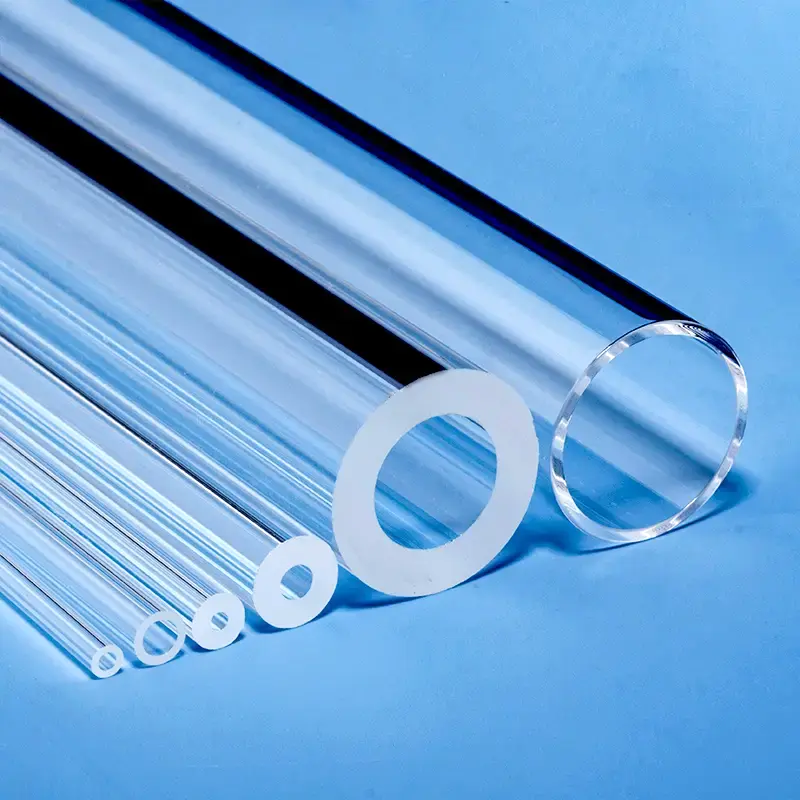
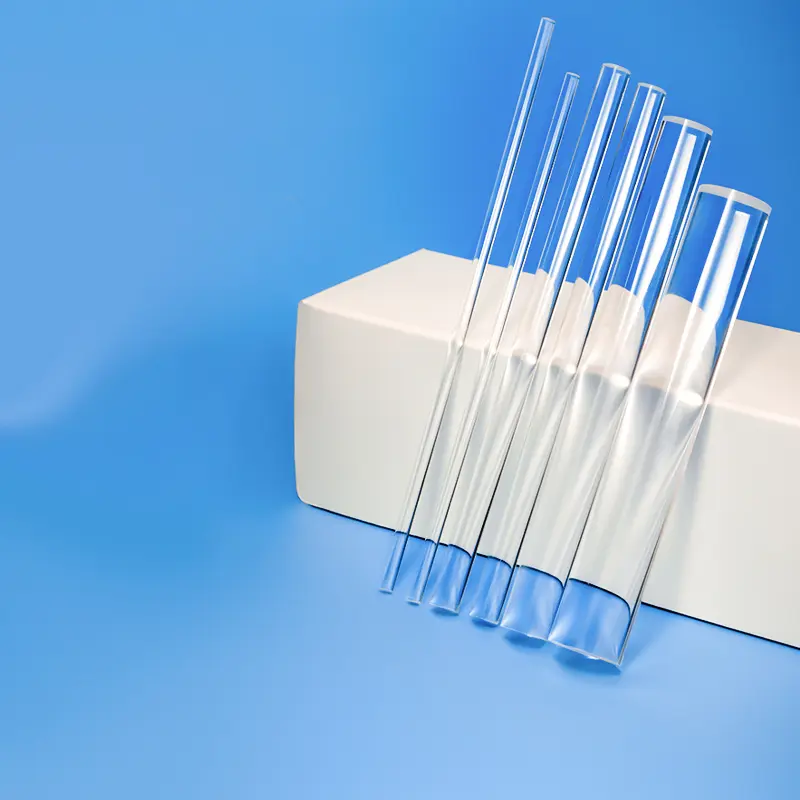
Unsere hochreinen Quarz-Lichtleitstäbe und Quarzglas-Lichtleiter bieten außergewöhnliche optische Klarheit und UV-Transmission. Entwickelt für anspruchsvolle Anwendungen, zeichnen sie sich durch überragende Hitzebeständigkeit und chemische Stabilität aus. Ideal für den Einsatz in optischen, analytischen und UV-bezogenen Geräten, sind diese Präzisionskomponenten in kundenspezifischen Abmessungen erhältlich.
