungen entsprechen.
Qualität ist in unserem Herstellungsprozess von größter Bedeutung. Wir sind ein ISO 9001:2015 zertifizierter Hersteller, der sicherstellt, dass unsere Prozesse internationale Qualitätsmanagementstandards erfüllen.Unsere Produkte durchlaufen zudem rigorose SGS-Prüfungen hinsichtlich Reinheit und Leistung. Wir verwenden hochreine Rohmaterialien (bis zu 99,998% SiO2), um Quarzglas- und Kieselglasprodukte mit außergewöhnlicher thermischer Stabilität, hoher Temperaturbeständigkeit und chemischer Inertheit herzustellen.
Wir haben unsere Prozesse maximal effizient gestaltet:
Senden Sie Ihre Angebotsanfrage (RFQ): Senden Sie uns Ihre technischen Zeichnungen, Spezifikationen und Anforderungen über unser Kontaktformular auf der Website oder per E-Mail.
Schnelle Reaktion: Sie können eine erste Antwort innerhalb weniger Minuten und eine detaillierte Kommunikation innerhalb einer halben Stunde erwarten.
Design & Angebot: Wir liefern Ihnen innerhalb von 24 Stunden einen detaillierten Designvorschlag und ein wettbewerbsfähiges Angebot.
Prototypenentwicklung & Produktion: Nach Freigabe gehen wir zügig von der Prototypenfertigung zur Serienproduktion über, um Ihre Fristen einzuhalten.
Eine Partnerschaft mit Aoxin Quartz bietet mehrere entscheidende Vorteile:
Nachgewiesene Expertise: Mit über 10 Jahren Branchenerfahrung verfügen wir über das technische Fachwissen, um komplexe Herausforderungen zu meistern.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Wettbewerbsfähiger Wert: Als Standort in einem wichtigen Quarzproduktionszentrum nutzen wir eine effiziente Lieferkette und fortschrittliche Fertigung, um außergewöhnliche Qualität zu einem wettbewerbsfähigen Preis anzubieten.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.