| Durchmesser | Länge |
|---|---|
| 10mm | 300mm |
| 10mm | 600mm |
| 12mm | 300mm |
| 12mm | 600mm |
| 14mm | 300mm |
| 14mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 300mm |
| 15mm | 600mm |
| 15mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 300mm |
| 16mm | 600mm |
| 16mm | 1000mm |
| 16mm | 1200mm |
| 18mm | 300mm |
| 18mm | 600mm |
| 18mm | 1000mm |
| 18mm | 1200mm |
| 20mm | 300mm |
| 20mm | 600mm |
| 20mm | 1000mm |
| 20mm | 1200mm |
| 22mm | 300mm |
| 22mm | 600mm |
| 22mm | 1000mm |
| 22mm | 1200mm |
| 25mm | 300mm |
| 25mm | 600mm |
| 25mm | 1000mm |
| 25mm | 1200mm |
| 28mm | 300mm |
| 28mm | 600mm |
| 28mm | 1000mm |
| 28mm | 1200mm |
| 30mm | 300mm |
| 30mm | 600mm |
| 30mm | 1000mm |
| 30mm | 1200mm |
| 32mm | 300mm |
| 32mm | 600mm |
| 32mm | 1000mm |
| 32mm | 1200mm |
| 35mm | 300mm |
| 35mm | 600mm |
| 35mm | 1000mm |
| 35mm | 1200mm |
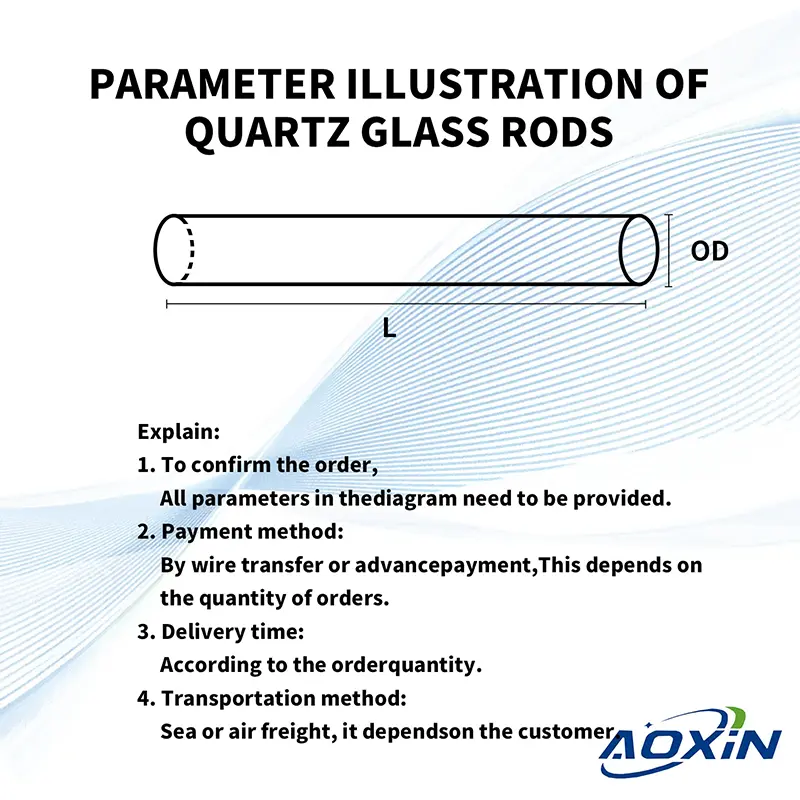
Anmerkungen:
注文を確認するために
Folgende Parameter sind erforderlich:
① Außendurchmesser ② Länge ③ Menge
- Zahlungsmethode:
Per Überweisung oder Vorauszahlung
Es hängt von der Bestellmenge ab. - Delivery time:
According to the order quantity. - Versandmethode:
Per See oder Luft
Es hängt vom Kunden ab.
| Eigenschaftsinhalt | Eigenschaftswerte |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 99.99% |
| Dichte | 2,2×10³ kg/cm³ |
| Härte | Mohs-Härte 5,5 - 6,5; Knoop-Härte 570 (bei 100 g Prüflast) |
| Zugfestigkeit | 4,8 × 10⁷ Pa (48 N/mm² bzw. 48 MPa); 7.000 psi |
| Druckfestigkeit | >1.1×10⁹ Pa (160,000 psi) |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient | 5.5×10⁻⁷ cm/cm·°C (20°C-320°C) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit | 1,4 W/m-°C |
| Spezifische Wärme | 670 J/kg-°C |
| Erweichungspunkt | 1730°C (3146°F) |
| Transformationspunkt | 1210°C (2210°F) |
| Spannungspunkt | 1120°C (2048°F) |
| Arbeitstemperatur | 1200°C (2192°F) |
| Elektrischer Widerstand | 7×10⁷ Ohm cm (350°C) |
| Größe | Kundenspezifisch |
| Logo | Personalisierung mit Logo |

Es gibt zwei Hauptmethoden zur Herstellung von Quarzstäben: das kontinuierliche Verfahren und das Flammenfusionsverfahren (auch bekannt als Gasfusionsverfahren).
Kontinuierliches Verfahren: In dieser Methode wird Quarzsand von oben in einen Ofen eingespeist, der aus einem metallischen Quarz-Krug besteht, der von elektrischen Heizelementen umgeben ist. Der Quarzsand schmilzt bei hohen Temperaturen. Das geschmolzene Material passiert dann eine Formöffnung am Boden des Krugs, wodurch Stäbe, Rohre, Platten oder andere spezifizierte Produktformen erzeugt werden.
Flammenfusionsmethode: Dieses Verfahren beinhaltet die Verwendung von Wasserstoff und Sauerstoff, um farblosen Quarzkristall zu schmelzen. Das geschmolzene Material wird durch das Schmelzen und Erstarren von Kristallpartikeln in der Flamme zu Quarzglas geformt. Das Quarzglas wird dann auf verschiedene Weisen aus der Flamme entfernt und zu Quarzstäben der gewünschten Form verarbeitet.
Hohe Temperaturbeständigkeit
Quarzglas zeigt eine ausgezeichnete Hochtemperaturbeständigkeit und bewahrt seine Stabilität in Hochtemperaturumgebungen.
Niedriger thermischer Ausdehnungskoeffizient
Der Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von Quarzglas ist extrem niedrig und reicht von 1/12 bis 1/20 des von gewöhnlichem Glas, was zu seiner Stabilität bei Temperaturschwankungen beiträgt.
Korrosionsbeständigkeit
Quarzglas ist widerstandsfähig gegen eine Vielzahl von Säuren, Basen und Salzen, mit Ausnahme von Flusssäure und heißer Phosphorsäure über 300 Grad Celsius.
Hohe Lichtdurchlässigkeit
Die Lichtübertragungsrate kann 99,9 % erreichen, was eine hohe Lichtdurchlässigkeit während der Übertragung gewährleistet.
Anwendungsszenario
Kommunikationsbereich
In optischen Faserkommunikationssystemen dienen Quarzlichtleiterstangen als Medium zur Übertragung von Lichtsignalen vom Sender zum Empfänger und ermöglichen so eine Hochgeschwindigkeits- und Hochkapazitätsdatenübertragung.
Sie werden auch in Geräten wie Lasern und optischen Verstärkern eingesetzt, um die Leistung und Stabilität von Kommunikationssystemen zu verbessern.
Medizinisches Feld
Bei der Laserchirurgie verwenden Ärzte Quarzlichtleitstäbe, um Laserstrahlen zum Behandlungsbereich zu übertragen, was präzise chirurgische Eingriffe ermöglicht.
Sie werden auch in optischen Abbildungssystemen verwendet, um Ärzten zu helfen, innere Strukturen zu beobachten, wodurch die diagnostische Genauigkeit verbessert wird.
Wissenschaftliches Forschungsfeld
Forscher verwenden Quarz-Lichtleitstäbe, um optische Experimentiersysteme zur Untersuchung optischer Phänomene und der Eigenschaften optischer Materialien einzurichten.
Sie werden auch in Geräten wie Laserinterferometern und optischen Sensoren für präzise Messungen und Experimente eingesetzt.
Andere Bereiche
Im Bereich der Biotechnologie werden Quarzlichtleitstäbe zur Fluoreszenzdetektion und -analyse eingesetzt, wodurch eine schnelle und hochsensible Erkennung von Biomolekülen ermöglicht wird.
In der Laserbearbeitung werden sie für den Laserschneiden und die Laserbeschriftung eingesetzt, gekennzeichnet durch hohe Energiedichte, hohe Präzision und hohe Effizienz.
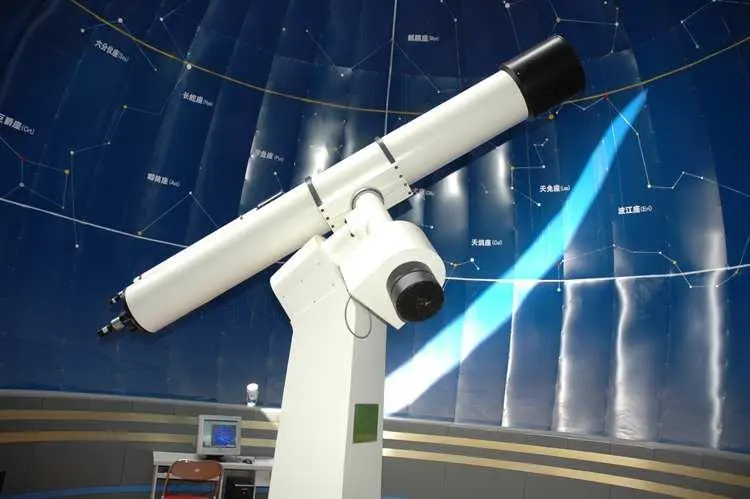
Sie werden auch bei der Herstellung verschiedener optischer Instrumente wie Mikroskopen, Teleskopen und Wärmebildkameras eingesetzt, wobei sie Licht übertragen und dessen Richtung ändern, um spezifische Beobachtungseffekte zu erzielen
Quarzlichtleiterstäbe zeigen eine hervorragende Langzeitstabilität in verschiedenen Umgebungen. Sie besitzen einen hohen Grad an chemischer Stabilität, der es ihnen ermöglicht, ihre Leistung und Integrität in einer Vielzahl von chemischen Umgebungen aufrechtzuerhalten. Darüber hinaus ist der thermische Ausdehnungskoeffizient von Quarzglas einer der niedrigsten unter den gängigen Industriegläsern, was bedeutet, dass es eine gute Maßstabilität während Temperaturänderungen aufrechterhält und eine hohe Beständigkeit gegen thermische Schocks aufweist.
Quarzsichtleitern besitzen eine extrem hohe chemische Stabilität und reagieren mit den meisten sauren und alkalischen Stoffen nahezu nicht, mit Ausnahme von Flusssäure. Dieser Korrosionsschutz macht sie in Umgebungen, in denen häufiger Kontakt mit korrosiven Materialien besteht, von unschätzbarem Wert.
Quarz-Rührstäbe bieten im Vergleich zu Kunststoff-Rührstäben eine hervorragende Hochtemperaturebeständigkeit und chemische Stabilität. Darüber hinaus besitzen sie eine hohe strukturelle Festigkeit, sind weniger bruchanfällig und haben eine lange Lebensdauer.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wir sind auf die durchgängige Fertigung von hochreinen Quarzglaskomponenten spezialisiert. Unsere Kernproduktlinien umfassen:
Quarzrohre & -stäbe: Eine große Auswahl an Durchmessern und Spezifikationen.
Quarzplatten & -scheiben: Präzisionsgeschnitten und poliert für optische und industrielle Anwendungen.
Quarzlaborglas: Ein komplettes Sortiment an Standard- und kundenspezifischen Glasgeräten, einschließlich Bechergläsern, Kolben und Booten.
Halbleiterquarz: Hochreine Komponenten wie Prozessrohre und Träger für die Halbleiterfertigung.
Kundenspezifische Fertigungskomponenten: Wir können komplexe Teile nach Ihren einzigartigen Designs und Spezifikationen fertigen.
Ja. Kundenspezifische Fertigung ist das Herzstück unseres Geschäfts. Mit über einem Jahrzehnt spezialisierter Erfahrung arbeiten wir eng mit Unternehmen zusammen, um erstklassige OEM/ODM-Dienstleistungen anzubieten. Unsere Kompetenzen umfassen Schweißen, Schleifen, Bohren, Polieren, Biegen und weitere Präzisionsbearbeitungstechniken, um Komponenten zu fertigen, die exakt Ihren Anforderungen entsprechen.
Qualität ist in unserem Herstellungsprozess von größter Bedeutung. Wir sind ein ISO 9001:2015 zertifizierter Hersteller, der sicherstellt, dass unsere Prozesse internationale Qualitätsmanagementstandards erfüllen.Unsere Produkte durchlaufen zudem rigorose SGS-Prüfungen hinsichtlich Reinheit und Leistung. Wir verwenden hochreine Rohmaterialien (bis zu 99,998% SiO2), um Quarzglas- und Kieselglasprodukte mit außergewöhnlicher thermischer Stabilität, hoher Temperaturbeständigkeit und chemischer Inertheit herzustellen.
Wir haben unsere Prozesse maximal effizient gestaltet:
Senden Sie Ihre Angebotsanfrage (RFQ): Senden Sie uns Ihre technischen Zeichnungen, Spezifikationen und Anforderungen über unser Kontaktformular auf der Website oder per E-Mail.
Schnelle Reaktion: Sie können eine erste Antwort innerhalb weniger Minuten und eine detaillierte Kommunikation innerhalb einer halben Stunde erwarten.
Design & Angebot: Wir liefern Ihnen innerhalb von 24 Stunden einen detaillierten Designvorschlag und ein wettbewerbsfähiges Angebot.
Prototypenentwicklung & Produktion: Nach Freigabe gehen wir zügig von der Prototypenfertigung zur Serienproduktion über, um Ihre Fristen einzuhalten.
Eine Partnerschaft mit Aoxin Quartz bietet mehrere entscheidende Vorteile:
Nachgewiesene Expertise: Mit über 10 Jahren Branchenerfahrung verfügen wir über das technische Fachwissen, um komplexe Herausforderungen zu meistern.
One-Stop Solution: We manage the entire production process, from sourcing high-purity raw materials to fabricating and finishing complex components.
Wettbewerbsfähiger Wert: Als Standort in einem wichtigen Quarzproduktionszentrum nutzen wir eine effiziente Lieferkette und fortschrittliche Fertigung, um außergewöhnliche Qualität zu einem wettbewerbsfähigen Preis anzubieten.
Dedicated Partnership: Over 90% of our clients become long-term partners. We are committed to your success through responsive service, reliable quality, and innovative solutions.